Contents
Hypervolemia is an increase in blood volume in the vascular bed. Depending on the characteristics of hematocrit, there are oligocythemic, simple and polycythemic hypervolemia.
If we are talking about hypervolemia of the pulmonary circulation, then this condition is called pulmonary hypertension. Hypervolemia is not just a physiological deviation from the norm, but a pathological syndrome that accompanies various disorders. Inside the vessels of a healthy person, an amount of blood should constantly circulate that corresponds to 6-8% of his weight. Thus, if the weight of an individual is 75 kg, then there should be about 5 liters of blood in his body. Exceeding these values is a deviation from the norm.
Why does hypervolemia develop?
An increase in the volume of blood circulating in the body does not occur by itself. Hypervolemia is always accompanied by a certain disorder in the body. Therefore, hypervolemia is not an independent pathology. It has a direct relationship with such a concept as hematocrit. Hematocrit characterizes the volume of red blood cells in relation to the total volume of blood. Normally, 360-480 ml of cells should be present in a liter of blood, and the rest of its composition will be plasma. Therefore, normal hematocrit values in percentage terms look like 36-48%.
Hypervolemia, depending on the cause of its development, can be of 3 types:
Simple.
Oligocythemic.
Polycythemic.
Approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of each type of hypervolemia will differ.
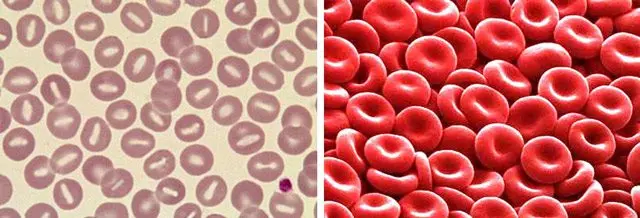
The photo below shows blood with polycythemic hypervolemia:
Simple hypervolemia
Simple hypervolemia develops when not only the volume of red blood cells increases in parallel, but also the level of blood plasma rises. The relationship between them is not broken.
Simple hypervolemia is not often diagnosed. Its development can be caused by such reasons as:
Blood transfusion in large volumes.
Excessive physical activity.
Finding a person in conditions of high temperatures.
Oxygen starvation.
If a person is transfused a lot of blood, then this naturally provokes an increase in its volume in the body. With increased physical exertion, while being in the heat, during hypoxia, blood volumes increase due to the body’s own reserves.
Oligocytemic hypervolemia
Oligocythemic hypervolemia is called hydremia. In this case, there is an increase in the volume of the liquid component of the blood, while the level of red blood cells remains unchanged.
The following conditions can lead to oligocythemic hypervolemia:
The conception of a child. In this case, an increase in the liquid component of the blood with a normal hematocrit is a variant of the norm. The body independently launches such mechanisms in order to stabilize the woman’s metabolism in accordance with her new position.
Abundant drinking, transfusion of plasma and plasma analogues, exit of fluid from edema into the vascular bed.
Acute or chronic renal failure, increased synthesis of antidiuretic hormone, sodium retention are situations that contribute to the retention of large volumes of fluid in the body.
Polycythemic hypervolemia
Polycythemic hypervolemia characterizes an increase in blood volume due to an increase in the number of red blood cells.
Reasons that can provoke this violation:
Oxygen starvation of a chronic course, to which heart defects lead, pathologies of the respiratory system with chronic respiratory failure, being a person at significant heights.
Blood diseases: cancerous growths (malignant and benign), increased formation of blood cells due to hereditary pathologies.
Symptoms of hypervolemia

If hypervolemia was provoked by physiological causes, then after a short time, blood volumes will return to normal without any consequences for human health. Specialized treatment is not required.
When hypervolemia was caused by chronic or acute pathologies, then it is necessary to direct efforts to eliminate the root cause that led to an increase in blood volumes. Symptomatic therapy is also carried out.
As for the symptoms of hypervolemia, they can be as follows:
Jumps in blood pressure in the direction of its increase.
The development of heart failure or angina pectoris, as the heart works under high stress.
Swelling of tissues.
The appearance of shortness of breath. In general, it becomes difficult for a person to breathe, despite the fact that the respiratory rate increases.
The patient gets tired quickly.
The skin becomes dry, dry mouth appears.
Dysuric disorders develop.
There are headaches and pain in the lumbar region.
Diagnosis of hypervolemia
Identification of hypervolemia is a rather difficult task that confronts doctors. There are no specific symptoms of the disorder, and it is quite difficult to calculate the total volume of blood in the body. Therefore, the diagnosis of hypervolemia is reduced to the determination of hematocrit parameters. This study makes it possible not only to detect hypervolemia itself, but also to determine its type, as well as to clarify the cause of the development of this condition.
Treatment of hypervolemia

Therapy of hypervolemia should be directed to the cause that provoked this violation:
Treatment of kidney pathology.
Treatment of heart defects.
Therapy of disorders in the work of the endocrine glands.
Surgical and medical treatment of tumor neoplasms.
Treatment of blood diseases.
Therapy of diseases of the respiratory system.
Performing blood transfusion in accordance with existing medical protocols, without violating the rules of the procedure.
To get rid of the symptoms of hypervolemia and alleviate the patient’s condition, the following measures may be recommended:
Taking drugs to lower blood pressure. Diuretics are prescribed for this purpose.
Reduced stress on the heart muscle.
Controlling the ambient temperature, ensuring sufficient oxygen supply to the tissues, which is aimed at eliminating hypoxia.
Also, in the treatment of hypervolemia, alternative medicine methods can be used:
Treatment with leeches, which helps to reduce the volume of circulating blood in the body, reduce its viscosity, normalize the qualitative composition.
Taking herbal diuretics. Bearberry, horsetail, viburnum, dill, fennel have such properties.
Hypervolemia should be treated by a doctor. Self-treatment can lead to serious health problems and even threaten life.
Hypervolemia of the pulmonary circulation

If we consider the distribution of blood in the vascular bed, then about 70% of its volume will always be present in the veins, about 15% in the arteries and about 12% in the capillaries. The remaining 3% falls on the cavity of the heart.
The circulatory system consists of a large and small circle. The systemic circulation includes the vessels of all organs and tissues, with the exception of the vessels of the lungs. The pulmonary circulation includes vessels that provide blood to the lungs.
About 25% of the total blood volume circulates in the pulmonary circulation, and the remaining 75% falls on the systemic circulation.
With the development of hypervolemia of small blood circulation, the lungs are included in the pathological process, so the main symptoms will appear precisely from these organs.
Why does hypervolemia of the pulmonary circulation develop?
The development of hypervolemia of the pulmonary circulation can occur for the following reasons:
Hypoxia of the alveoli to which oxygen will not reach. The cause of such a violation is chronic bronchitis, chronic pulmonary obstruction, silicosis, anthracosis, bronchiectasis, etc.
Spasm of the small arteries of the lungs. Stress, pulmonary embolism, mitral valve stenosis can lead to the development of such a disorder.
High airway pressure, which leads to a strong cough, a jump in barometric pressure, technology violations when performing mechanical ventilation.
Failures in the work of the left ventricle of the heart, which is observed with myocardial infarction, against the background of arrhythmias and with myocarditis.
Blood clots.
Excessive ejection of blood from the right ventricle of the heart.
Tumors, aneurysms, adhesions, and other disorders that get in the way of the blood vessels that carry blood from the lungs.
Chronic poisoning of the body with narcotic substances.
Genetic disorders leading to enzymatic failures.
An increase in pressure in the portal vein system, which can occur due to cirrhosis, syndrome and Budd-Chiari disease.
AIDS virus.
Brief pauses in breathing during night rest.
In addition, there is a kind of hypervolemia of the pulmonary circulation, which develops for unknown reasons.
Symptoms of pulmonary hypervolemia
When the disorder is just beginning to develop, the person will not experience any symptoms.
As the hypervolemia of the pulmonary circulation progresses, the following health problems are possible:
A person gets tired quickly, he has mood swings, weight goes off, he will suffer from insomnia.
The patient is often dizzy.
Shortness of breath increases, it will be very difficult to breathe with severe physical exertion.
In severe cases, fainting may occur.
A person begins to suffer from a paroxysmal cough, accompanied by sputum with blood.
Periodically there are attacks of heart pain.
The skin is pale, as the disease progresses, cyanosis increases.
Ascites may develop.
In the area of the liver, painful sensations begin to disturb.
The heart works intermittently.
How to detect hypervolemia of the pulmonary circulation?
A preliminary diagnosis is made on the basis of symptoms of hypervolemia. To confirm it, the doctor directs the patient to the following examinations:
An electrocardiogram can detect abnormalities in the work of the heart.
A chest x-ray provides information about the state of the lungs, with hypervolemia, their vascular pattern increases. The heart is enlarged.
Carrying out CT.
Ultrasound of the heart allows you to assess its size, clarify the speed of blood flow and the volume of pumped blood.
The level of pressure in the pulmonary system can be determined using the method of catheterization of the pulmonary trunk. This is an invasive procedure during which special sensors are inserted into the lumen of the vessels of the lungs. This study allows with a high degree of probability to detect hypervolemia, even at the earliest stages of its development.
How to treat?
To eliminate hypervolemia of the pulmonary circulation, it will be necessary to direct efforts to the cause that provoked such a violation. It makes no sense to treat hypervolemia without establishing an etiological factor.
Most often, drugs are used in therapy that are effective in correcting high blood pressure. A drug such as Eufillin has proven itself well. It is also necessary to carry out measures aimed at eliminating tissue hypoxia (oxygen therapy).









