Contents
Hyperthyroidism is the release of large amounts of thyroid hormones into the blood. The disease can be congenital, in which case it will make itself felt almost immediately after the birth of the child. Acquired hyperthyroidism develops at any age. Most often, women suffer from pathology. Men get sick 5 times less often.
All processes in the body with hyperthyroidism are gaining maximum speed, and feelings are aggravated. As a result, organs wear out quickly, a person can die. To start treatment on time, you need to know the main symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
What is hyperthyroidism?
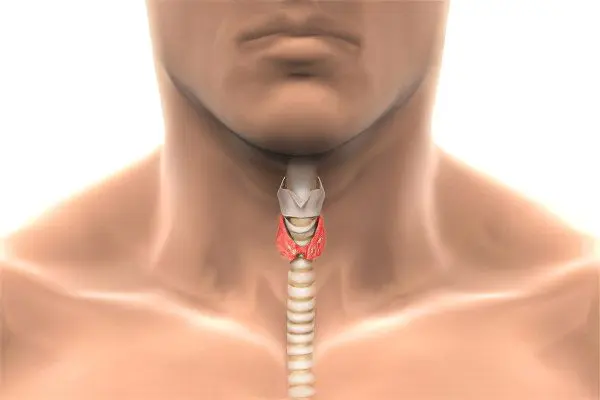
Hyperthyroidism – This is a disease in which the thyroid gland works too actively, which leads to an excessive release of its hormones T3 (thyroxine) and T4 (triiodothyronine) into the blood. They enter all tissues of the body and accelerate their natural metabolic processes. Hormonal imbalance negatively affects the state of the immune system, leads to a general deterioration in well-being and damage to the adrenal glands. Moreover, with hyperthyroidism, the patient may develop a coma, which will lead to death. Therefore, the symptoms of pathology should not be ignored. In medicine, hyperthyroidism can be found under the term “thyrotoxicosis”.
Features of hyperthyroidism in women
According to some statistics, hyperthyroidism occurs in women not 5, but 10 times more often than in men. Experts attribute this to the fact that it is the female body that is more susceptible to hormonal fluctuations throughout life. A surge of hormones occurs during each menstrual cycle, during pregnancy, childbirth, breastfeeding, and during menopause. First of all, the load falls on the thyroid gland.
Therefore, all women need to visit an endocrinologist for preventive purposes at least once a year. The doctor should not only examine the thyroid gland, but also give a referral for blood donation to determine the level of thyroid hormones in it.
Features of hyperthyroidism during pregnancy
If a woman suffers from hyperthyroidism, then after the conception of a child, the symptoms of the disease will become more intense. Treatment is carried out without fail, otherwise the patient may develop myxedema coma. This condition is fatal in 80% of cases.
Congenital hyperthyroidism is dangerous for newborns. If the child does not receive treatment, he will die. Therefore, all women who plan to become a mother should be tested for latent hyperthyroidism. This will allow you to have a healthy baby.
Features of hyperthyroidism in men
In men, hyperthyroidism develops less frequently, but at the same time they develop a latent form of the disease that does not give pronounced symptoms. For this reason, men start receiving treatment when it is already ineffective. Moreover, it is not possible to cope with the violation either with the help of drugs or with the help of an operation.
Hyperthyroidism affects the functioning of the organs of the reproductive system. High levels of thyroid hormones lead to increased levels of SHBG (a protein that binds male sex hormones). For this reason, the level of testosterone and dihydrotestosterone decreases, which means that potency worsens, serious changes occur in the qualitative composition of the seminal fluid.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism
Even in the early stages of the development of bulging eyes, a person immediately seeks medical help. While he can endure a goiter growing in his neck for years, despite the fact that it disrupts the process of swallowing food. In addition to these symptoms, a patient with hyperthyroidism has disturbances in the functioning of all internal organs. They suffer from the toxic effect on them of a huge amount of thyroid hormones.
Symptoms in women
In women, the symptoms of hyperthyroidism cannot go unnoticed, as they immediately affect the appearance. The thyroid gland regulates the work of all internal organs, so they will also suffer. The patient will begin to gain weight, her performance will deteriorate, certain changes in mood will occur.
The central nervous system of patients with hyperthyroidism works with disorders. A woman becomes tearful, her sleep worsens, and sudden mood swings occur. Other signs of hyperthyroidism include changes in appearance. The patient’s hair begins to fall out, nails exfoliate, and the skin worsens. The thyroid gland itself increases in size. Therefore, even with a slight swelling, you need to consult a doctor.
Violations by systems and organs:
Central nervous system. Sleep worsens, irritability appears. A woman may notice panic attacks that were previously absent. Cognitive abilities are deteriorating.
Cardiovascular system. The patient develops a stable sinus tachycardia, the pulse quickens, blood pressure rises.
Vision. The eyeball moves forward, becomes inactive. A woman has a split in the eyes, lacrimation intensifies.
exchange processes. The woman loses weight dramatically, although her appetite increases. In parallel, excessive sweating develops.
Muscles. The woman looks tired and weakened, she cannot endure intense physical activity. Even walking short distances becomes impossible for her. Muscle pain and weakness lead to difficulty in habitual movements.
Sexual system. The menstrual cycle is disturbed, infertility may develop. Even if it is possible to conceive a child, the patient most often has a miscarriage. Bleeding during menstruation is scanty, the abdomen is swollen and very sore.
Symptoms in men
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism in men have certain differences from the symptoms of the disease in women.
At the same time, there are some similar signs, among which:
Fatigue.
Appetite disturbance.
Increased sweating.
Increased anxiety.
Poor heat tolerance.
Deterioration of cognitive abilities.
Weight loss.
First, the man begins to lose body weight. Activation of metabolic processes leads to increased appetite. With age, a man begins to gain weight, and significantly.
Rare symptoms of hyperthyroidism in men include:
The skin becomes sticky.
Hair starts to fall out.
The hands are shaky.
Diarrhea develops.
May experience nausea and vomiting.
Weakness increases.
The heart can beat faster, and the acceleration of its rhythm occurs even at rest. Contractions of the heart muscle lose their former regularity, become stronger. Many patients indicate that their heart is literally “bursting out of their chest.” Older men develop heart failure.
The cause of hyperthyroidism in men is often an autoimmune disease that occurs against the background of Graves’ disease. Therefore, immune cells begin to attack the tissues of the gland, forcing it to produce hormones in excess. If Graves’ disease really became the cause of hyperthyroidism, then the organs of vision will be involved in the pathological process.
Changes that occur in men:
There are swelling around the eyes.
The eyeballs begin to bulge outward.
The eyes are very irritated.
The tearing intensifies.
Causes of hyperthyroidism
To date, the exact causes of hyperthyroidism have not been established. Often the latent (subclinical) form of the disease is inherited. Various external factors affect the performance of the thyroid gland in a negative way. The disease develops mainly in people over 50 years of age.
Causes in men
In men, hyperthyroidism can develop for the following reasons:
Genetic predisposition.
Frequent stress.
Living in areas with low levels of iodine in food.
Alcohol abuse, smoking.
Poor environmental situation in the area.
Effects on the body of radiation.
Postponed autoimmune thyrotoxicosis of the thyroid gland (AIT).
Work on harmful production.
DTG (diffuse toxic goiter) leads to the development of hyperthyroidism in 80% of cases.
Nodular toxic goiter.
Toxic prostate adenoma, which independently produces hormones.
Thyroid diseases that have been treated incorrectly.
Long-term use of iodine preparations in high dosages.
Diabetes.
Violations in the interaction of the thyroid gland and pituitary gland.
Thyroid size.
Decreased body defenses.
Tuberculosis.
With diffuse toxic goiter, your own immune cells begin to attack the tissues of the thyroid gland. In response, she will produce an excess amount of hormones.
Causes in women

Causes that can provoke the development of hyperthyroidism in women:
Diffuse toxic goiter or Graves’ disease. This reason is considered leading in terms of the development of hyperthyroidism. Basedow’s disease is an autoimmune pathology in which a person’s immunity begins to produce antibodies that cause the thyroid gland to produce a large amount of hormones. Many people with toxic goiter also have other autoimmune pathologies, such as glomerulonephritis, gastritis, and hepatitis. Hyperthyroidism and the presence of goiter are the two main signs of Graves’ disease.
Thyroiditis. In this disease, inflammation is concentrated in the thyroid gland. Viral infections become the impetus for the development of pathology.
Excess intake of thyroid hormones in the body. Most often this happens while taking medications.
Nodular goiter. In this disorder, pathological activity is observed in a certain area of the thyroid gland. Doctors call these areas hot knots.
Hypothyroidism vs Hypothyroidism: What’s the Difference?
Hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism are different diseases. With hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland works poorly, it produces an insufficient amount of hormones, so their level will be reduced. All processes in which they take part slow down. Patients begin to gain weight, their skin is pale and dry, the heartbeat is rare, speech suffers, movements become inhibited.
In hyperthyroidism, metabolism, on the contrary, accelerates, as there are too many thyroid hormones in the body. This provokes the acceleration of all processes. Therefore, the symptoms of hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism are different. Patients become very irritable, their skin is moist, weight decreases, appetite increases, heart rate increases, etc.
Types of hyperthyroidism
In the process of producing thyroid hormones, not only the thyroid gland takes part, but also the pituitary gland with the hypothalamus.
Depending on what is the cause of hyperthyroidism, the types of the disease will differ:
primary hyperthyroidism. It occurs due to a malfunction in the thyroid gland itself, or ectopic thyroid tissue. Pathology occurs in the presence of goiter, due to excessive intake of iodine hormones in the body, or with toxic adenoma of the thyroid gland.
secondary hyperthyroidism. It manifests itself due to disorders in the work of the pituitary gland, which causes the thyroid gland to produce an excess amount of hormones. Most often, a violation develops due to the growth of a pituitary adenoma.
Tertiary hyperthyroidism. It develops due to malfunctions in the hypothalamus, which most often occur against the background of neuroses.
Forms of hyperthyroidism
Forms of primary hyperthyroidism can be as follows:
subclinical hyperthyroidism. In this case, the disease has an asymptomatic course, so it is difficult to identify it. The level of T3 and T4 in the blood test will be normal, and the level of TSH, which is produced by the pituitary gland, will be low.
Manifest or overt hyperthyroidism. With this form of the disease, the level of T3 and T4 is increased, and the level of TSH is lowered.
Complicated hyperthyroidism. A patient with this form of the disease develops atrial fibrillation, psychoses, renal and heart failure, sudden weight loss, etc.
Diagnosis of hyperthyroidism
To identify hyperthyroidism, the patient is examined, and then sent for laboratory and instrumental examinations, including:
Blood donation for T3, T4, TSH and antibodies.
ECG, designed to detect abnormalities in the work of the heart.
Ultrasound and CT of the thyroid gland. These studies allow you to assess the state of the thyroid gland, its size, the presence of nodes and inflammatory infiltrate.
Biopsy of the thyroid nodule with further histology of the material taken.
Thyroid scintigraphy allows you to determine the activity of the body.
Assessment of vision using various ophthalmological tests.
In addition, patients with hyperthyroidism have certain changes in appearance, and also present characteristic complaints to the doctor. They are the basis for a detailed examination of the patient.
Treatment of hyperthyroidism
If treatment is started on time, then hyperthyroidism can be dealt with. Only in this case, you can count on success and avoid the development of serious diseases. When therapy is absent, the patient develops severe disorders in the work of the cardiovascular system, bone pathologies and thyrotoxic crisis.
Treatment can be medical or surgical. In addition, radioactive iodine therapy is practiced. Do not forget about diet and physiotherapy.
Medication
The main goal of drug correction of hyperthyroidism is to achieve a stable decrease in the level of thyroid hormones in the body. This will eliminate their toxic effect on organs.
If the patient is under 50 years old and the disease was diagnosed in him at an early stage, then he is prescribed thyreostatic drugs that suppress the functioning of the thyroid gland. It takes a long time to take them. When a person stops using the medication, all symptoms of hyperthyroidism return.
Mercazolil is the drug of choice in the treatment of hyperthyroidism. It is aimed at blocking the synthesis of thyroid hormones. It is prescribed in the case when their increase is insignificant and was discovered for the first time. If hyperthyroidism has a severe course, then Mercazolil is not used for treatment. Therapy with this drug can last no more than 2 years. Moreover, sometimes the blockage of hormones is so intense that replacement therapy with the same hormones is necessary.
As a rule, after 21 days from the start of treatment, the patient’s state of health stabilizes. All symptoms of the disease disappear. Indicators of successful treatment is the normalization of the pulse, as well as weight gain. During therapy, you need to control the blood picture.
It is impossible to abruptly cancel Mercazolil, as this can cause a crisis. The most common complications from taking the drug include agranulocytosis, leukopenia and agranulocytic tonsillitis.
Treatment of hyperthyroidism with radioactive iodine
Radioactive iodine is prescribed at an early stage of the disease. If therapy does not give an effect, then the patient is shown taking Mercazolil. In severe cases of the disease and in preparation for surgery, the doctor may prescribe the simultaneous administration of radioactive iodine and Mercazolil.
Radioactive iodine may be indicated for older people who need surgery, but for health reasons they will not be able to endure it. Iodine helps to reduce the activity of the thyroid gland, but at the same time it destroys its tissues. Therefore, it is so important to correctly calculate the dose.
The main side effect of iodine therapy is the release of large amounts of hormones into the blood. This happens on the 7-10th day from the start of treatment. To prevent the development of a crisis, a parallel intake of thyreostatics is required.
Surgery

If the patient has one goiter, which leads to excessive activity of the thyroid gland, as well as with the growth of its separate area, then an operation is indicated for him. If you remove it, the organ will start working as before. When a patient has a significant proliferation of gland tissues, or several nodes in it, the operation is contraindicated. Otherwise, the patient will develop hypothyroidism.
So, indications for surgery:
Large goiter.
Individual intolerance to drugs for blocking thyroid hormones.
Relapse of the disease after conservative therapy.
During treatment and during the recovery phase, you will need to strictly follow the diet. To eliminate disturbances in the work of the cardiovascular system, patients are shown 2 specialized treatment courses per year.
Diet
To be successful in the treatment of hyperthyroidism, you need to strictly follow the diet. It allows not only to cope with the disease, but also to prevent its development. Make a diet should be a doctor. Sometimes a well-chosen diet allows you to do without taking medications.
Food should be as vitaminized as possible.
Products that must be on the menu:
Low-fat chicken and rabbit meat.
Seafood: squid, mussels, shrimp.
Coffee and chocolate, but only good quality.
Kefir and yogurt.
Tea mushroom.
Sauerkraut.
Cereals.
The use of these products will normalize the functioning of the intestines, as well as saturate the body with vitamins. In addition to proper nutrition, the patient should receive enough water, which will help get rid of constipation, normalize metabolic processes and regulate the function of digestion.
Video: surgeon, doctor of medical sciences Kosovan Viktor Nikolaevich will talk about the methods of treating hyperthyroidism:









