Contents
Exceeding the norm of cholesterol in the blood is defined by medical terminology as hypercholesterolemia. The cause of this condition can be both diseases and culinary traditions associated with the use of large amounts of animal fats.
Basic Concepts
Genetic predisposition is one of the causes of hypercholesterolemia. The etiology of the disease may be associated with a genetically determined pathology, when a child inherits from his parents a defective gene associated with the synthesis of cholesterol (the so-called familial or primary hypercholesterolemia). In children and adolescents, pathology is often not diagnosed, showing its symptoms already in adulthood.
The generally accepted classification of lipid metabolism disorders according to Frederickson, which is widely used in hematology and other fields of medicine.
In the etiology of secondary hypercholesterolemia, there are several factors that trigger the onset of the disease. Sometimes a combination of conditions, the manifestation of which is provoked by risk factors, becomes a catalyst for the disease.
Forms of the disease are divided on the basis of the etiology of its development, each of them does not have specific manifestations and other features:
Primary hypercholesterolemia most often occurs due to a genetic failure, so it cannot be prevented. The homozygous familial form of the disease occurs when both mother and father have abnormal genes. The frequency of occurrence is 1 case per million healthy people. The heterozygous hereditary form is caused by a defective gene of one of the parents, occurs in 90% of cases of the primary form.
Secondary hypercholesterolemia is caused by metabolic disorders, somatic diseases.
Alimentary hypercholesterolemia is caused by unhealthy eating habits.
When it appears
Factors that provoke hypercholesterolemia:
Liver disease
Diabetes;
Hypothyroidism;
Nephrotic syndrome;
The use of medicines on an ongoing basis.
Risk factors:
Heredity;
Sedentary lifestyle;
Excess body weight caused by an improperly composed diet, impaired metabolism;
Pathological eating habits, for example, addiction to cooking with lard;
Frequent drinking of alcoholic beverages, accompanied by a plentiful snack;
A combination of several factors.
External signs and symptoms
Lipidogram is an uninformative laboratory indicator, since an elevated cholesterol level does not mean anything. Total cholesterol is made up of triglycerides, high and low density lipoproteins. It is important to divide this indicator into components by calculating the effect of lipoproteins of various fractions on the walls of blood vessels.
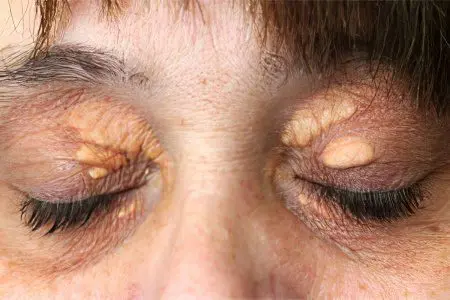
External manifestations that are critical for the diagnosis of secondary or genetically determined hypercholesterolemia by a specialist:
Xanthelasmas – formations of a dirty yellow color on the eyelids, located under the upper epithelium, may be invisible to the layman.
Lipoid corneal arch in a patient under 50 years of age.
Xanthomas are formations consisting of cholesterol located above the tendons.
When the disease progresses, the symptoms become massive.
Methods of diagnosis

The most informative is the study of the lipid spectrum, during which cholesterol is divided into “good” and “bad”, the coefficient of its atherogenicity is determined.
Additional research methods:
The study of the anamnesis, complaints of the patient, his opinion about the causes of the appearance of xanthomas and xanthellasms;
Determination of probable familial hypercholesterolemia, somatic diseases;
Examination of the patient with measurement of blood pressure and auscultation;
General analysis of blood and urine to determine the presence of inflammation;
Blood test for biochemistry (determination of the level of sugar, creatinine, uric acid);
Lipidogram for the presence of elevated levels of lipoproteins;
Study of the immunological status;
The study of the genetic pattern of hereditary diseases in all family members.
Possible consequences and complications

The most dangerous consequence of hypercholesterolemia is atherosclerosis, when cholesterol plaques accumulate on the walls of blood vessels, leading to a loss of elasticity and, as a result, disruption of the activity of the cardiovascular system. An increase in the size and prevalence of atherosclerotic plaques leads to narrowing and occlusion of blood vessels, the development of heart attack and stroke.
The consequence of chronic dysfunction of the circulatory system is ischemia of the arteries or organs such as the heart, brain.
The most dangerous complication is dysfunction of the circulatory system, in an acute form leading to vasospasm. The consequence of this is a heart attack with rupture of small and large vessels – typical manifestations of diseases associated with hypercholesterolemia.
The norm of cholesterol in the blood is no more than 5,2 mmol / l (200 mg / dl). Exceeding these indicators is the reason for the study of the entire lipid spectrum. With an increased level of “harmful” cholesterol of low and very low density, lifestyle correction is required.
Features of food
The appointment of a diet for hypercholesterolemia is one of the important therapeutic measures designed to remove “bad” cholesterol, to provide an anti-sclerotic effect with the help of a specially selected diet.
The goal of following the general rules of nutrition is getting used to new eating habits, normalizing metabolism.
Basic nutritional principles:
Reducing the total amount of fat in the menu;
Exclusion from the diet of foods high in cholesterol;
An increase in the proportion of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the menu;
Replacement of animal fats with vegetable oils;
The use of salt to a minimum (up to 3-4 g per day);
Inclusion in the diet of complex carbohydrates and a large amount of fiber;
Minimal intake of saturated fatty acids.
A diet designed to lower cholesterol must necessarily include vitamins, trace elements and nutrients. This diet will have to be followed for at least a month, maximizing the variety of the diet.
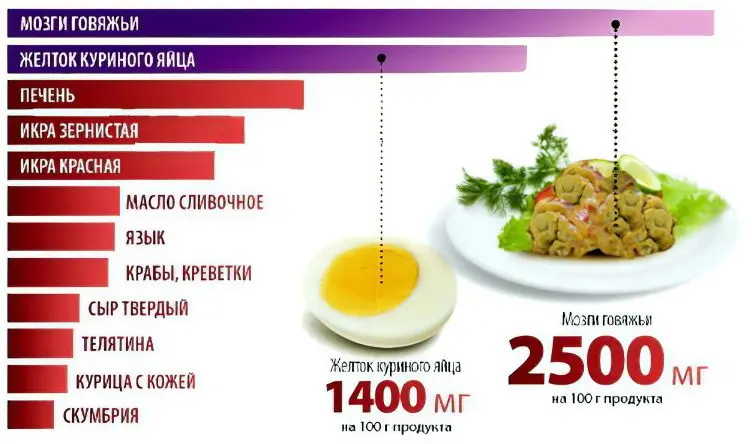
The menu excludes liver, veal, beef brains, red and granular caviar, tongue, butter, mackerel and hard cheese, that is, foods high in cholesterol.
Video: foods that lower cholesterol:









