Contents
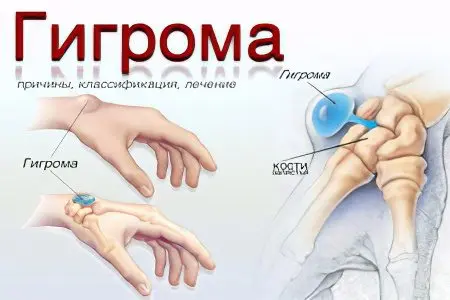
Hygroma is a tumor that is located next to the joints, or tendon sheaths. Her favorite place of localization is the wrist joint, hand, foot and ankle joint. The tumor is represented by a sac that contains sero-fibrous or sero-mucous fluid. Hygroma is a neoplasm of a benign nature. In fact, it is a cyst.
Until now, the causes of the appearance of hygroma are not fully known, but doctors note that it often develops in blood relatives, as well as in people who have repeatedly been injured in the joints.
If the hygroma is small, then it does not cause discomfort to a person, but it can worsen the appearance of the limb. When the hygroma is large, it begins to put pressure on the tissues and nerve endings, causing pain and worsening the sensitivity of the area in which it is located.
The probability of degeneration of hygroma into a malignant tumor is absent. This neoplasm does not pose a threat to human life. It is difficult to cope with it by methods of conservative therapy; in order to remove it, the help of a surgeon will be required.
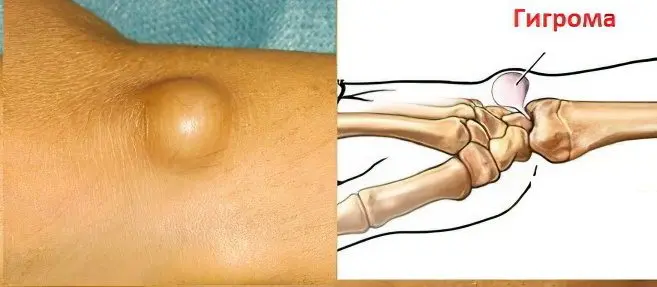
Hygroma – what is this disease?
The hygroma is surrounded by a dense mesh, which consists of connective tissue fibers. Inside it is a viscous liquid. Its consistency resembles jelly, which can be transparent or yellow. This serous fluid often contains fibrin or mucus.
Hygroma always has a connection with the sheath of the tendon, or with the joint. It begins to grow next to these structures. Some hygromas are soft, others are elastic, and still others are hard and resemble bone tissue.
Most often, such articular cysts are diagnosed in women at a young age – from 20 to 30 years. In men, hygromas develop 3 times less frequently. They make up 50% of all benign tumors of the wrist joint. Hygromas are not dangerous to human health and life, but often after their removal, they form again. In the elderly and in children, cysts rarely form.
There are two types of hygroma – single-chamber and multi-chamber hygroma. Inside the hygroma there is a special liquid with mucin. The egg itself is inelastic. There are also so-called multi-chamber hygromas, which, thanks to their branches, are able to expand in the tissues.
Code according to mkb 10
In the international classification of diseases, the 10th revision of the hygroma is determined by the code M71.3. It belongs to the category of bursopathy.
Causes of hygroma

There is an opinion that hygroma is a protrusion of the joint capsule, or tendon sheath, which was infringed in the isthmus. In fact this is not true. Hygromas are connected with articular structures and with tendon sheaths, their capsule is also represented by connective tissue. At the same time, the tumor has its own characteristic features and structural features. If we examine the structure of the capsule under a microscope, we can find that its cells have degenerative changes. Therefore, there is a theory that hygroma is the result of the degeneration of connective tissue cells. As a result of this process, 2 types of cells are formed. Spindle-shaped cells form a hygroma capsule, and spherical cells are filled with fluid, which subsequently enters the intercellular space.
Therefore, it will not be possible to cope with hygroma with the help of drugs, and the operation is associated with a high probability of relapse. Provided that even a small area of the altered tissue remains in the affected area, its cells will begin to divide again, which will lead to the re-formation of the tumor.
To date, the exact causes of the appearance of hygroma have not been established. Traumatologists are of the opinion that hygroma is a consequence of the simultaneous impact on healthy body tissues of several factors at once. First of all, it is necessary to take into account the hereditary predisposition to the formation of such cysts. In addition, there is evidence that about 30% of hygromas appear as a result of a single injury.
Scientists also suggest that the hygroma develops due to repeated trauma and a high load on the articular element or on the tendon.
Hygroma can begin its growth anywhere where there is connective tissue. However, most often it is formed in the distal parts of the arms and legs.
Hygromas are detected in such areas of the body as:
Back side of the wrist joint. This is a favorite place for localization of the cyst.
Palmar surface of the wrist joint.
Hands.
Fingers.
Feet.
Ankle joints.
Video: orthopedic traumatologist Nikolai Antonovich Karpinsky about the treatment of wrist hygroma:
Physiotherapy in the treatment of hygroma
Physiotherapy allows you to get rid of aseptic inflammation of the tumor:
Procedure | How does work | A course of treatment |
UHF | During the procedure, tissues are heated to the required depth, which helps to relieve inflammation, improve blood supply and accelerate tissue regeneration. | Assign 8-10 procedures that are performed every day. The duration of one session is 10-12 minutes. |
Ultrasound | The procedure promotes muscle relaxation, improves blood circulation in the affected area, promotes oxygenation of tissues, relieves inflammation, and accelerates healing. | Assign 8-10 procedures that are performed every day. The duration of one session is 8-10 minutes. |
Magnetotherapy | Inflammation will be stopped by heating the tissues. | Assign 10 procedures that are performed every day or every other day. The duration of one session is 10-15 minutes. |
Baths with baking soda and salt | The procedure helps to reduce the inflammatory response, resolve adhesions and strictures, and develop contractures. | Assign 15-30 procedures that are performed every day. The duration of one session is 15-20 minutes. The water temperature should be from 36 to 40 ° C, and the salt concentration in the solution should be 20%. |
Performing a hygroma puncture
The puncture allows for some time to reduce the size of the tumor, but it will not be possible to completely get rid of it. This procedure is carried out if the hygroma hurts, but a person, due to some circumstances, cannot be operated on.
To begin with, the patient’s skin is treated with a disinfectant composition, after which a needle is inserted into the cyst at an angle of 30 ° C. The fluid is aspirated until the tumor has completely subsided. To slightly reduce the risk of re-development of hygroma during the puncture, it is possible to introduce sclerosing solutions. However, it is impossible to guarantee a positive effect by 100%. With such treatment, the likelihood that the administered composition will enter the cavity of the joint or tendon sheath increases. This can lead to the formation of adhesions and limited movement of the limb.
A puncture can be performed not only for therapeutic, but also for diagnostic purposes, as it allows you to study the fluid that filled the cyst.
Operative intervention

The probability of recurrence of the disease after the operation is 20%. Surgical intervention allows you to remove the hygroma with minimal damage to surrounding tissues. Most often, the operation is prescribed in the case when the hygroma gives the patient aesthetic discomfort.
Other indications include:
The pressure of the hygroma on the vessels and nerve fibers.
Decreased joint mobility.
High probability of tumor rupture.
Inflammation of the hygroma against the background of bursitis or tendovaginitis.
If the blood counts are normal and the person is generally healthy, then he is sent for surgery. Most often, local anesthesia is sufficient, although inhalation anesthesia with nitrous oxide is sometimes used. In the morning, on the day of the upcoming intervention, the patient is prescribed a broad-spectrum antibiotic.
The skin in the area of the hygroma is disinfected, after which an incision is made. It can be performed diagonally across the top of the hygroma, or at its base. The capsule is isolated, its base is found and it is crossed. Then stitches are applied, or the wounds are simply tightened if the incision was small.
As a rule, on the 5-7th day after the operation, the sutures are removed, during which time the wound is completely healed. The working capacity of the limb will be fully restored in 10-14 days. To minimize the likelihood of adhesion formation, you need to perform therapeutic exercises. Specific exercises will be recommended by the doctor. It is also allowed to massage tissues that are at some distance from the scar. All steps must be performed carefully so as not to displace the seams.









