Contents
Every year orchards are attacked by many pests and diseases. Throughout the warm season, gardeners are struggling with this problem by all available means. Especially important is the processing of the garden in early spring, because it is during this period that it is possible to nip all misfortunes in the bud before they have time to wake up and multiply. In order for the effect to be long-lasting and give one hundred percent protection, trees and shrubs will have to be sprayed more than once: only in the spring months, the treatment is repeated three to four times. An approximate spraying scheme will help the gardener not to get confused and not forget anything.
How and how to process fruit trees in spring will be discussed in this article. It will also offer a calendar of orchard treatments by months, and consider popular preparations, remedies for pests and garden diseases.
Preparation now
The gardener’s work should begin from the first days of spring. When the last snow still lies on the branches, and the paths are shackled with frost, it’s time to go out into the garden for the first inspection. It’s time to shake off the snow caps from the crown so that the melting heavy snow does not break off the shoots starting to grow. You can take a pruner with you, trim the crowns, cut out damaged or dried branches.
The gardener must inspect every fruit tree and every shrub in order to identify areas of exfoliated bark, cut off mummified fruits, and remove insect nests. If there are hollows, large cracks on the trunk, they need to be cleaned out, because it is in such shelters that insect larvae like to winter, pests lay their eggs there.

When it gets a little warmer, you need to whitewash the tree trunks. It would also be useful to collect last year’s leaves, garbage, cut branches – all this should be taken away from the garden and burned.
As a rule, the trees are whitened in autumn, and in the spring they only touch up the applied layer of lime. Whitewash is able to cope with fungi, lichens, eggs and insect larvae.
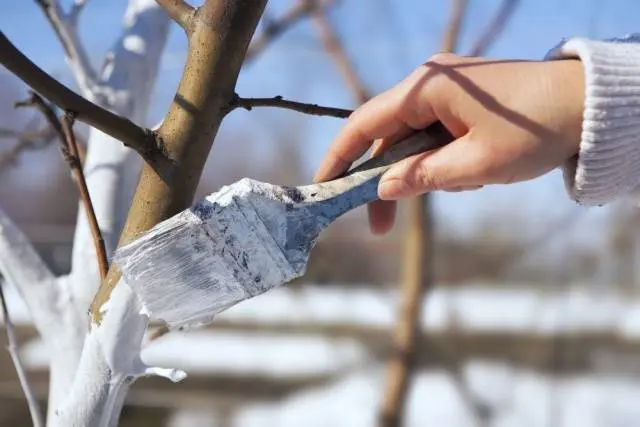

You can prepare a mixture for whitewashing trees in spring like this, mix:
- 2 kg of lime or lime paste;
- 10 liters of water;
- 1 kg of clay;
- 300 grams of copper sulfate.
The resulting composition is thoroughly kneaded and the trunks and lower shoots of fruit trees are painted with it.

In early spring, you can process the crown of trees. For these purposes, an old proven tool is perfect – ordinary diesel fuel. The branches sprayed with diesel fuel are covered with a thin oily film, under which the larvae and spores simply suffocate and die.
Stages and timing of spraying
Spring treatment of the garden with chemicals should begin when stable heat is established on the street – the air temperature during the day will be kept at +5 degrees, and at night it will not fall below zero.
Spraying should not be postponed – when the buds begin to bloom, and sap flow is activated in the tree, the concentration of drugs will have to be reduced. The very first treatment is most effective – while the trees are “sleeping”, and insect larvae and infectious agents are still inactive.
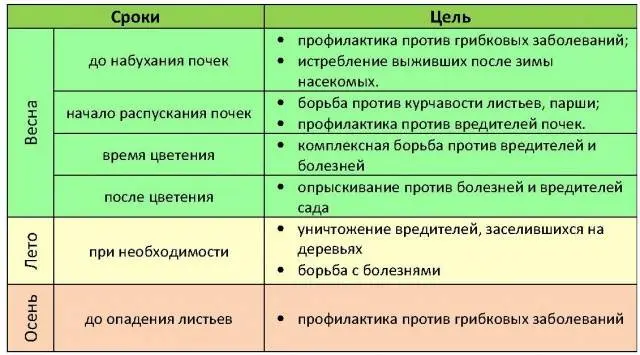
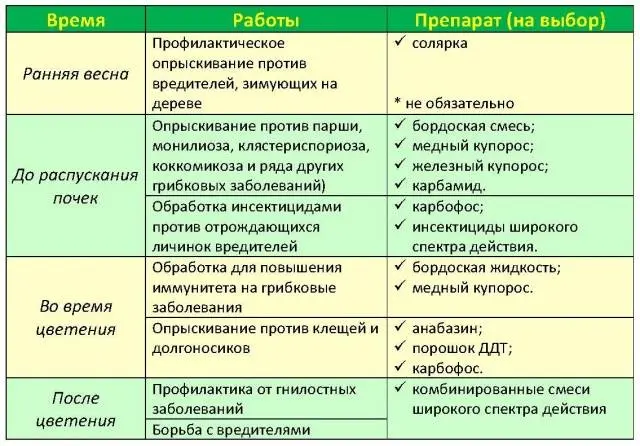
An approximate calendar for spraying a fruit orchard looks like this:
- Treatment of trees and shrubs in early spring, until the plants buds swell.
- Spraying flowering trees and shrubs.
- Treatment of plants after flowering.
- During the formation of ovaries and fruit growth.
In any case, it is recommended to spray trees in calm, dry weather, in the absence of strong solar activity (on a cloudy day, before 10 am, after sunset).
First spraying of the garden
The first spring treatment of fruit trees and berry bushes should begin before bud break. This stage is considered the most important, because the entire further spraying scheme will depend on its effectiveness.

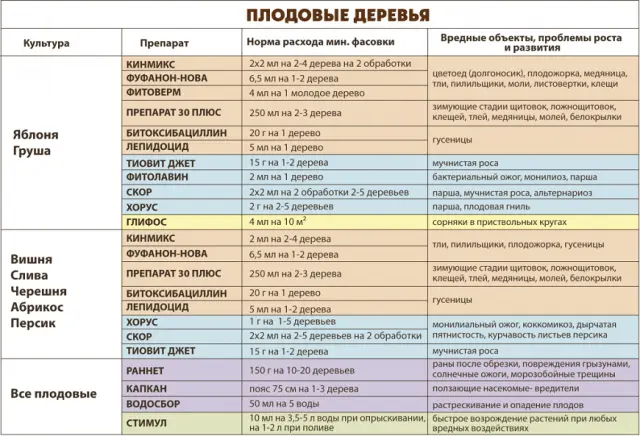
The most dangerous diseases of the garden in the early spring: black cancer, coccomycosis, scab, anthracnose, moniliosis. Of the pests at this time, you can find soil insects, codling moth, aphids, caterpillars, mites.
For the first spring spraying, it is recommended to use one of the old and proven products, such as urea, blue vitriol, Bordeaux mixture (“blue spray”). If these drugs are ineffective, you will have to purchase chemicals: Anabasin, Trichlorol, Strobi, Teldor, which perfectly cope with parasites and fungi.
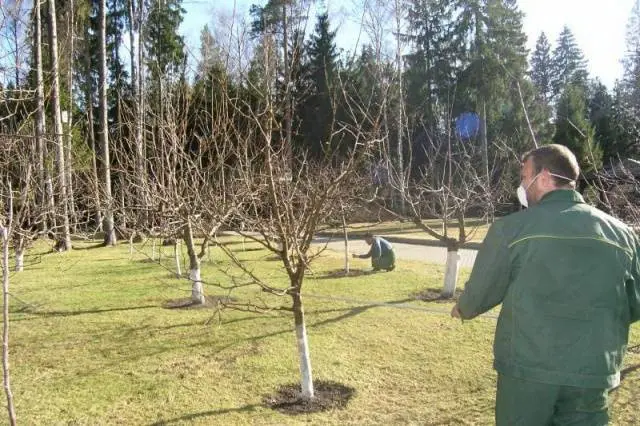

Modern gardeners often oppose chemical garden protection products, so a homemade solution can be advised. Prepare it like this:
- Pour two stacks of crushed tobacco leaves into a three-liter jar.
- There also add a handful of onion and garlic husks, pine needles and chopped orange peels.
- All this should be poured with hot water (about 70 degrees), covered with a nylon lid and put away in a dark place for about a week.
- After a week, the solution is filtered through several layers of gauze and diluted with ten liters of water.
- The resulting product is mixed and poured into it 100 grams of tar soap rubbed on a fine grater.
Fruit trees and berry bushes are sprayed with the finished solution, repeating the treatment after 10-12 days until the garden blooms.
Spraying the garden before and during flowering
Immediately before flowering, orchards are usually treated for codling moth caterpillars, scab and spotting. At this stage, karbofos is very effective. For the treatment of trees, a 10% agent is taken, diluting 70 grams of the substance in 10 liters of water.

Immediately after flowering, the trees are treated again, this time to protect against various diseases. Together with blossoming flowers, mites crawl out of shelters, from which you can protect yourself with colloidal sulfur. To prepare the solution, you need to take 80 grams of 70% sulfur and dilute it in 10 liters of soapy water. If ticks are not destroyed in time, they can cause irreparable harm to the orchard.
Spraying at the stage of fruit formation
The processing of fruit trees and shrubs does not end there. When the ovaries are formed, spraying is carried out a third time – the plants protect against the remaining insects and various putrefactive infections.

It is not necessary to carry out the third treatment of the garden for preventive purposes, because chemicals at this stage can greatly harm the environmental friendliness of the crop – toxins accumulate very well in fruits. Before spraying, trees and shrubs are carefully inspected, trying to identify a trace of infection or the presence of insects.

For processing trees at the stage of formation of ovaries, it is recommended to use:
- copper oxychloride;
- Bordeaux liquid;
- urea;
- combined chemicals with a wide spectrum of action;
- biological preparations that do not harm the garden and are not toxic.
Rules and Recommendations
The fact that the garden after the winter needs preventive treatment is understandable. Now the main thing is to correctly spray it so as not to harm the trees and shrubs.
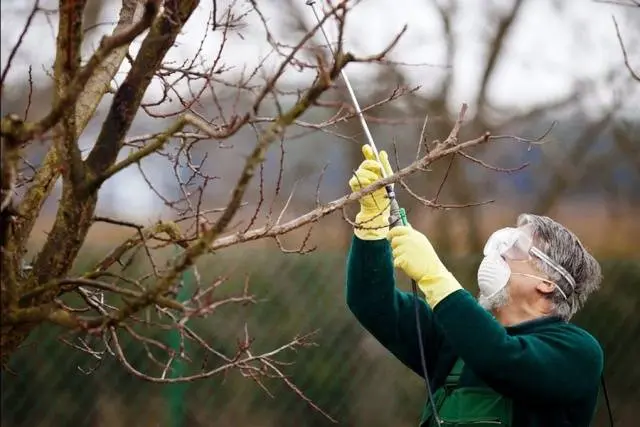

It is recommended to follow the following rules for spring garden processing:
- spray the tree completely, “from head to toe.” To do this, first process the crown, then select large branches and spray them alternately in the direction from the edge to the trunk. Lastly, the trunk and the ground in the near-stem circle are irrigated.
- If it rains within a day after treatment, you will have to repeat everything again.
- It is necessary to prepare the solution after certain calculations: about 5,5 liters of liquid will be required for an adult tree, 1,5 liters will be enough for a young tree or a large berry bush.
- For spraying, special cylinders, pumps and sprayers are used. After work, they must be washed with clean water and dried.
- The gardener must use personal protective equipment: mask, goggles, gloves. After processing the garden, wash your face and hands thoroughly with soap.
Conclusion

Every spring, absolutely all gardeners and summer residents face the question of how to process fruit trees from diseases and pests. To date, the choice of special means is quite large: these are chemical preparations, and folk remedies, and modern bio-insecticides. It is much more important to spray at the right time, before infections and pests have had time to spread and cause irreparable harm.









