Contents
What is uterine bleeding?
Uterine bleeding is the discharge of blood from the uterus. Most often, it is a serious symptom of diseases of the female body. Any uterine bleeding should be diagnosed in time, and the woman should receive medical assistance. Ignoring such a symptom leads to serious consequences, even death. It is important to know that normal uterine bleeding includes only menstruation, the duration of which is up to 5 days, with stable interruptions, 28 days long. All other bleeding is a pathology and requires medical supervision.
Menstruation (menstruation) is the only physiologically normal type of uterine bleeding. Usually its duration is from three to five days, and the interval between menstruation (menstrual cycle) normally lasts from 21 to 35 days. Most often, the first couple of days of menstruation are not abundant, the next two are intensified and, at the end, again become scarce; blood loss these days should be no more than 80 ml. Otherwise, iron deficiency anemia develops.
In healthy women, menstruation is painless. In case of pain, weakness and dizziness, a woman should consult a doctor.
The onset of menstruation usually occurs at 11-15 years of age and lasts until the end of the reproductive period (menopause). During pregnancy and breastfeeding, menstruation is absent, but this phenomenon is temporary.
It is important to remember that the early appearance of spotting in girls (under 10 years old), as well as in women after menopause (45-55 years old) is an alarming sign of serious illness.
Sometimes spotting in the middle of the cycle (on the 10-15th day after the end of menstruation) can become a variant of the norm. Their cause is hormonal fluctuations after ovulation: the walls of the uterine vessels become excessively permeable, so vaginal discharge may have blood impurities. Such discharge should not last more than two days. Sometimes the cause of spotting becomes an inflammatory process, so a woman should definitely consult a gynecologist.
A variant of the norm is also implantation bleeding, which occurs as a result of the introduction of the embryo into the uterine wall. This process occurs a week after conception.
Why are uterine bleeding dangerous?
Uterine bleeding has the ability to increase rapidly, not stop for a long time and difficult to stop.
Therefore, depending on what type of bleeding a woman has, it can be dangerous with such consequences as:
With moderate but regular blood loss, anemia of varying severity can develop. It begins if the volume of released blood is 80 ml. Although in such conditions there is no direct threat to the life of a woman, however, this process cannot be left without attention.
A large loss of blood may be due to simultaneous heavy bleeding, which is difficult to stop. Most often, surgery is required, with the replacement of lost blood and removal of the uterus.
The risk of progression of the underlying disease. In this case, we are talking about small blood loss, to which the woman does not pay attention and does not go for medical help. At the same time, blood loss, even in a small amount, can eventually lead either to profuse bleeding, or to the fact that the disease that caused it will go into a neglected form.
The danger of bleeding in pregnant women or in women in the postpartum period is that it can end in a state of shock. The intensity and severity of this condition is due to the fact that the uterus is not able to fully contract and stop blood loss on its own.
Causes of uterine bleeding
There are many reasons that can cause uterine bleeding. In order to systematize them, it should be understood that the resulting blood loss can be a disruption in the organ systems, as well as disorders in the genital area.
Extragenital causes of uterine bleeding, that is, those caused by disorders in the work of non-genital organs include:
Some diseases of an infectious nature are: sepsis, typhoid fever, influenza, measles.
Diseases of the hematopoietic system, these are: hemophilia, hemorrhagic vasculitis, low levels of vitamin C and K, etc.
Cirrhosis of the liver.
Prolapse of the urethra.
Disorders in the activity of the cardiovascular system, for example, hypertension, atherosclerosis, etc.
Decreased functionality of the thyroid gland.
The causes of uterine bleeding are genital, in turn, may be associated with the bearing of a child by a woman.
During pregnancy, the following causes of bleeding from the uterus are distinguished:
Ectopic pregnancy.
Pathology of the fetal egg.
The presence of a scar on the uterus.
Placenta previa, its low location or early detachment.
Various processes of destruction of uterine tissues.
Rupture of the uterus during labor.
Injury to the birth canal (vagina or vulva).
Infringement or delay of the departed placenta.
Enometritis.
trophoblastic disease.
Myoma of the uterus.
Cesarean section.
Chorioepithelioma.
Genital bleeding can occur in a woman who is not carrying a child. Causes for them include:
Discirculatory bleeding, which, in turn, can be climateric, reproductive and juvenile.
Tumors of the ovaries or uterus, both benign and malignant, such as fibromyomas.
Adenomyosis, characterized by the introduction of the uterine mucosa into its wall.
Rupture of a cyst or rupture of the ovary itself.
Any injury to the uterus.
Diseases of an inflammatory nature, these include cervicitis, vaginitis, endometritis, erosion, endocervicosis.
Damage to the external genitalia.
Taking oral contraceptives.
Sexual assault.
Uterine bleeding with menopause
It is a mistake to assume that a woman does not have discharge during menopause. However, even during the premenopausal period, she needs to pay attention to their nature and quantity. Sometimes menstruation may be absent for several months, and sometimes go regularly. This is due to the fact that ovulation has a different frequency, and fluctuations in hormone levels also occur. Such changes are considered normal and should not cause concern for a woman.
The following should alert her and become a reason for contacting a doctor:
Heavy bleeding that hygiene products cannot cope with.
Discharges accompanied by clots.
Bleeding between periods.
The duration of bleeding is more than three days than usual.
You can not leave such uterine bleeding during menopause, because they may indicate a hormonal imbalance, uterine polyps or fibroids, endocrine disorders, ovarian tumors and other serious diseases.
Uterine bleeding due to hormonal failure

Uterine bleeding can occur in a woman with a hormonal failure that has occurred in the body. This problem is relevant for the fairer sex at any age. This happens when there is a violation of the amount of hormones or when their ratio changes.
Hormonal failure can be caused by a number of reasons:
Violations occur due to the fact that the brain incorrectly regulates their production, for example, in pathologies of the pituitary gland.
Sometimes bleeding opens due to the pathology of the gonads. This can occur due to inflammatory processes in the ovaries, with tumors, cysts.
Chronic fatigue syndrome, especially enhanced by starvation and exhaustion of the body, can also cause bleeding.
Pronounced hormonal disorders occur during puberty girls, during pregnancy and after childbirth, after abortion.
Sometimes hereditary predisposition and taking certain hormonal pills can affect.
Prolonged bleeding can develop against the background of a medical abortion, which has recently gained momentum in popularity.
For the treatment of bleeding caused by hormonal disruptions, an individual approach is required. It will depend on the cause that caused bloody discharge from the uterus.
Uterine bleeding after cesarean
After a caesarean section, a woman should be under medical supervision. Most often, bleeding lasts a little longer than after natural childbirth. This is due to the fact that a scar is formed on the uterus, which makes it difficult to contract. Normally, bleeding stops completely after a couple of months. If it continues, then the woman needs to report this problem to the doctor.
The cause of pathological bleeding after surgery is most often hemostasis. Therefore, to eliminate this problem, doctors must carefully but carefully scrape the walls of the uterus. If the bleeding cannot be stopped, it must be extirpated.
If the bleeding is hypotonic, then it is not always possible to stop it, since it occurs after the uterus begins to contract. Profuse blood loss can lead to hypotonic shock. Replenishment of blood supplies by transfusion and manual examination of the uterus are necessary in order to detect possible remains of the placenta, determine the contractile function of the uterus and establish the existing rupture.
The critical measure that doctors take to save a woman’s life is the removal of the uterus. This method is used if bleeding after caesarean section by other means (electrical stimulation of the uterus, ligation of blood vessels, administration of uterotonics) cannot be stopped.
Types of pathological uterine bleeding

Gynecologists divide uterine bleeding into many types. But there are those that are most common:
Juvenile bleeding. They are characteristic of the onset of puberty in girls. They can be triggered by a number of factors, such as frequent illnesses, increased physical activity, poor nutrition, etc. Depending on the amount of blood lost, such bleeding can lead to anemia of varying severity.
About profuse uterine bleeding should be said if it is not accompanied by pain. In this case, the volume of fluid lost may vary. There are many reasons, it can be an abortion, and vaginal infections, and taking hormone-containing drugs, etc.
Acyclic bleeding characterized by the fact that it appears in the intervals between menstrual cycles. It can be caused by fibroids, cysts, endometriosis and other pathologies. If acyclic bleeding is observed regularly, then a doctor’s consultation is necessary. Although this type is not always a symptom of any pathology.
Anovulatory bleeding characteristic of women who have entered the period of menopause and for adolescents undergoing puberty. It is caused by the fact that the maturation of the follicles and the production of progesterone are disturbed, in the absence of ovulation. This species is dangerous because, without treatment, it can provoke the development of malignant tumors.
dysfunctional uterine bleeding occurs when the functioning of the ovaries is disrupted. A distinctive feature is that it occurs after menstruation has been absent for a long time, and blood loss with it is plentiful.
Hypotonic bleeding occurs due to low tone of the myometrium, after an abortion, etc. most often appears after childbirth.
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding includes those that are associated with a violation of the production of sex hormones produced by the endocrine glands. They can appear at almost any age, both during puberty and during menopause, and in the reproductive period of a woman’s life. This pathology is widespread.
This type of bleeding is expressed by the fact that the period of menstruation is lengthened, and the amount of fluid lost increases. Without treatment, it always leads to the development of anemia. The main feature is the prolonged absence of menstruation, sometimes up to six months, and then the occurrence of bleeding, which has a different strength.
Dysfunctional bleeding can be ovulatory (concerns women of reproductive age) and anovulatory (more common in adolescents and premenopausal women). Cycle disorders in this case are expressed in abundant and irregular periods, with long (more than 35 days) and short-term (less than 21 days) intervals, in the absence of menstruation for more than six months.
The tactics of treatment depends on the age of the patient and on the presence of concomitant pathology. It can be either medical or surgical. However, in adolescence, surgery is resorted to only in emergency cases. Conservative therapy consists in taking hormones. If left untreated, dysfunctional uterine bleeding can lead to infertility, miscarriage, chronic anemia, endometrial cancer, shock, and even death.
Atonic uterine bleeding
Atonic bleeding is characterized by the fact that it is formed when the uterus becomes unable to contract. The lack of contractility in obstetric practice is called the uterus of Kuveler. A characteristic feature of atonic bleeding is zero tone and a similar reaction to the introduction of uterotonics.
When it is not possible to stop the bleeding with the help of specialized drugs, a thick suture is applied to the posterior lip of the cervix, clamps are additionally applied to clamp the uterine artery.
If these methods were ineffective, and blood loss could not be stopped, then they are considered as preparation for an operation to remove the uterus. Mass loss of blood is considered to be from 1200 ml. Before the uterus is completely removed, attempts are made to ligate the vessels using the Tsitsishvili method, electrical stimulation (this method is becoming less popular, and doctors are gradually abandoning it), acupuncture. It is important to constantly replenish the reserves of lost blood.
Hypotonic uterine bleeding

This type is characterized by the fact that the tone of the myometrium decreases. Such bleeding occurs when the fetal egg is retained in the uterine cavity, during the separation of the placenta, after its release. The reason lies in the hypotension of the uterus after childbirth, when contractions occur rarely and are spontaneous. The critical degree of such a state is referred to as atony, when contractions are completely absent.
The main tasks facing physicians are:
Stop bleeding as soon as possible.
Replenishment of the deficit of the BCC.
Avoiding blood loss of more than 1200 ml.
Tracking blood pressure and preventing it from falling to a critical level.
Treatment is aimed at ensuring that the motor function of the uterus is restored as soon as possible. If there are remnants of the fetal egg, then it must be removed either by hand or with a curette. When hypotonic bleeding occurs after childbirth, it is necessary to squeeze out the placenta as soon as possible, if it does not work, then it is removed manually. Most often, it is the removal of the placenta that helps restore the motor function of the uterus. If necessary, her gentle massage on the fist is carried out.
As drugs, the introduction of pituitrin or oxytocin is indicated. Effective in some cases is the imposition of a bladder containing ice on the abdomen or irritation of the uterus with ether. For this purpose, a moistened swab is inserted into the posterior fornix of the vagina. If hypotension does not respond to this therapy, then measures are taken that are characteristic of uterine atony.
Acyclic uterine bleeding
Acyclic uterine bleeding is called metrorrhagia. It is not associated with the menstrual cycle, which is normal, it is characterized by the complete absence of any periodicity.
This condition can occur suddenly and be associated with the pregnancy of a woman, with an incomplete abortion, with placenta previa, with the development of an ectopic pregnancy, retention of part of the placenta, etc.
Acyclic bleeding, if a woman does not bear a child, can be observed in pathologies such as uterine fibroids, benign tumors. If the tumor is malignant, then metrorrhagia is observed at the stage of its decay.
It is not possible to describe the degree of intensity of blood loss, since the discharge can be spotting, profuse, with and without admixtures of blood clots.
It is important to pay close attention to acyclic bleeding for women who are in menopause, both at its initial stage and several years later, after the cessation of constant menstruation. In no case should they be perceived as renewed ovulation. Metrorrhagia in this period requires careful study, as they are often signs of a malignant process, such as sarcoma.
Breakthrough uterine bleeding
Breakthrough uterine bleeding develops against the background of hormonal disorders. They are characterized by an imbalance between estrogen and progesterone. Sometimes this type of bleeding occurs when a woman takes oral contraceptives. In this case, breakthrough bleeding is an adaptation reaction to the drug. If, after taking the prescribed remedy, bleeding occurs that does not correspond to the menstrual cycle, then it is necessary to consult a doctor about adjusting the dose or replacing the remedy.
Breakthrough bleeding can also be observed when the uterine wall is damaged by a spiral. This cannot be ignored, the spiral must be removed immediately.
Most often, blood loss from breakthrough bleeding is minor, however, a visit to the doctor should not be postponed.
Anovulatory uterine bleeding
These bleedings occur during the break between menstruation, their causes are varied, including they can be a manifestation of any disease. Most often, anovulatory bleeding is prolonged in time, lasts more than 10 days, and is acyclic. Women suffer such blood loss either during the extinction of reproductive function, or during its formation.
This bleeding is also called single-phase, during its opening the corpus luteum is not formed, the development of the follicle occurs with disturbances, ovulation is absent.
This bleeding can be hyperestrogenic, when the follicle matures but does not rupture, and hypoestrogenic, when several follicles mature but do not fully mature.
Rarely, anovular uterine bleeding occurs during the reproductive period of a woman’s life. Such phenomena are associated with violations of the hypophozotropic zone, after suffering stress, poisoning, infections.
Among adolescents, according to statistics, this type of bleeding is quite common. Such violations account for up to 12% of all gynecological diseases. In this case, the decisive factor may be irrational nutrition, mental trauma, physiological overload.
Discirculatory uterine bleeding
The occurrence of discirculatory uterine bleeding is caused by impaired ovarian function. Sometimes such external factors as past viral infections, stress, etc. serve as an impetus. Blood loss is not great, it is observed after menstruation has been absent for a long time.
Uterine bleeding with clots

Often, women observe the presence of clots in uterine bleeding. Most often, doctors explain their appearance by the fact that the uterus during fetal development has undergone certain anomalies. Therefore, the blood stagnates in its cavity, forming clots.
Most often, menstruation causes more pronounced discomfort in such women, especially when it occurs with an increased hormonal background. Sometimes it is precisely such a congenital anomaly that can cause increased bleeding and the presence of numerous clots in the discharge.
In addition to the fact that anomalies are congenital in nature, they can be acquired during life. Such phenomena are associated with the professional characteristics of a woman and with the abuse of bad habits. Often, during menstruation with blood clots, women experience severe cutting pains. In order to exclude the presence of a pathological process, it is important to consult a gynecologist.
Sometimes changes in the hormonal background can also lead to the formation of clots. To clarify the cause, you need to pass a series of tests, including thyroid hormones and adrenal hormones, and examine the level of progesterone and estrogen.
The presence of clots, severe pain in the lower abdomen, heavy blood loss during menstruation, acyclic mini-bleeding – all this most often indicates endometriosis. Such a diagnosis is established after a thorough diagnosis and requires appropriate treatment.
Sometimes the cause can be poor blood clotting and some complications that have arisen after childbirth.
Uterine bleeding during pregnancy
The most common causes of uterine bleeding during pregnancy are miscarriage, uterine disease, ectopic pregnancy, and damage to the placenta.
A miscarriage is accompanied by severe cramping pains in the lower abdomen, bleeding is intense, the color of the blood is from bright scarlet to dark. With an ectopic pregnancy, bleeding is accompanied by a deterioration in the general condition, malaise, nausea, vomiting, sweating and fainting. Blood is dark in color and usually comes out in clots.
Damage to the blood vessels of the cervix during pregnancy can occur during sexual intercourse or a gynecological examination. This bleeding is usually not heavy or prolonged.
If the placenta is damaged or previa, uterine bleeding may occur in the second or third trimester. The bleeding is usually very heavy. It poses a serious threat to the life and health of the expectant mother and her child.
It should be remembered that uterine bleeding in pregnant women is very dangerous, so a woman must definitely call a medical team that will provide her with urgent assistance.
First aid for uterine bleeding
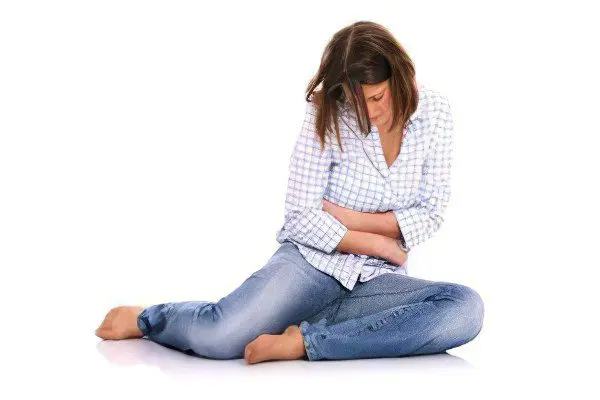

First aid for uterine bleeding is to call an ambulance as soon as possible. This is especially true in the case when a woman is carrying a child, her blood loss is plentiful, her condition deteriorates sharply. In this case, every minute counts. If it is not possible to call a team of doctors, then it is necessary to take the woman to the hospital on her own.
Any uterine bleeding is a serious threat to life and health, so the reaction must be appropriate.
It is strictly forbidden to apply a hot or warm heating pad to the stomach in case of dysfunctional bleeding, douching with any compositions, take a bath, use drugs that promote uterine contraction.
Independently, at home until the ambulance arrives, a woman can be helped as follows:
The woman must be put to bed, preferably on her back, and her legs placed on some kind of elevation. To do this, you can put a pillow or a roller from a blanket. Thus, it will be possible to preserve the consciousness of the patient, especially if the blood loss is impressive.
Something cold should be applied to the stomach. If there was no heating pad at hand, then the ice can be wrapped in a regular cloth. You can replace the ice with an ordinary bottle filled with cold water. Cold exposure time – up to 15 minutes, then a break of 5 minutes. This will achieve vasoconstriction, and therefore, somewhat reduce bleeding.
The woman needs to drink. Since it is not possible to put a dropper at home, it is necessary to offer the patient a plentiful drink. Plain water and sweet tea will do. This will contribute to the loss of fluid along with the blood, glucose will provide nutrition to the nerve cells of the brain.
Taking medications should be treated with extreme caution, especially if a woman is carrying a child. Before taking them, you should always consult with your doctor, but sometimes it happens that there is no such possibility. Therefore, it is necessary to know the names of hemostatic agents and their minimum dosage. These include Vikasol (taken 3 times a day, at a dosage of 0,015 g), ascorbic acid (maximum daily dose of 1 g), Dicinon (taken 4 times a day, at a dosage of 0,25), calcium gluconate (1 tablet up to 4 times per day). Before use, it is important to remember that all drugs have side effects.
How to stop uterine bleeding?
When the ambulance arrives at the scene, its actions will be as follows:
A bubble containing ice is applied to the woman’s stomach.
If the bleeding is heavy, then the woman should be taken to the car on a stretcher.
Hospitalization of the patient with transfer directly to a specialist.
The introduction of a solution of magnesium sulfate, with the threat or the beginning of a miscarriage. Or if a spontaneous abortion occurs, the woman is given intravenous calcium chloride and ascorbic acid diluted in glucose. An injection of Etamzilat can be made.
Doctors in the hospital use hormonal drugs to stop bleeding, in the event that a woman has not yet given birth, she does not have a suspicion of a tumor. Hormonal drugs include Jeannine Regulon, etc. On the first day they give an increased dose (up to 6 tablets), in the following days one tablet less, bringing it up to 1 piece. Sometimes gestogens are used, but it can be used only in the absence of severe anemia.
Hemostatic agents can also be used, for example, Dicinon, Vikasol, Askorutin, Aminocaproic acid.
Sometimes surgery is used, such as curettage of the uterus (an effective method to stop blood loss), cryodestruction (a method without contraindications), laser removal of the endometrium (used in those women who do not plan to have more children).
Treatment of uterine bleeding
Treatment of uterine bleeding largely depends on its causes and the age of the patient.
Adolescents are most often prescribed drugs that reduce the uterus, drugs that stop blood and strengthen the walls of blood vessels. It is also recommended to take vitamins, herbal medicine, less often – hormonal drugs that regulate the menstrual cycle. Women of reproductive age are prescribed hormonal drugs, sometimes surgical operations are performed (for fibroids, endometriosis of the uterus, etc.) After menopause, uterine bleeding most often indicates oncological pathologies of the uterus and ovaries, so treatment requires predominantly surgical intervention, including appendages.
In treatment, it is most important to diagnose the causes of bleeding in time, so sick women should seek medical help without delay.









