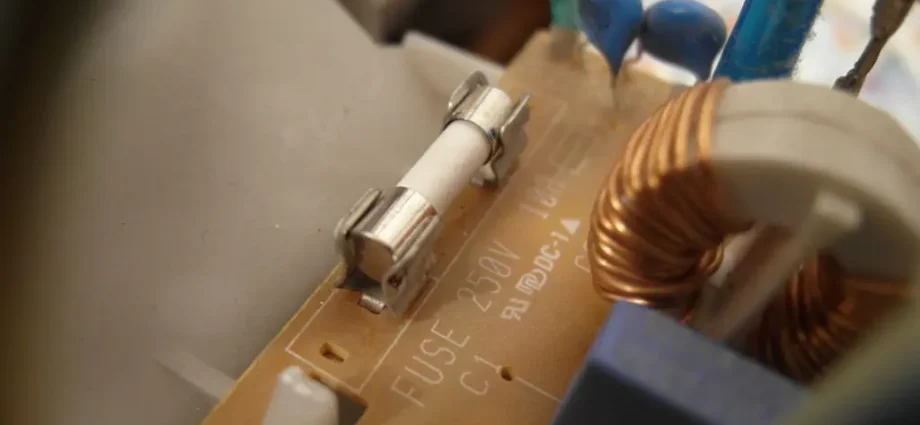
The breakdown of the microwave oven knocks us out of the rut: we have to take out the pans and pans again to heat up. One of the frequent breakdowns of the device is a blown fuse during a power surge. How and what to replace the fuse, everyone should know in order to quickly restore the operation of the microwave.
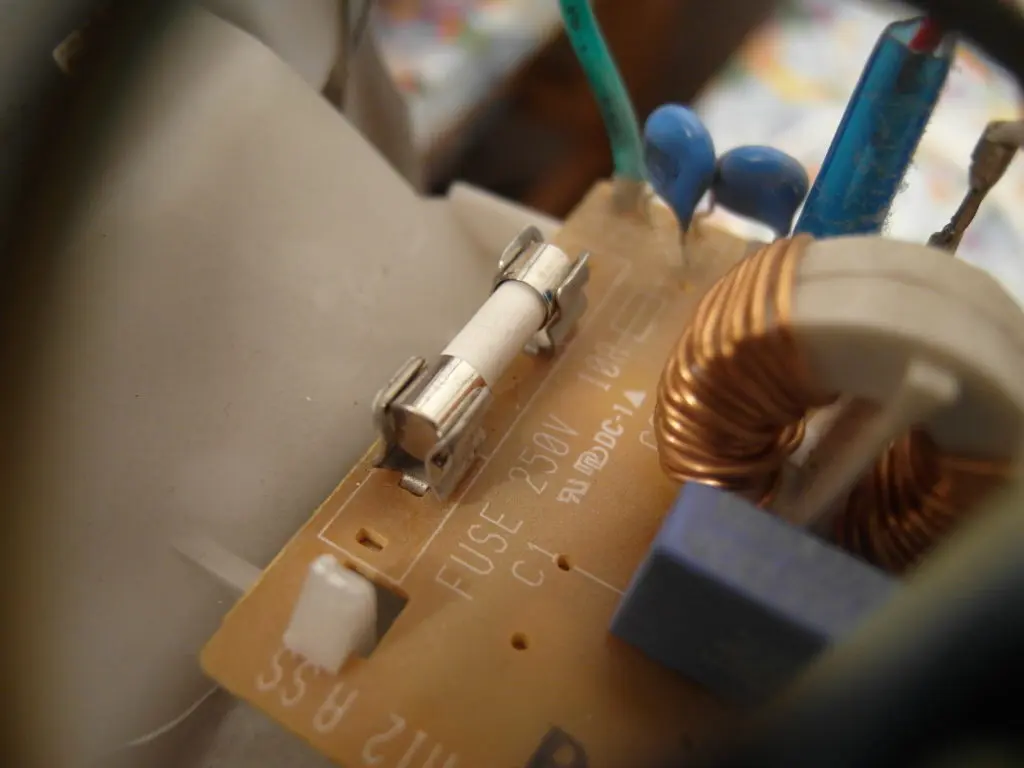
Fuse design, varieties
Why do you need a microwave fuse? It protects electronics from voltage surges, or rather, its consequences. Instability in the network leads to a sharp surge in voltage and burnout of the electronic components of the microwave oven.
Therefore, before the current flows to the “stuffing” of the technique, it passes through a flask with a metal thread. If the value in the network exceeds the nominal, then the thread burns out, breaking the circuit and protecting the device.
A glass (ceramic) fuse bulb serves as a protective sheath against splashes when the filament melts.
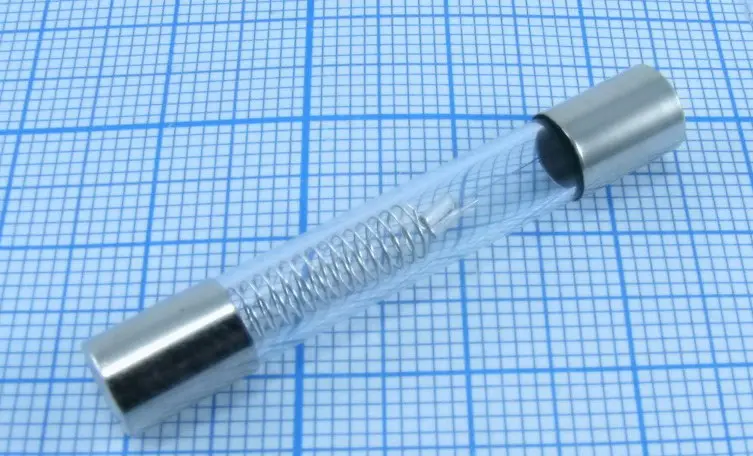

When a part burns out, a Samsung microwave oven (Samsung), Daewoo may not turn on.
How many are in the microwave? There are three types of protective devices:
- Network. Located on the input cable. They provide protection not only for equipment from surges in the network, but also for the entire home circuit from a short circuit (short circuit). The latter often happens when one of the elements of the microwave is malfunctioning. In case of any malfunction, protection disconnects the equipment from the network.
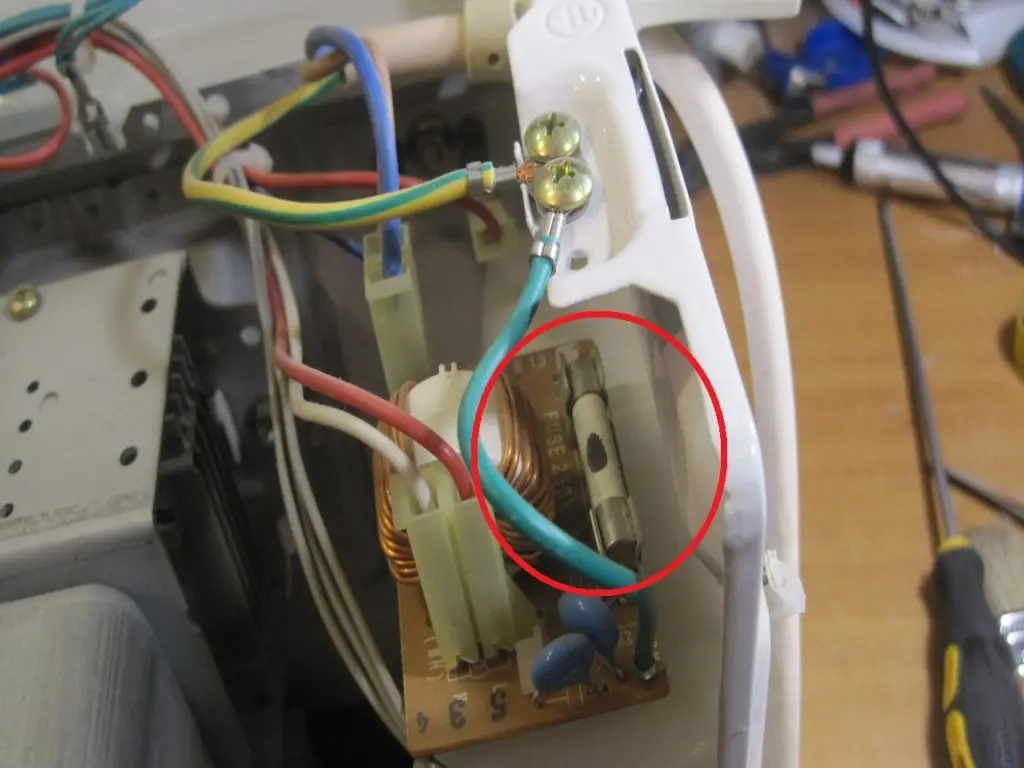
- High voltage. Why do they work? As soon as an overload occurs, the fuse breaks the circuit for the safety of the magnetron and transformer – one of the main components of the microwave oven. Sometimes at the same time knocks out a machine gun on the dashboard. What does it look like and where is it located? It is located right next to the transformer and is enclosed in a plastic case with latches.
- Another fuse is installed on the electronically controlled microwave oven. In addition, it converts electrical current into a suitable voltage for the electronics. Where is? The protection element is located above the primary winding of the transformer and is enclosed in insulation. Therefore, if it burns out, it is quite difficult to change it.
How do you determine the type of fuse in your model? To do this, look at the instructions. High voltage products are very rare. And the point here is not in the structural features, but in the fact that they are not installed at all factories. Most often you can find network.
If the high-voltage protection is burnt out, everything except heating will work in the microwave oven. You can put the dish to reheat, the circle will rotate, but the food will remain cold.
If the network element burns out, then the operation of the technology is impossible.
DIY Replacement
Disconnect the microwave oven from the mains before replacing a part. Arm yourself with a Phillips screwdriver and remove the screws securing the cover.
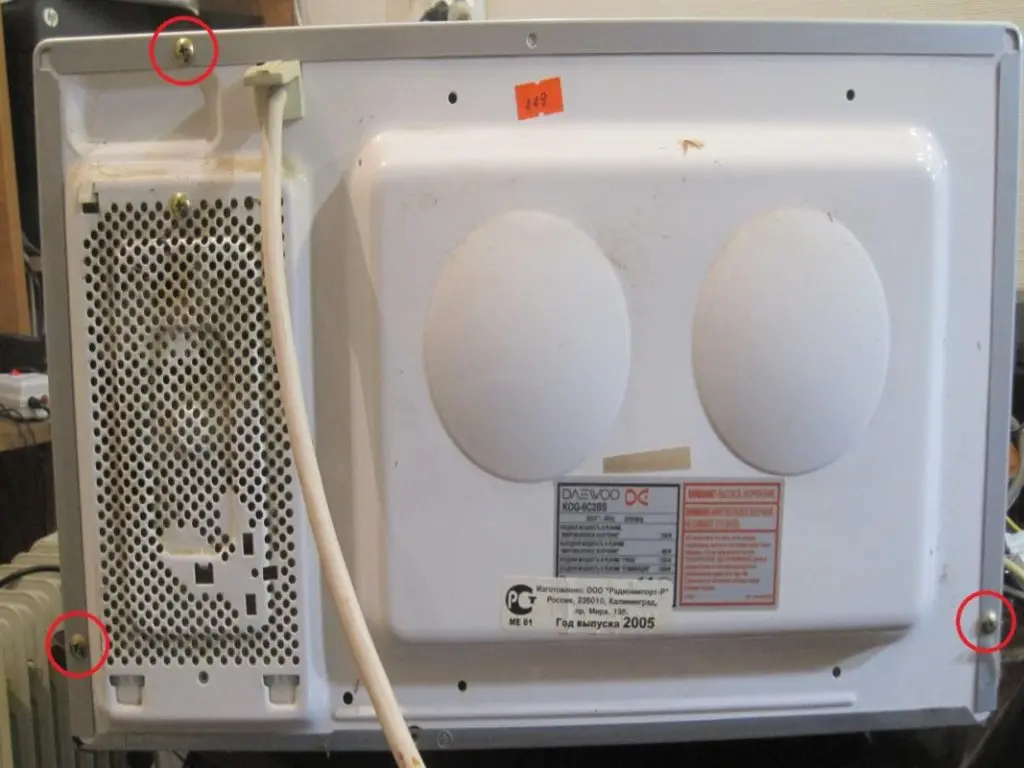

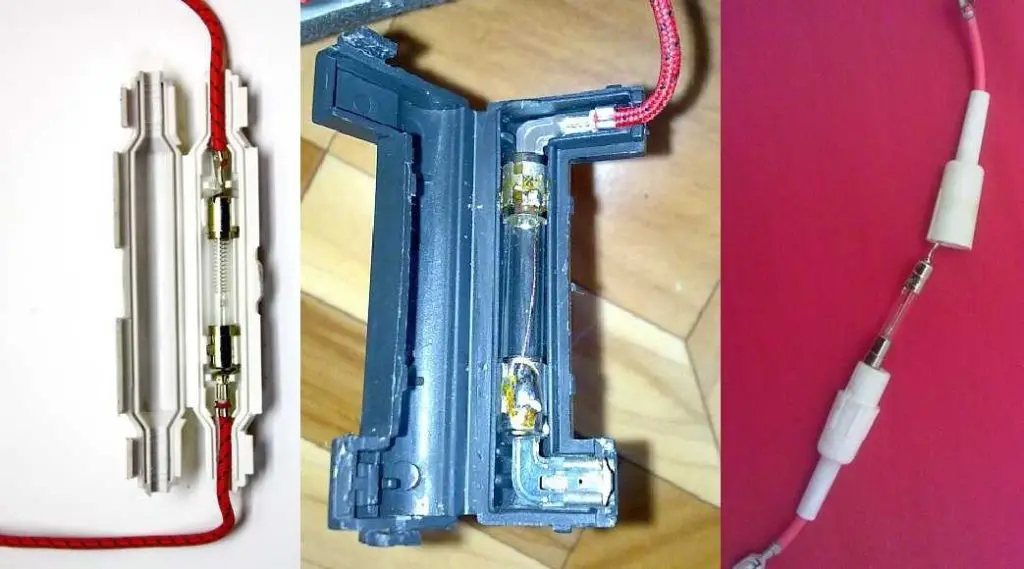
Now inspect the constituent elements. What does a blown fuse look like? On visual inspection, it will be swollen or black traces of burns will be visible.
If the bulb is glass, you can see the broken thread inside. If the circuit is short-circuited, the breakdown is more difficult to detect. For this, tests are carried out with a multimeter in resistance mode:
- Attach the test leads to the contacts on the device.
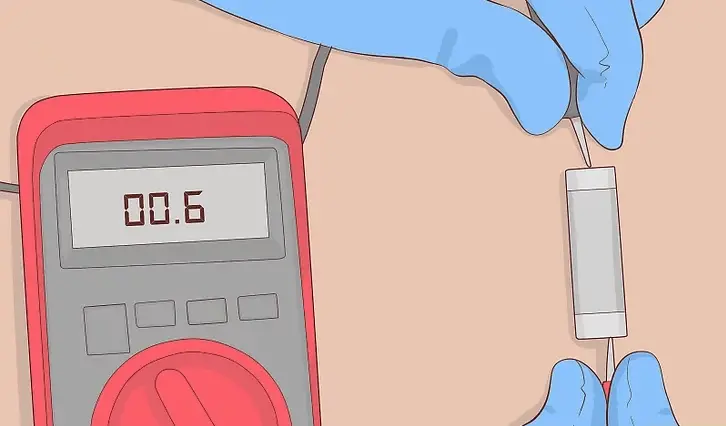

- Everything is fine if the screen displays zero.
- If it displays a value other than zero or “OL” – the part is burned out, it is necessary to change it.
For repairs, you will need identical items. They must have the same dimensions and current range. Usually these indicators are indicated on the case. You can see them through a magnifying glass.

Important! Do not install a new fuse with your bare hands. Use pliers or rubber gloves. Some parts of the microwave maintain their voltage even when disconnected from the mains.
After installation, reassemble the device in the reverse order. When switching on, make sure that all elements are working properly.
Do not do DIY repairs if you have not done so before. Ignorance of the microwave device can lead not only to complete breakdown, but also to electric shock.