Contents
 Before processing milk mushrooms before salting or preparing any other culinary dish, we suggest reading simple and very useful tips from eminent chefs. They talk about how to process milk mushrooms at home using an improvised tool. Knowledge of how to properly process milk mushrooms is very useful, because if mistakes are made, the housewives risk losing all the prepared preservation due to its deterioration. It is important to understand that before you process mushrooms after harvesting in the forest, you need to simply disassemble them, sort them into piles by size and remove the garbage. This is the most important rule. Because it is absolutely impossible to salt mushrooms of different sizes together. Some of them will not salt, while others will be very salty. So, read about how to properly process milk mushrooms – all the tips are given in an accessible form on this page.
Before processing milk mushrooms before salting or preparing any other culinary dish, we suggest reading simple and very useful tips from eminent chefs. They talk about how to process milk mushrooms at home using an improvised tool. Knowledge of how to properly process milk mushrooms is very useful, because if mistakes are made, the housewives risk losing all the prepared preservation due to its deterioration. It is important to understand that before you process mushrooms after harvesting in the forest, you need to simply disassemble them, sort them into piles by size and remove the garbage. This is the most important rule. Because it is absolutely impossible to salt mushrooms of different sizes together. Some of them will not salt, while others will be very salty. So, read about how to properly process milk mushrooms – all the tips are given in an accessible form on this page.
[ »wp-content/plugins/include-me/ya1-h2.php»]
How to process dry milk mushrooms
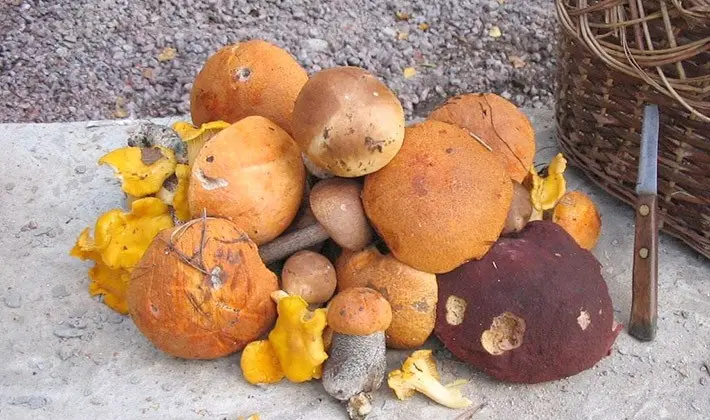

The value of mushrooms is in flavoring and aromatic substances, which determines the widespread use of mushrooms in the manufacture of various dishes, as well as sauces and soups. Dried mushrooms are usually sorted, washed in 3-4 waters and soaked in cold water. Salted and pickled milk mushrooms are also sorted out and, if necessary, cut. Salted milk mushrooms must be in brine before processing, otherwise their taste and appearance deteriorate.
Before processing dry milk mushrooms, you need to soak them for swelling.
How to process black mushrooms for pickling
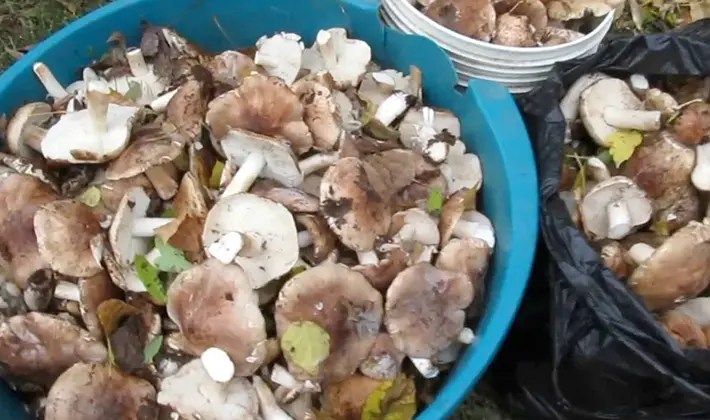

[ »wp-content/plugins/include-me/goog-left.php»]The purpose of cooking mushrooms is to reduce or eliminate the bitter taste or toxicity. But it lowers the nutritional value of mushrooms and weakens their taste and aroma. Therefore, mushrooms should be used whenever possible without prior heat treatment. Before processing milk mushrooms for salting, they are boiled for 15–30 minutes in a large amount of water. The decoction is poured out. There are two ways: bring water to a boil (1/1 tablespoon of salt is added to 2 liter of water), mushrooms are dipped in boiling water, kept for 5-15 minutes and transferred to cold water. Or the mushrooms are dipped in cold salted water, quickly brought to a boil. After boiling, the dishes are removed from the heat and the mushrooms are allowed to cool in the same water or poured with clean water. After the water is drained, the mushrooms are transferred to a cloth bag or on a sieve so that the water is glass. Before you process black milk mushrooms, remember that you should not dry them by strong squeezing, many valuable substances are removed.
 This is necessary to maintain integrity and elasticity during the cold method of salting and fermentation. Washed mushrooms are thrown onto a sieve and doused with boiling water, dipped in boiling water for several minutes or held over hot steam. After that, the mushrooms become more elastic and do not break.
This is necessary to maintain integrity and elasticity during the cold method of salting and fermentation. Washed mushrooms are thrown onto a sieve and doused with boiling water, dipped in boiling water for several minutes or held over hot steam. After that, the mushrooms become more elastic and do not break.
How to process a white milk mushroom before drying

Before processing the white mushroom before drying, you need to remove all forest debris and sort the raw materials by size. Mushrooms are not washed before drying. Common to all drying methods is the rule in which the mushrooms are dried for 2-3 hours at a temperature of + 40-50 ° C to evaporate the main amount of moisture. Then the mushrooms are dried at a temperature of + 70-80 ° C. Mushrooms dried for several hours in the shade are dried in the sun. It is impossible to dry them in ovens, as they burn easily. Mushrooms should feel dry to the touch, bend slightly and break easily. The top of the cap is yellowish or brown in different shades: dark brown in white mushrooms and from yellow-brown to black in black ones. Dried mushrooms are stored in dry, well-ventilated areas, on racks in packaged form or suspended in bundles. It is unacceptable to store dried mushrooms together with salted and pickled, with odorous herbs and wet foods. If the mushrooms are damp or moldy, they must be sorted out and dried, removing the spoiled ones.
Collection and processing of mushrooms
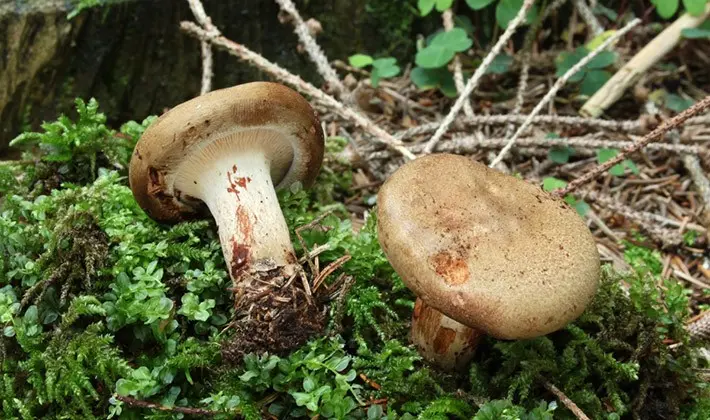

[ »wp-content/plugins/include-me/goog-left.php»]Mushrooms must be harvested and processed on the same day as fresh mushrooms cannot be stored for long periods due to the high percentage of water they contain. A few days after harvest, mushrooms wither, lose their freshness and juiciness, and become unfit for consumption. Therefore, mushrooms should only be used for consumption after a suitable heat treatment or processing into stable food products, i.e. canned, only a few hours after harvest. The processing of milk mushrooms begins with the choice of a suitable method for subsequent culinary processing. At home, mushrooms are harvested for future use by drying, pickling, salting and canning in hermetically sealed glass jars. When drying mushrooms, up to 76% of their water is removed from them. The remaining moisture for the development of microorganisms is not enough, which leads to their death. When preparing natural canned food, the microflora is killed by the high temperature at which canned food is sterilized. During pickling, the vital activity of microorganisms is suppressed by high temperature during cooking, and then by the action of acetic acid and common salt. When mushrooms are salted, fermentation occurs, during which sugars are converted into lactic acid. The latter, together with table salt, is a preservative.
Safe handling of dry mushrooms
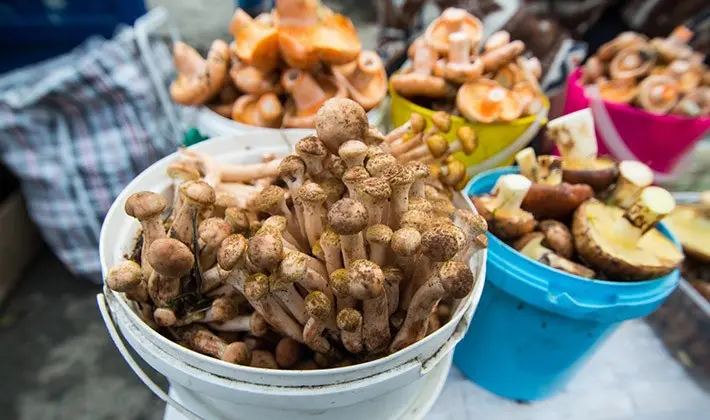

At home, when harvesting mushrooms for the future (salting, pickling, pickling, etc.), you must strictly follow the rule – do not close the mushrooms hermetically.
Safe processing of dry mushrooms is a long soak in several waters in order to remove all possible toxins and poisons.
There must be air access to dishes with mushrooms, otherwise they can cause a serious disease – botulism, which, according to medical statistics, is fatal in 60% of cases. It has been established that the disease is caused by toxins secreted by a bacillus (rod) – botulinum.
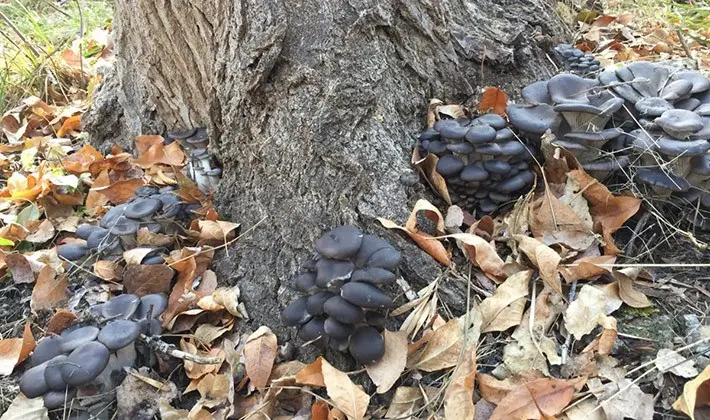 This microbe develops and multiplies in an environment where there is no air at all. The main source of infection is the soil. Therefore, the fungi that come into contact with it, and often immersed in it, are one of the most potentially dangerous carriers of spores and botulism bacilli. Moreover, the causative agent of the disease can be found in soil particles, on the surface of mushroom caps, from below, between the plates, and on the legs, especially in their lower part.
This microbe develops and multiplies in an environment where there is no air at all. The main source of infection is the soil. Therefore, the fungi that come into contact with it, and often immersed in it, are one of the most potentially dangerous carriers of spores and botulism bacilli. Moreover, the causative agent of the disease can be found in soil particles, on the surface of mushroom caps, from below, between the plates, and on the legs, especially in their lower part.
Therefore, cutting the mushrooms in the forest, and not uprooting them, the picker thus, as it were, takes the first preventive measure against the onset of the disease, as it leaves the lower, most soil-contaminated part of the leg in place (and at the same time protects the mycelium from destruction – mycelium). [ »]
Processing black mushroom before salting
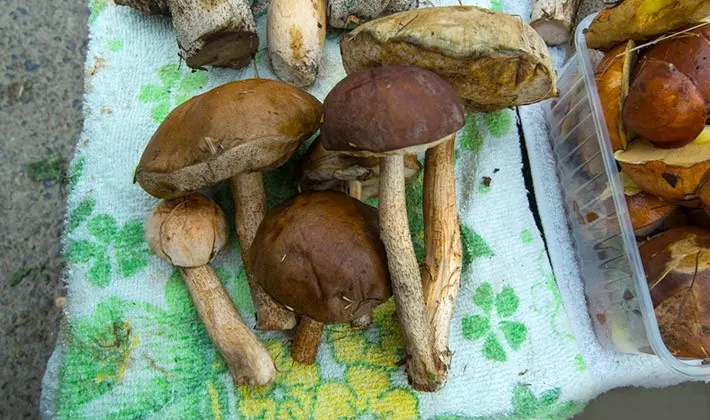

When processing black mushrooms before salting, you should very carefully remove the soil, adhering leaves, blades of grass, various debris, etc. Mushrooms are washed (except for those intended for drying), changing the water several times in order to clean them from the ground as best as possible. Despite this, the ingress of spores and botulinum bacilli into mushrooms harvested for future use is not excluded, which especially need to be remembered by those who like to store this product in hermetically sealed containers, in jars corked (rolled up) with metal lids or glass with “locks”.
No home treatment of milk mushrooms before salting and sterilization prevents the release of poison by botulinus, since its spores die at a temperature not lower than 120–125 ° C, which can only be reached in autoclaves at industrial food enterprises, although the toxin itself is destroyed by boiling.
Meanwhile, at home, along with salting, pickling, pickling, mushrooms are often preserved fried, stewed in their own juice, and also boiled in lightly salted or acidified (citric acid, vinegar) water, after which the jars are rolled up.
 In such cases, it is necessary to sterilize the jars at least before seaming in boiling salted water (400 g of salt per 1 liter of water), since its boiling point is above 100 ° C. Such canned food immediately before use must be boiled for at least 30 minutes, counting from the moment of boiling. To do this, the mushrooms, along with the broth, are laid out from the cans in a saucepan, pour in a little cold water (to boil) and put on fire.
In such cases, it is necessary to sterilize the jars at least before seaming in boiling salted water (400 g of salt per 1 liter of water), since its boiling point is above 100 ° C. Such canned food immediately before use must be boiled for at least 30 minutes, counting from the moment of boiling. To do this, the mushrooms, along with the broth, are laid out from the cans in a saucepan, pour in a little cold water (to boil) and put on fire.
 After 25 minutes of boiling (not earlier), mushrooms and broth can be tasted. During this time, botulinum toxin, if present, is already destroyed. With a lack of salt, the mushrooms are added with salt, with an excess, water is added. If necessary, the broth is acidified and spices are added to it at will – bay leaf, dill, allspice. After boiling for another 5 minutes, the mushrooms are cooled and served. You can store them in the refrigerator for no more than 2 days. This method of processing canned mushrooms is approved by microbiologists and sanitary doctors.
After 25 minutes of boiling (not earlier), mushrooms and broth can be tasted. During this time, botulinum toxin, if present, is already destroyed. With a lack of salt, the mushrooms are added with salt, with an excess, water is added. If necessary, the broth is acidified and spices are added to it at will – bay leaf, dill, allspice. After boiling for another 5 minutes, the mushrooms are cooled and served. You can store them in the refrigerator for no more than 2 days. This method of processing canned mushrooms is approved by microbiologists and sanitary doctors.
 Nevertheless, home hermetic capping of mushrooms is undesirable. It may be acceptable for pickled mushrooms, and in the only case: when the acidity of the marinade is not lower than 1,6%. In such an environment, there is no development of spores and reproduction of botulism sticks, and, consequently, the formation of dangerous botulinum toxin.
Nevertheless, home hermetic capping of mushrooms is undesirable. It may be acceptable for pickled mushrooms, and in the only case: when the acidity of the marinade is not lower than 1,6%. In such an environment, there is no development of spores and reproduction of botulism sticks, and, consequently, the formation of dangerous botulinum toxin.
Salted mushrooms should be stored only in conditions of free air access. Do not roll up jars with pickled and salted mushrooms with metal lids – this can lead to the development of the botulinum microbe. It is enough to cover the jar with two sheets of paper – plain and waxed, tie tightly and put in a cool place.
First aid for botulism
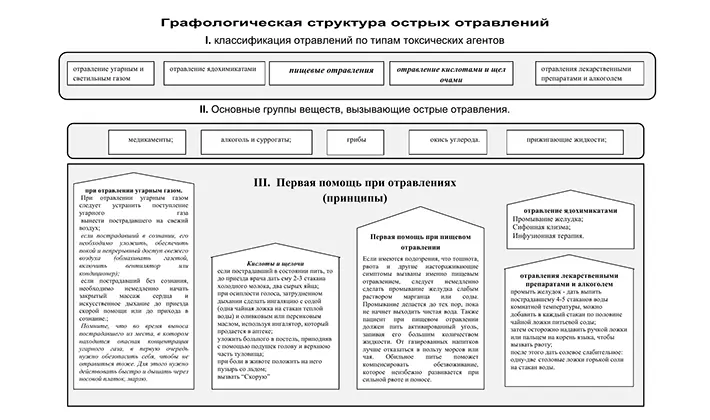
Botulism leads to general poisoning of the body, the disease develops very quickly. Within a few hours after eating food containing the toxin, weakness, dizziness, loss of visual acuity occur. A person suffers from pain in the stomach, he becomes ill. The victim must be taken to the hospital immediately. And as first aid, you should take the most vigorous washing of the stomach and intestines with a 5% solution of baking soda, apply radical laxatives and enemas. To avoid this serious illness, one more rule must be followed: do not buy salted or pickled mushrooms in the market from private traders. Only home-made mushrooms should be eaten when there is full confidence that they are all edible, carefully processed, salted or pickled in compliance with preventive measures against botulism, stored under proper conditions and with systematic care (removing mold, digesting marinades if necessary, etc.). . P.).
Watch how to process milk mushrooms in the video, which contains tips from experienced chefs on how mushrooms are prepared culinary.









