Contents
Cherry trees are very popular with gardeners. If you want to start a cherry orchard but don’t know how to propagate cherries, read this article. Cherry propagation is a relatively simple procedure that requires minimal breeding knowledge. The article will provide information on the most popular and effective methods of reproduction: how to implement them and what results you can get in the end.
Reproduction by cuttings
If you are a beginner gardener, then try the easiest way – propagation of cherries by cuttings. With the onset of June, start preparing the shoots. The most suitable will be cuttings that have begun to turn red and harden at the base. Having selected such branches on the mother tree, they must be cut. The length of cut shoots should be 30 cm. Pruning is recommended in the morning or evening, preferably in cool weather. Cut branches must be immediately put into the water.
Growth regulators can be used to achieve rapid root formation. Usually used heteroauxin. 100 ml of the drug is dissolved with ethyl alcohol and diluted with cold water to obtain a solution in a volume of 1 liter. The cuttings are collected in bundles of 30 pieces, tied and immersed for 18 hours in the prepared solution. At the same time, the shoot itself sinks only 1,5 cm and no more.
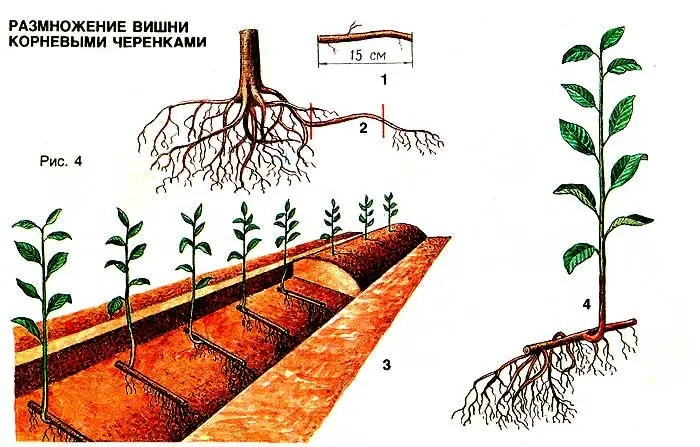
It is advisable to prepare the soil the day before. In well-dug soil, it is necessary to make beds and fill them with a 10-centimeter layer, consisting in equal proportions of peat and sand. A layer of river, preferably coarse-grained sand, is poured over it. All layers should be leveled with a rake and compacted a little. Before planting, be sure to thoroughly moisten the soil and feed with mineral fertilizers. Usually superphosphate is used. To prepare it, you need 10 liters of water, in which a teaspoon of fertilizer is diluted. Cooked cuttings are planted vertically in the beds. Planting depth no more than 3 cm, keep a distance of 7 cm between rows.
Depending on whether you used growth stimulants or not, it will depend on what time of day to plant. If growth stimulants were used, then planting is best done in the morning, and if not, then in the evening.
The planted cuttings are covered with a film and provide appropriate care, namely, in the first month they are protected from sunlight and carefully watered with a watering can or sprayer. After about 2 weeks, the cuttings will have adventitious roots, and after a month – hard-to-root.
In this way, varieties reproduce well: Polevka, Turgenevka, Vladimirskaya, Molodezhnaya and Shubinka.
Video “Propagation of cherries by green cuttings”
This video will show you how to propagate cherries from cuttings.
By vaccination
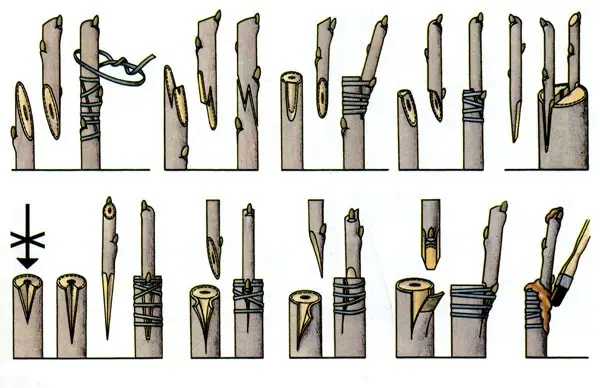
Reproduction of cherries by grafting according to its technology is very simple and very effective. For it, one- or two-year-old wild seedlings are used, in which more improved, intensive varieties will be grafted with improved fruit quality characteristics, ripening speed and a low crown.
Annual shoots with a trunk diameter of at least 5 mm are harvested in the first half of winter. But if you live in the southern regions, this can be done immediately before the vaccination itself, in the spring.
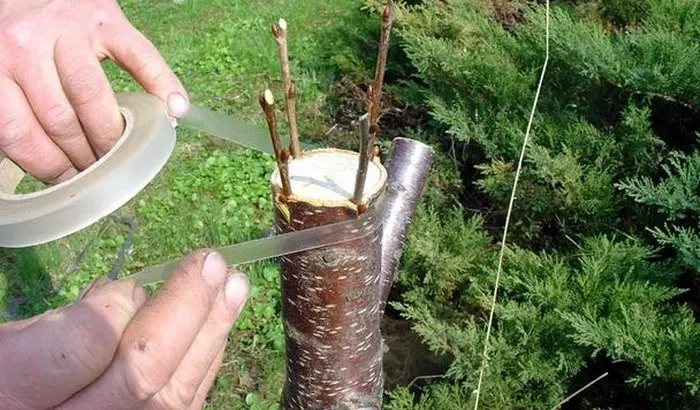

Shoots are cut from mother trees and their cuts are placed for several hours in water at room temperature. When the shoot is saturated with moisture, the required number of cuttings are cut from it, each of which should contain at least 4 buds. Also, in parallel, a special mixture (anti-transpiration) is prepared from wax or paraffin and the resulting cuttings are processed to prevent drying. In the event that you do not carry out this treatment, then it is necessary to cover the grafted part with a plastic bag and leave it until the shoots from the buds grow. The grafting procedure must be carried out until the period of active sap flow begins. The best time is mid-March.
This method is suitable for any cherry varieties, including Saniya, Vladimirskaya or Fertile Michurina.
Good results are obtained by grafting cherries on cherries. Thus, excellent varieties Sashenka, Kubanskaya, Miracle Cherry, Nadezhda, Poppy, Yuzhnaya, Dessert Morozova were obtained.
Reproduction by bones
Cherries, like all seeds, can be propagated by seeds. This procedure is carried out in spring or autumn. You can also plant a stone in the summer immediately after separating the stone from the pulp.
During the autumn planting, the bones, washed well and dipped in a weak solution of potassium permanganate (0,25 g per liter of water), are placed in a humid environment (sawdust, moss) without drying. In October, it is preferably sown at a permanent place of growth in loose, moist soil to a depth of 3-4 cm. The distance between the holes is 25-30 cm. Several seeds (4-5 pieces) can be placed in one hole. After overwintering and undergoing stratification, in the spring the seeds germinate and give young shoots, after which they are thinned out, leaving only the strongest and healthiest.
During the spring planting of seeds, the seeds must undergo stratification – the stage of post-harvest ripening. During this period, lasting 3-4 months, the seeds are stored in a moist substrate (wood chips or sand can be used) at a temperature of 15-20 degrees. Before the start of stratification, the seeds are soaked for 4-5 days, changing the water daily. During storage, it is necessary to ensure that the substrate does not dry out, and also mix it for fresh air access. Then the seeds are placed in a cellar or refrigerator, where the temperature is 2-6 degrees and stored there until germination. The sprouts are placed in snow or glacier until spring, where they go through the last stage of maturation. In early spring, seedlings are transplanted to a permanent place in the garden.
It should be noted that varietal cherries are propagated only vegetatively (by cuttings or seedlings), since when seeding seeds, such varieties do not transmit traits well to offspring and the fruits can be small.
Varieties for reproduction by bone (seeds): all varieties of felt cherries, Magalebskaya, Vladimirskaya and Lyubskaya, Shubinka, Rastunya, Kostychevka, Raspletka, Late pink, Kostychevka, Polevka, Polzhir, Menzelinskaya.
Reproduction by shoots
Cherries have been propagated by root shoots since ancient times – this is the easiest and most affordable way to get new trees. This type of reproduction is especially relevant for the northern regions, where, as a result of severe frosts, cherry trees can freeze slightly.
When propagating by shoots, one must be careful – not all young growth fully inherits the signs of the mother tree, which leads to a deterioration in the quality of the fruit and a decrease in yield. Strong healthy offspring should also be selected, weak ones usually do not take root in a new place after transplantation. Do not take perennial or closely growing plants. In the first case, a weak root system will not allow the tree to grow strong and healthy, in the second case, there is a risk of damaging the horses of the mother tree during transplantation, which can lead to its death.
The highest quality material for this type of propagation is two-year-old offspring with well-developed branches and a root system, growing at some distance from the mother tree.
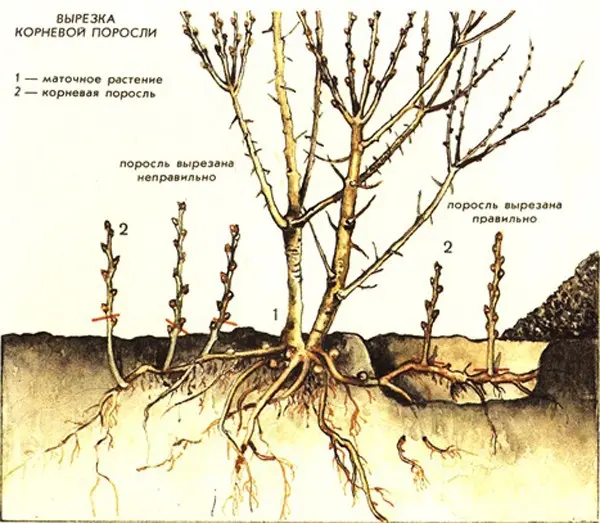
The technology of propagation by shoots is quite millet. In the spring, we select samples that are suitable in all respects and, at a distance of 20 cm from the trunk, chop off the root that connects the offspring with the mother tree with a shovel. It is first necessary to fertilize the mother trees, it is good to loosen the ground under them and around them in order to avoid the growth of weeds. After separation, we leave the young for the summer, during which time it will grow a decent root system and in the fall it can be dug up and transplanted to a permanent place in the garden.
The main disadvantage of this type is that many good varieties have a low survival rate after transplanting.
Varieties that give good results when using this method: Vladimirskaya and Lyubskaya, Shubinka, Apukhtinskaya, Rastunya, Shubinka, Korostynskaya, Fertile Michurina.
Before you start choosing cherry breeding, consider the timing of fruiting. So, trees grown from seeds begin to bear fruit in the fourth year of life, growing from cuttings – in the third, and on seedlings obtained by grafting, berries are obtained already in the second year.









