Contents
Peppers and tomatoes have long been the two most beloved and popular crops among gardeners, without growing which no one can imagine their garden, whether in the north or in the south. And both cultures, even with subsequent planting in open ground, certainly require the cultivation of seedlings in order for truly tasty and beautiful fruits to ripen under the conditions of our rather short summer.

And of course, every gardener dreams that he will get the best, strong and healthy seedlings of tomatoes and peppers. This article will help you take into account all the possible nuances in this difficult matter, reveal some of the secrets of growing these plants. In general, everything you would like to know about seedlings of tomatoes and peppers, you can learn from this article.
General comparative characteristics of plants
Because both the tomato and pepper belong to the same nightshade family, both plants have a lot in common in terms of growing and care requirements. Both are very thermophilic, both are very fond of good lighting from the very first minutes of life, both need good watering and intensive nutrition. But these are only general requirements, characteristic of most native tropical plants, abandoned by fate in our northern lands.
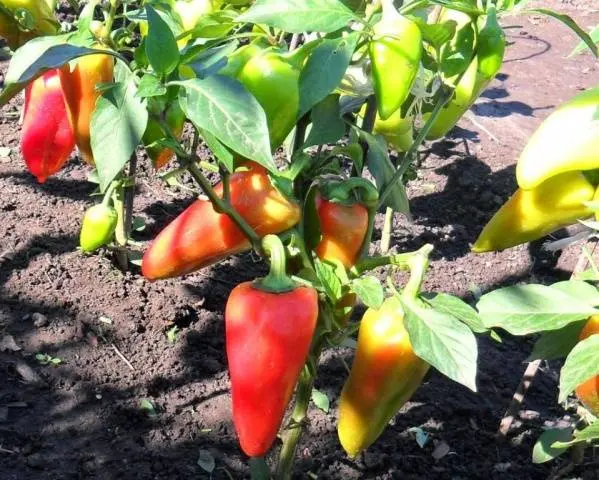

The table below briefly shows the main differences in the requirements of these cultures. They will be discussed in detail later in the article.
| Tomatoes | Peppers |
|---|---|---|
Seed germination period | 5 to 10 years, depending on variety | 2-3 years |
How many days germinate without pre-soaking and sprouting | 3 to 10 days (average 4-7 days) | 7 to 25 days (average 10 to 15 days) |
Attitude towards light | Very demanding: preferably the sun from the first hours of life | Demanding: but can withstand light shade compared to tomatoes |
Germination: is it necessary? | Not necessary | It is desirable, especially if the seeds are purchased, or they are more than 2 years old |
Seed germination temperature | +20°С +25°С | +25°С +30° |
Seeding depth | 1-1,5 see | 1,5-2 see |
Relation to transplant | Easily survive both a pick and a transplant, recover in a few hours | Poor experience, can lag behind in growth up to two weeks. No root pinching |
Landing depth attitude | It is possible and even necessary to deepen, for the development of additional roots | Deepening is contraindicated, plant at the same depth + – 5 mm |
Day/night temperature after emergence | +14+16°С /+11+13°С | +16°С+18°С /+13°С+15°С |
How many days from germination to the appearance of 1 true leaves | 8-12 days | 15-20 days |
Day/night temperature after emergence of 1 true leaves and before transplanting | +18+20°С / +14+16° | +19°С+22°С/ +17°С+19°С |
Seedling age before planting | Depends on variety Early 35-40 days Average 45-60 days Late 60-70 days | Depends on variety Early 55-65 days Late 65-80 days |
Average number of leaves per seedling planted in the ground | 6-9 leaves | 6-8 leaves |
How many days from germination to technical maturity of the first fruits | Depends on variety | Depends on variety |
Number of leaves per plant, relation to pinching | Be sure to remove the lower leaves when planting in the ground, further pinching and removal of stepchildren is required for tall varieties | Each leaf is priceless, the more there are, the better and more successful the fruiting will be, remove only yellow and diseased leaves |
Sowing seeds for seedlings
The easiest and most effective way to find out when to plant peppers and tomatoes for seedlings is the following: determine for yourself the time for planting seedlings in the ground (for greenhouses and open ground, the difference can be a month or more).

Given that both peppers and tomatoes are heat-loving plants, all frosts should be a thing of the past in your area by this time. Subtract from this period the average age of seedlings of tomatoes and peppers before planting in the ground and also the average time of seed germination. Get the same approximate date. But keep in mind that these figures are average and are mainly calculated for fairly good seedling growing conditions: a lot of light, heat, suitable containers, etc.
Under the influence of at least one unfavorable factor, a delay in the development of seedlings of tomatoes and peppers can reach from two weeks to a month. On the other hand, by preparing seeds for sowing, germination and subsequent treatment with various stimulants, it is possible to accelerate the development of seedlings of tomatoes and peppers by 2-3 weeks. That is why very often in many manuals the average terms of sowing seeds are indicated:
For pepper, as a rule, the end of February is the first decade of March. For a tomato – usually the whole month of March and sometimes the beginning of April.
After all, late-ripening indeterminate tomatoes for seedlings are sometimes sown even earlier than some early-ripening peppers.

Selection of seeds, their preparation for sowing
The seeds that you buy in stores should ideally comply with GOST, and go through the main stages of pre-sowing processing. But in reality, what you will not find in bright, colorful-looking packages. Therefore, for the seeds of both crops, even if the seeds are their own, homemade, it is necessary to carry out a series of procedures that will help select defective, obviously dissimilar and enhance the energy of life in the rest.
Selection of the best seeds
Prepare a 3% solution of table salt (30 g per 1 liter of water), dip the seeds of those varieties of tomatoes and peppers that you are going to plant into it, shake well with a spoon and wait 5-10 minutes. All those that come up are weak, not suitable for sowing – it is better to throw them away. In extreme cases, if there are few seeds and you feel sorry for them, you can make a single mixture from defective seeds of all varieties and sow them in a separate container – all of a sudden something will come up.

After washing with water, tomato and pepper seeds are scattered on paper and dried.
Etching
Immediately before sowing, the seeds are immersed in a 1% solution of potassium permanganate and kept there for 10-15 minutes. Be sure to rinse after in running water and dry. This procedure is highly desirable for both pepper seeds and tomatoes. Since such treatment is the prevention of many diseases and infections, which can then damage the development of seedlings, and even more so adult plants. If you cannot find potassium permanganate, a working solution of phytosporin will be a good replacement for it (dilute according to the instructions on the package). For many infections, it will be even more effective than potassium permanganate.

Processing with trace elements and growth stimulants
The easiest option is to soak the seeds of tomatoes and peppers in a wood ash solution, which contains about 30 different trace elements. To do this, dissolve 2 g of ash (an incomplete tablespoon) in a liter of water and insist the solution for a day, stirring occasionally. Then the seeds placed in gauze bags are lowered into it for 3 hours, washed with water and dried.
Soaking seeds in various growth stimulants is often used. You can use both home remedies: honey, aloe juice, and purchased ones: epin, zircon, energen, HB-101, humates, Baikal-EM and others.
You can simply buy a ready-made set of trace elements, dilute it according to the instructions and soak the seeds in it for 12-24 hours. It is not necessary to rinse the seeds after this procedure, you can either dry them for sowing in a dry form (possibly for tomato seeds), or start germination (preferably for pepper seeds).
Soaking and sprouting
This method is necessary only if you are somewhat late with the sowing dates and want to speed up the emergence of seedlings. In other cases, there is no need for germination for tomato seeds. For pepper seeds, especially if they are not the freshest (more than 2 years old), sprouting can help.

To do this, pickled and soaked in various solutions, pepper seeds are placed in a humid environment. You can use wet cotton swabs, between which the seeds are laid out, and placed in any plastic container with a lid or just in a plastic bag. The temperature for germination should be at least +25°C. Seeds of peppers can begin to germinate in a day. Nipped seeds are sown only in a moist substrate.
Hardening
This procedure makes sense mainly for northern regions with unstable weather conditions. However, if you have a lot of free time and a desire to experiment, then you can harden the seeds even in more southern regions, so that later you can plant tomato and pepper seedlings earlier and in open ground. It is carried out in two ways.
- After dressing, the seeds are soaked in warm water, and after swelling for 3-6 hours, they are placed in a cold place (+1°+2°C) for 24-36 hours. After drying, the seeds are sown.
- A more complicated way is when swollen tomato and pepper seeds are exposed to variable temperatures during the week: 12 hours are kept at a temperature of +20°+24°C, and the next 12 hours at +2°+6°C.
When choosing the latter method, you need to remember that it is impossible to delay the hardening due to the possible overgrowth of the sprouts.
Preparation of the substrate and containers for sowing seeds
Deciding in which soil mixture and in what containers to grow pepper and tomato seedlings is equally important for both the seedlings themselves and for the gardener, who may have limited space on the windowsills.
If you are a novice gardener and you do not have a lot of seedlings, then it is safe to advise you to use peat tablets for the first time.
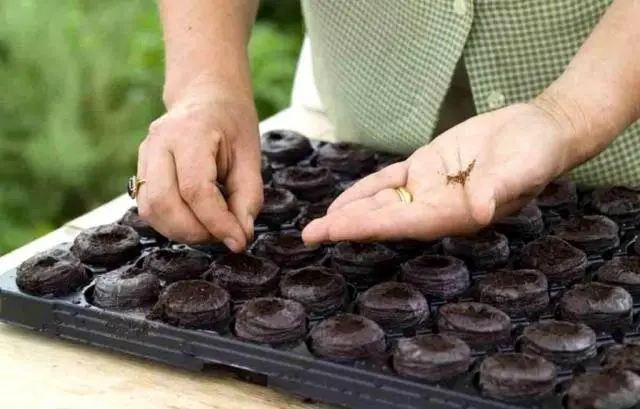

When using them, at the first stage, the problem with both containers and soil is solved at the same time. It is especially important to use peat tablets for planting pepper seedlings, since this culture does not like picks.
Tomatoes, on the other hand, can be sown to begin with in any flat containers, so that after the appearance of the first two or three true leaves, pick them into separate pots. As pots, you can also use any cardboard and plastic containers with a volume of 500 ml or more. Before filling, it must be rinsed well and disinfected for 15-30 minutes in a dark pink solution of potassium permanganate. You can use peat tablets for sowing tomatoes, but it makes sense only for some especially valuable varieties, the seeds of which you have literally a few pieces.
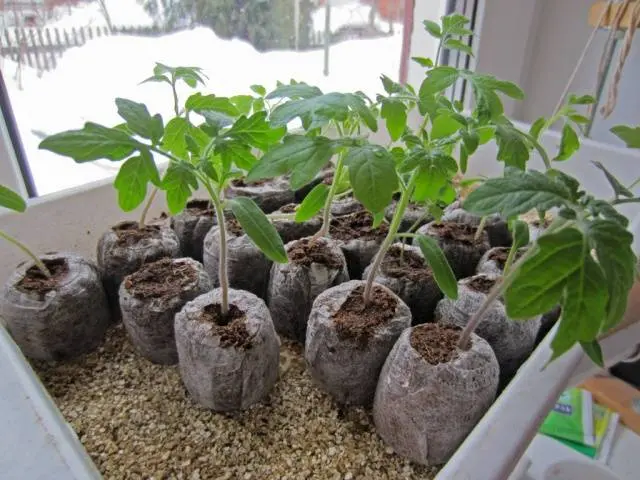

The tablets must be placed in a tray container, gradually moistened to 5-6 times their height, sow the prepared seeds in the recesses, cover with a substrate and, after closing the container with a lid, place in a warm place.
If you have a large number of seedlings and enough experience, you can sow peppers in special plastic cassettes for seedlings and in separate cups, including even self-made from paper or polyethylene.
In this case, you will need soil. Of course, you can buy any specialized soil for seedlings or for peppers and tomatoes in the store. But even it must first be calcined in the oven before use, and then spilled with Baikal EM to restore soil microflora.

If you want to make the soil yourself, then the following composition is quite suitable for both tomatoes and peppers: turf land (land from the garden) – 1 part, leafy land (taken in a park or forest from under any trees, except oak and willow) – 1 part, humus – 1 part, sand (perlite, vermiculite) – 1 part. You can add some wood ash and crushed eggshells. Before use, this soil mixture must also be processed in the oven.
From sowing seeds to seedling emergence
So, you have decided on the sowing dates, even guessed the right day according to the lunar calendar, prepared the seeds for sowing, as well as the soil and the corresponding containers. You can start sowing. There is nothing complicated in this procedure. Sowing in peat tablets was discussed above. When using soil, it is also desirable to shed it a day before sowing to ensure uniform moisture. Fill all the containers with soil and, having made indentations, sow the seeds to the depth indicated in the table above, respectively for tomatoes and peppers. Compact the earth a little.

After that, the containers must be covered with polyethylene on top to create greenhouse conditions and placed in a warm place. Warmth for sown seeds is now the most important thing. They don’t need light.
After a few days, it is advisable to place the tomatoes closer to the light so as not to miss the long-awaited sprouts. When the first loops of seedlings appear, containers with tomato seedlings must be placed in the brightest place and it is advisable to illuminate around the clock even in the first few days.
Pepper seedlings are also treated 5-6 days after sowing. But compared to tomatoes, peppers do not need the sun as much in the first stage, and therefore their sprouts can even stand second row on the windowsill. True, they will also react favorably to the illumination.
There is also a small difference between day and night temperatures.

Lowering the temperature during the first two weeks of seedling development until the opening of the first true leaf allows the seedlings of tomatoes and peppers to get stronger, harden and not stretch. See table above for specific values.
Sometimes it happens that the seed coat remains on the sprouts that come out of the ground. This is usually due to insufficient seed penetration. It must be regularly and gently moistened with a spray bottle until it softens and rebounds on its own. Helping her is undesirable, you can destroy the sprout.
From germination to planting in the ground
It is undesirable to additionally water the soil before the opening of the first leaf; at the cool temperature in which the seedlings should be during this period, the substrate should not dry out. But if it seems to you that it is completely dry, you can lightly sprinkle it on the sides of the planting container.
In general, watering in the first weeks of seedling life is a very delicate matter. This is especially true for tomatoes, which are often poured. The frequency of watering should depend entirely on the temperature at which the seedlings are kept. In the future, on hot and sunny days, the frequency of watering can reach up to 2 times a day, on cloudy and cold days, you can limit yourself to watering 2-3 times a week. Peppers also need to be watered only when the top layer of the earth dries out.
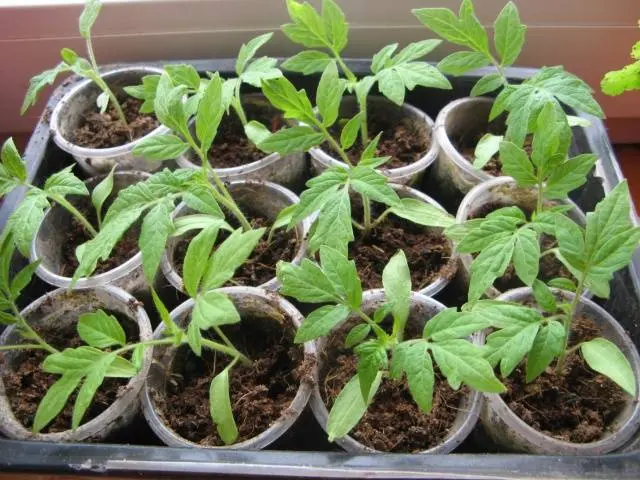

When tomato seedlings release 2-3 true leaves, they must be transplanted into separate containers. Land for transplantation can be taken with a high content of humus. Seedlings of tomatoes are planted with deepening to the cotyledon leaves and even deeper if it is still stretched out. It is only important to remove the lowest leaves so that they do not touch the ground.
Pepper does not like picks and transplants, but even if you grow pepper for seedlings in peat tablets, then when 2-3 true leaves appear (and even better, when roots appear from the tablet), it must be transferred to large containers.
When installing a tablet with a plant in a new pot, practically do not cover the seedlings with earth.
You can take liter pots right away, or you can take half-liter ones, so that after three weeks you can transfer them to even larger pots. Only in this case, the seedlings of tomatoes and peppers will develop fully and will subsequently be able to give a good harvest.
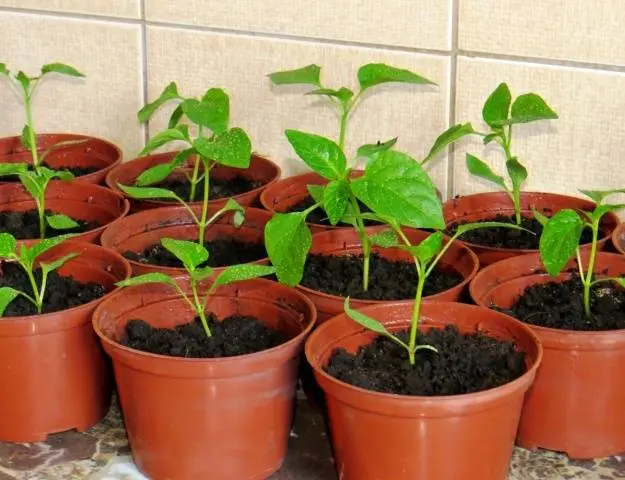

After picking, it is advisable to shade the seedlings of tomatoes and peppers from direct sun for several days. Two weeks after transplanting, seedlings can be fed with any complex fertilizer, preferably with a complete set of trace elements. Before landing in the ground, you can feed 2-3 more times.
A few weeks before the date when we want to plant seedlings of tomatoes and peppers in open ground, be sure to start hardening the seedlings. On warm sunny days, take containers with seedlings outside, in extreme cases to the balcony. You can start with 20-30 minutes a day at a temperature of + 15 ° C, further increasing the time spent by tomato and pepper seedlings in the fresh air up to the whole day, bringing it into the house only at night.
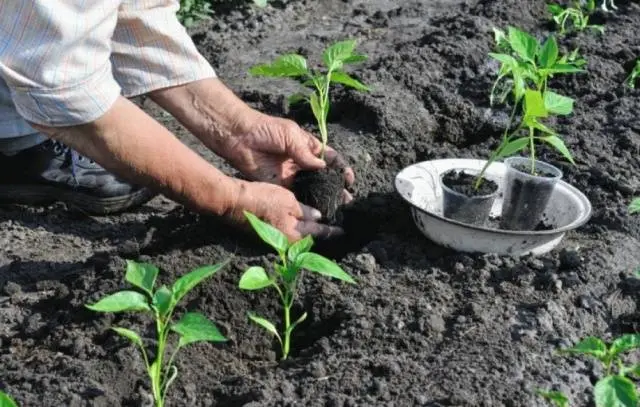

For planting seedlings in the ground, it is better to choose a cloudy warm day. As with transplanting, tomato seedlings are buried to the bottom leaf, and pepper seedlings are planted without burying at all. Planted plants are best immediately tied to a suitable support.
With planting in the ground, the seedling stage of growing tomatoes and peppers ends and another story begins.









