Contents
Grafting is one of the most common ways to propagate fruit trees and shrubs. This method has a lot of advantages, the main of which is significant savings: the gardener does not have to buy a full-fledged seedling, because even one bud can be enough for grafting. It is possible to graft fruit trees in spring or summer, while the spring option is more preferable, as it provides a greater likelihood of grafting. Not every gardener takes up propagating fruit trees with buds or cuttings, but in practice it turns out that this is not so difficult: you just need to choose the appropriate method of grafting.

The spring grafting of fruit trees will be described in detail in pictures and videos. This article will describe the features of the most popular fruit grafting methods, describe the rules of this procedure, and provide specific recommendations for each tree.
The essence of the method and its advantages
For beginner gardeners, grafting fruit trees may seem like an impossible task, but if done correctly, the result is sure to please. In horticulture, grafting is a method of propagating trees and shrubs by engrafting part of one plant to another.

As a rootstock, a gardener can use almost any tree on his site – a new variety or other crop will take root to it. The graft is the part of the plant that needs to be propagated. An eye or cutting can be used as a scion, sometimes even a whole plant is taken.
There are about two hundred officially registered methods of grafting fruit trees and shrubs. Not only the ways of connecting the parts of two plants can differ, but also the timing of the vaccination, the quality of the stock and scion.

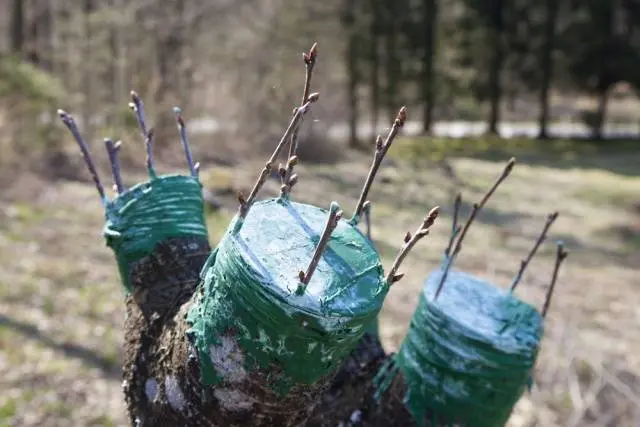
It is very popular to propagate fruit trees by grafting not only in large gardens, but also in small summer cottages. This method has a number of advantages:
- to propagate a valuable variety, you do not need to buy a full-fledged seedling with roots – just take one bud or a small process;
- you can not uproot the stumps of old or disliked trees – new varieties are grafted onto their roots or shoots;
- grafted crops begin to bear fruit several years earlier than those propagated by seedlings;
- on a small area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe plot, the gardener can get many different crops; for this, different types of fruit trees are grafted onto one stock;
- grafting improves frost resistance – a southern heat-loving plant is grafted onto the roots of a local variety;
- in large gardens, grafting significantly increases the yield of trees by replacing old or damaged shoots with young and fresh ones.

Such advantages of grafting should be an incentive for a gardener who has never used this method. Besides in practice, it turns out that there is nothing complicated in grafting – you just need to choose the appropriate method.
When can you vaccinate
In principle, you can plant fruit trees throughout the year. However spring vaccination is considered more effective, because it is more natural and physiological. With the onset of heat, sap flow begins in the trees, so the cambium of the scion and rootstock grow together well.

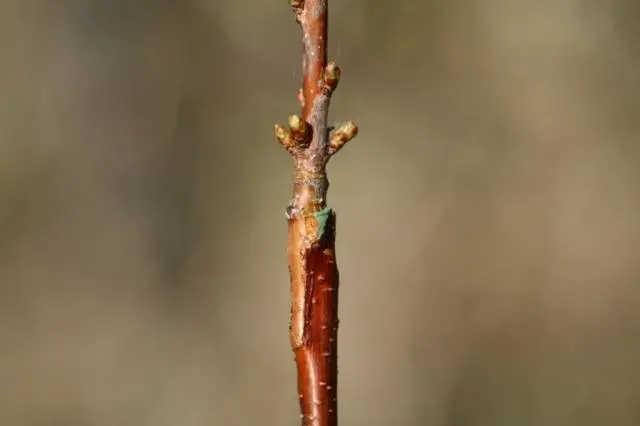
In order for the fusion of crops to be successful, the scion, on the contrary, must still “sleep”, that is, the buds on the cuttings should not swell and hatch. Therefore, cuttings for grafting are prepared in advance. For the spring procedure, they can be cut in the same season, but for summer grafting, last year’s cuttings should be used, which can be stored in the basement.
Spring harvesting of cuttings should be carried out immediately before the grafting procedure itself. All cuts on the scion and rootstock should be done quickly, avoiding weathering and drying of the cambium.
Rules for Successful Grafting

In order for fruit grafting to be successful in the spring, some recommendations must be followed:
- use a special tool (garden and copulation knives, secateurs, electrical tape, garden pitch, saw, alcohol);
- choose a healthy tree as a stock without traces of disease, damage or frostbite;
- the age of the stock of a stone fruit crop should not exceed 10 years, for pome trees this is not so important, since they live longer;
- if several different crops or varieties are grafted onto one stock, it should be borne in mind that the timing of their ripening must coincide;
- scion cuttings must also be absolutely healthy, have several large buds that have not yet woken up;
- tools, hands and cuts on the stock and scion must be clean, for this they are wiped with alcohol;
- sections of the bark and layers of the cambium in grafted crops should match as much as possible;
- the whole procedure is carried out very quickly so that light and air have minimal contact with the wood slices.

Most Popular Methods
Methods for grafting fruit trees in spring may differ depending on the type of scion, weather conditions, and time of year. Each gardener chooses the most suitable option for specific conditions.

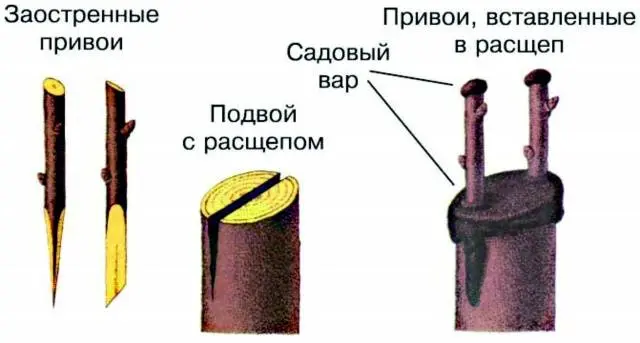
In the cleavage
In the past, most gardeners used this method, and it was called “clothespin”. It is advisable to use this option when the bark of the rootstock is too thick, the tree itself is damaged by previous unsuccessful vaccinations. Trees are best chosen mature, with a well-developed root system. And the thickness of the cuttings for the scion should be a little more than usual, the number of buds should be at least five.
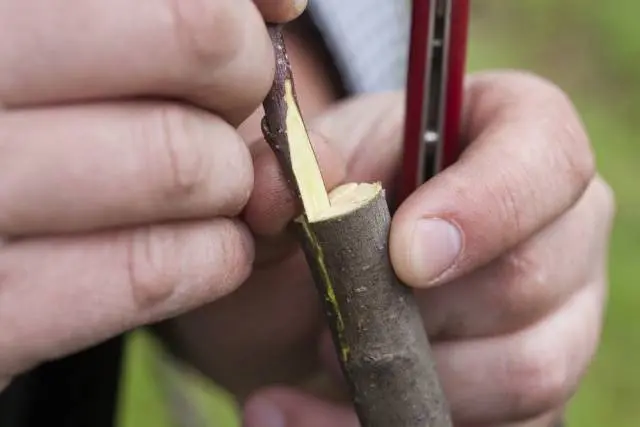

In practice, the method of grafting into a split looks like this:
- The stock is cut 10-12 cm above ground level.
- An incision is made in the trunk or shoot with a hatchet, into which a wedge must be temporarily inserted (for example, a screwdriver or a sliver).
- The lower part of the scion must be cut obliquely with a knife on both sides. The cutting height is approximately 4 cm.
- Now the scion is inserted into the crevice of the rootstock, the wedge is removed.
- The cuttings are held so tightly that often it is not even necessary to fix the grafting site with electrical tape. It is only necessary to carefully fill the entire area with garden pitch.
Behind the bark
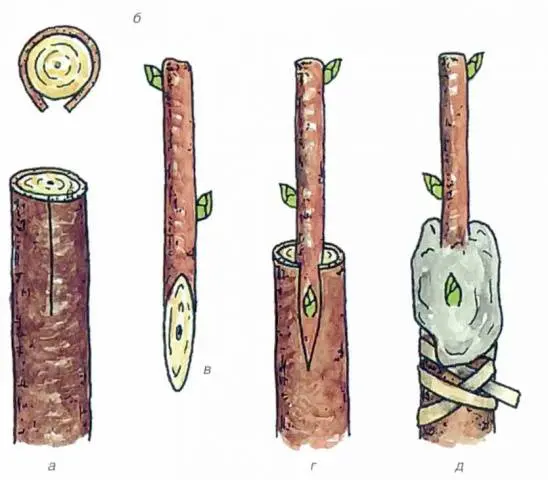
In this way, it is customary to graft adult fruit trees (from three to ten years), you can use an overgrown scion of a large diameter. A suitable time for grafting is the middle of the sap flow, when the bark is easily separated from the trunk.
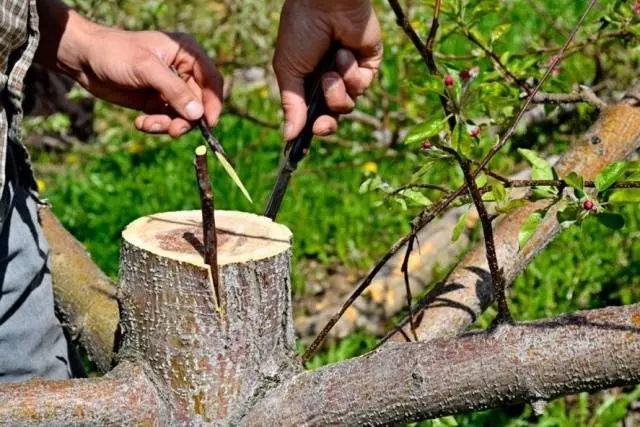

The optimal rootstock diameter is from two to twenty centimeters. The scion is chosen with a thickness of about 0,7-1,5 cm. The method is executed like this:
- The trunk of the stock is cut at a height of 7-10 cm from the ground. If the vaccination is carried out on the shoot, you need to make a cut 2-4 cm from the fork.
- The cut should be cleaned with a sharp disinfected knife. Do not touch the cut with your hands.
- A scion is cut out, 10-15 cm long.
- The lower part of the scion is smoothly cut at a slight angle. Cut length – 3-4 cm.
- On the lateral surface of the stock, an incision is made in the bark, 4 cm long. The edges of the bark are slightly bent.
- The stalk is inserted into the “pocket” formed by the rootstock bark so that its edge protrudes slightly from above (by 1-2 mm).
- The open parts of the vaccination are covered with garden pitch, and then this place is rewound with electrical tape.
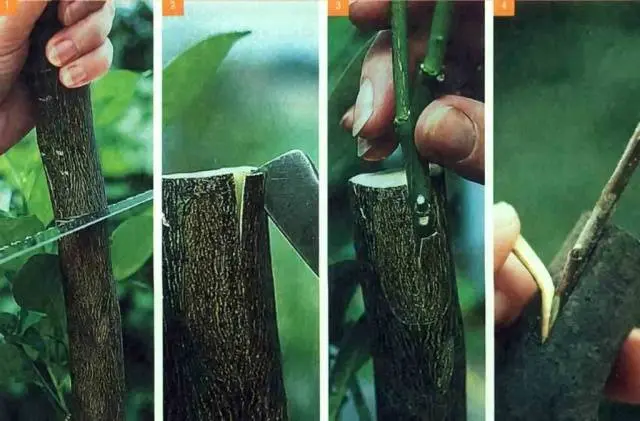
Improved copulation
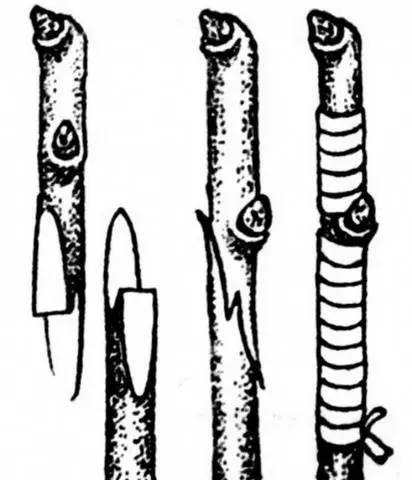
Copulation can be performed in several ways, there is copulation with a “saddle”, with a “tongue”, simple. But it is the improved copulation of fruit trees that is considered the most effective. It is also the easiest to perform.
The timing of copulation is in the spring, until the juices move in the tree and the buds swell. The diameters of the rootstock and scion for such a vaccination should be the same and equal to 0,7-1,5 cm.
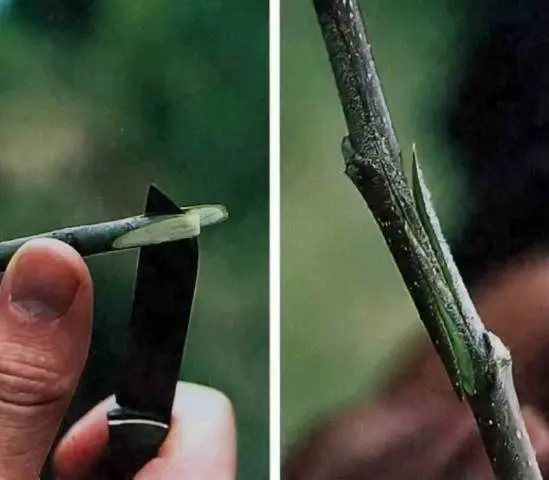

The vaccination method is implemented as follows:
- Two identical oblique cuts are made on the scion and rootstock, the knife is held at an angle of 25-30 degrees.
- In the middle of each cut, you need to make a small incision (“tongue”) – about a centimeter in length.
- The graft with the stock must be connected so that their “tongues” interlock, and the layers of the cambium (a thin green layer between the bark and wood) coincide.
- The vaccination site must be rewound with electrical tape so that the sticky layer is outside. A plastic bag is put on top of the grafted cutting.
V comma
The method of grafting fruit trees into a cut is rarely used in nurseries or industrial gardens, but amateur gardeners like it. To implement the method, a stock of any thickness is suitable. Incision grafting provides good and fast fusion. The most effective way to rejuvenate trees is when gardeners replace the crown and fruiting shoots.
Vaccination is performed as follows:
- A shallow oblique incision is made in the bark of the stock, tapering downwards.
- A graft is taken with two buds.
- The lower edge of the scion is cut off on both sides with an oblique cut. The result should be a sharp cut.
- The graft is wedged into the gap of the stock (into the cut), the graft is wrapped with electrical tape and putty with garden pitch.
You can graft fruit trees into the cut in spring, summer or winter.
Optimal timing and methods
What is good for an apple tree may not be suitable for a cherry. That’s why for each tree in the garden, there are recommended grafting dates and the most suitable methods:
- apricots it is better to graft from late April to early May, using split grafting, behind the bark, with a bridge;
- apple tree can be grafted by budding in April-early May, March-April is more suitable for grafting with cuttings;
- before bud break pear grafted behind the bark, at the beginning of sap flow – with a bridge, from mid-April – in a split or in a side cut;
- for vaccination cherries you need to wait for the peak of sap flow, this tree can be grafted at the end of summer;

- in some regions plum grafted already at the end of February, using the splitting method, butt and behind the bark;
- cherries grafted throughout the warm season, before grafting, the tree should be watered abundantly;
- peaches they begin to vaccinate from mid-March, after the procedure, the grafting site is covered with polyethylene, which is replaced with paper in May.
If the vaccine did not work the first time, do not despair – you need to experiment, using all new methods.
Conclusion
How to plant trees in the garden, the gardener himself must decide. All methods of fruit grafting are effective and can be completed successfully if the technology is followed and the right time is chosen.










