Grafting of fruit trees is a process of plant propagation while maintaining the varietal qualities of the crop. In horticulture, different methods of grafting are used, and there are many purposes for using this method. Experts who have mastered several methods can already share them with novice young amateurs, their experience will help solve many problems associated with grafting fruit trees in the garden. There are a huge number of recommendations on how best to plant trees, at what time and at what time of the year you can do this. Not all of them are distinguished by the completeness of information, we hope that our article will be the most informative and useful for readers.

Fruit tree grafting secrets
It is necessary to start studying the “basics” of the process of grafting fruit trees with an understanding of the questions: why do I and my garden need grafting, what tools and devices do I need to use, what is the best way to graft plants, what time of year will grafting be most effective. Let’s take a closer look at each stage of the event together.
Why this is necessary
Many gardeners at certain times and for a number of reasons come to the decision that they need to learn the skills of grafting fruit trees in their garden. We list some of the reasons:
- there is a need to propagate good varieties of woody plants, but propagation by other methods (not by grafting) does not bring the desired results;
- weak plants, grafted on a sufficiently strong rootstock, become the most hardy and healthy, compared with growth on their own roots;
- plants grafted onto a rootstock that has been growing for many years in a certain environment and soil adapt faster and more efficiently to living conditions, in close contact with the “foster parent”;
- as a result of grafting, a strong stock with excellent properties: frost resistance, resistance to diseases and pests, the ability to produce significant growth in one season, and many others, transfers these qualities to a scion with low viability;
- grafting can solve the problem when the variety of a particular tree does not suit you and there is a desire to replace it with a better look;
- a tree with remarkable qualities grows in your garden, but it is already quite old, having collected the necessary number of cuttings when pruning it, you can graft them onto a younger stock;
- grafting will allow you to fulfill your desire to grow several varieties of the same species on one rootstock;
- grafting can change the decorative shape of a tree, increase or decrease the hanging of branches, make the plant stem high, medium or low;
- in crop farms: agricultural firms, nurseries, farms, grafting is used to breed new varieties and hybrids, as well as to grow ready-made grafted seedlings for the purpose of selling to the population.
As you can see, there are many reasons for grafting fruit trees; each gardener will have their own individual needs in this matter.

Tools
Grafting a scion on a rootstock can be compared with a surgical operation, sterility must be observed and special tools must be used. The entire operation during inoculation is carried out manually, and the instruments become more convenient to use every year. Ordinary kitchen knives are considered unsuitable for grafting trees; special garden tools are needed for grafting work. These are very sharp knives with comfortable handles and strong blades. Not only will they be needed when grafting fruit trees, the complete set for gardeners includes:
- professional grafting device (secateurs);
- U-shaped knife (installed in the grafting mechanism);
- V-shaped knife for grafting very thin twigs;
- Ω-shaped knife (produces a locking connection of a scion with a rootstock);
- screwdriver and wrench.
The vaccination kit may include a tube of garden pitch and a disk with a thin grafting tape, if they are not included in the kit, you will have to purchase separately. Such sets are sold in retail chains or online stores.
Methods
Grafting of fruit trees has been used by gardeners for a very long time; there are more than 150 species and methods of propagating crops around the world using this method. Trees are grafted in the old-fashioned ways and with the use of cutting-edge devices. In one article it is impossible to talk in detail about all the methods of vaccination, we will describe only some of them, the most popular and not too difficult to use.
Ablactation
Such grafting of fruit trees occurs randomly in a natural way: with a strong gust of wind, the branches of neighboring trees can catch on to each other, a tight hook occurs, and later, from close contact, the branches grow together. This grafting method can be used to create live impenetrable hedges.
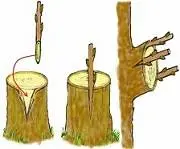
Inoculation in cleavage

The stock in this case can be from 1 to 10 cm thick. A horizontal cut is made on it. Depending on the diameter of the trunk, one longitudinal or two cross-shaped incisions (see photo) are made on the saw cut with a depth of 2 to 3 cm, 1, 2 or 4 cuttings with 2-4 buds are placed in the cut, the cuttings are cut in the form of a double-sided wedge. The scion should be placed as close as possible to the bark of the rootstock in order for the fusion to take place more efficiently. This vaccination is simple, every amateur gardener can master it.
Simple copulation
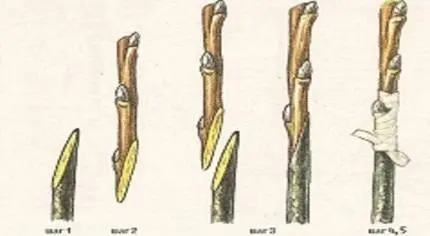
The diameter of the scion and rootstock, in this case, do not really matter; using this method, fruit trees with the smallest thickness of cuttings can be grafted, but it is necessary to have an accurate eye in order to select branches of the same diameter. A sharp oblique cut is made on the grafted cuttings, and they are connected to the rootstock exactly along the cut, then a small tire stick is applied, and the whole structure is tightly wrapped with insulating or grafting tape. The disadvantage of this grafting method is that the joint is at risk of breakage in the first few years, so an additional splint is needed, which is changed or removed as the graft heals.
English copulation (with tongue)

The tongue, in this method of grafting, plays the role of a holder that holds the cuttings in one place, preventing them from moving when wrapped with tape. In the center of the oblique cut on the cuttings, another transverse incision is made and slightly bent in the form of tongues, which are tightly connected in a groove-to-groove type, and are also wrapped with grafting tape. Cuttings grafted with plain or English copulation grow well and quickly. These methods are most popular with gardeners, as they do not require special skills and are easy to learn.
Inoculation per bark
Larger cuttings of fruit trees (up to 20 cm in diameter) can be grafted in this way. The method of such grafting is very simple to perform, but it can be performed only during the period of active movement of the juice inside the plant, preferably in spring or summer. At this time of the year, the bark of the tree is much more elastic. On the rootstock stump, a horizontal cut is made, the bark is cut across in 2-3 places up to 3-5 cm deep, the edges are slightly moved apart to the sides. The end of the scion cutting is cut off in the form of a one-sided wedge and placed under the bark, the grafting site is treated with garden pitch and tightly wrapped with tape. For the stability of the scion, small tire sticks are used.
Parasitic inoculation
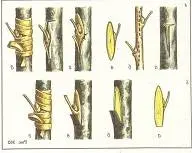
This method of grafting is applied on the branches or trunks of a growing tree. The stock is not cut down, a small segment ¼ diameter deep is cut out on the trunk or branch in the form of a corner. In the lower part of the triangle, the bark is incised, its edges are slightly moved apart, a grafted cutting up to 3 cm thick is inserted into this cut. In this way, grafting beginner gardeners can learn the skills of grafting fruit trees without much damage to the tree. Even if the stalk does not take root, it is easy to remove it later, treat the wound on the tree, and after 1-2 years, the grafting process can be carried out again in the same place.
Grafting in the lateral incision
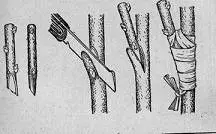
As shown in the photo on the left, on one side of the rootstock, which does not have to be cut, an oblique incision is made, deepened into the stock from above by 1-1,5 mm, and from below by 3-6 mm, a graft with an unequal wedge-shaped end up to 2,5 mm thick is inserted into it. .XNUMX cm. This vaccination is carried out in spring, autumn or even summer. Scion buds wake up next spring.
Budding with a shield (with a kidney) behind the bark

Grafting fruit trees using one bud per scion is called budding. A cut of the bark is made on the stock in the form of the letter T, a small fragment of the scion with one bud (shield) is prepared and inserted into this cut, the upper ends of which should be slightly moved apart so that the shield can be conveniently inserted. This method of grafting is used if there are not enough cuttings for propagation, therefore, 1-2 cuttings available are divided into several shield buds. The survival rate of the shields in this case is quite high. Budding is carried out during the period of active vegetation of plants, in spring or at the end of summer.
Budding with a shield (with a kidney) in the butt

As is clear from the name of the method, grafting is done by applying a shield with a kidney to the rootstock, on which a section of bark (pocket) of the same shape and size as the shield is cut out, the scion is inserted into the pocket and fixed to the rootstock. You can get practical experience in grafting fruit trees with a bud by watching the video posted at the end of this paragraph.
Bark bridge grafting
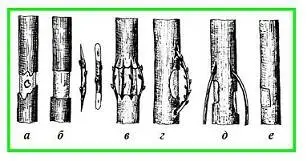
There is another way of grafting fruit trees, which is effective in restoring a plant if for some reason only part of it was damaged: hares gnawed the lower part of the trunk, as a result of extraneous mechanical action, part of the branches was damaged. Before grafting, it is necessary to protect the tree from further adverse effects – the leakage of cadmium and the drying of the damaged area of the bark and wood. If cadmium could not be saved, it is necessary to save the tree by grafting a “bridge”. The entire damaged part of the tree is cleaned, cuts are made above and below this area (see grafting for the bark), several long cuttings are prepared (see copulation). Insert them from above and below. The cuttings should be of sufficient length to have the appearance of an arc over the injury site. The number of cuttings depends on the thickness of the trunk, the thicker it is, the more cuttings should be (from 2 to 7 pieces).
Deadlines
Some types of fruit tree grafting can be done in spring, some in spring, summer and autumn, others even in winter. Most of them take root faster and more efficiently during the movement of juices, but vaccinations made in the winter also have a fairly high percentage of effectiveness, although slightly lower than vaccinations carried out in the warm period. The gardener himself must choose which season suits him.
A good adviser in determining the timing of vaccinations can be the Lunar calendar of the gardener and gardener, which indicates the most unfavorable time for vaccinations. Forbidden days are the Full Moon and New Moon, when you can not disturb any plants, they change the activity of the movement of juices – from the roots to the upper crowns or, conversely – from the top to the root system.
Conclusion
It is impossible to cover such a capacious material within the framework of one article, but we hope that young gardeners will find enough information here to satisfy their interest in grafting fruit trees. See also the video where experienced gardeners talk about their experience with vaccinations, show in practice how to do it. Learn, learn from their experience, we wish you good luck.









