Contents
Since purchased fruit-bearing lemon trees acclimatize for a long time, and waiting for ovaries from a plant grown from seeds can also be delayed, citrus lovers are grafted with lemon. If the culture obtained from the stone blooms only after 9 years, then properly carried out vegetative propagation will make it possible to taste the fruits after 3 years.
Why do you need a lemon graft
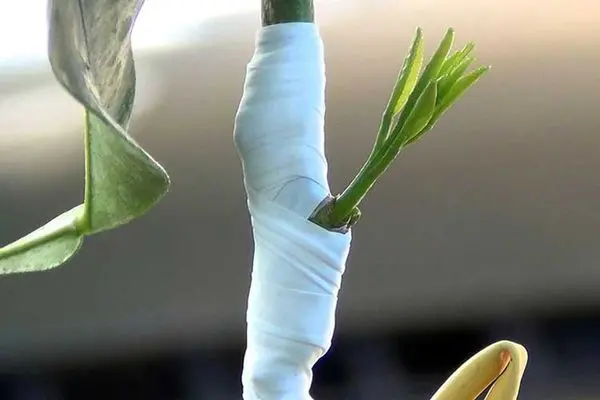

Grafting is the process of moving buds or shoots from one culture to another in order to grow together. Spring is considered the best time to complete the procedure.
Grafting a homemade lemon tree is necessary so that it begins to bear fruit faster. Even on the branches, varietal fruits will ripen, which will be of high quality, and not hybrid ones without transferring their properties to “descendants”, as in the case of growing from seeds. It is possible to plant a room lemon on a cultivated orange or other citrus plant.
Video “How to plant a lemon at home”
From this video you will learn how to plant a lemon at home with your own hands.
The right choice of rootstock
There are also such varieties of lemons as Dioscuria and Meyer, which take root well, flowering occurs in the year of grafting, and the fruits can be tasted the very next year.
The rootstock for any lemon variety can be strong seedlings of oranges, grapefruits or lemons grown on their own. They have isolated, developed and strong roots, are hardy and quickly get used to new conditions. Undersized and dwarf plants are considered the best option for stock.
When choosing, you should pay attention not only to growth, but also to taste, as well as the tendency of the culture to disease. A good mother plant will be a sprout obtained from a seed, having a diameter of 0,5 cm. The graft is taken from a fruit-bearing crop. The processes must be cleared of foliage and thorns, petioles and rudimentary shoots are left on the branches.
Required Tools
To graft a homemade citrus, you need to prepare a well-sharpened small scalpel or a budding knife, insulating tape or a garden bandage to fix the rootstock with a scion, as well as a garden pitch. The last one will need to lubricate the cut of the tree so that the infection does not get there and it heals normally. For self-preparation of such a solution, take 100 g of coniferous resin, 25 g of wax and 20 ml of alcohol, mix and heat. Shoots in places of future cuts are wiped with wet wipes.
Vaccination methods and their features
It is best to plan the procedure from April to August, to work on a cloudy and rainy day, when the air humidity is high, after wiping a knife or pruner with alcohol and washing your hands. Next, we will talk in more detail about each of the three methods of vegetative propagation.
Copulation
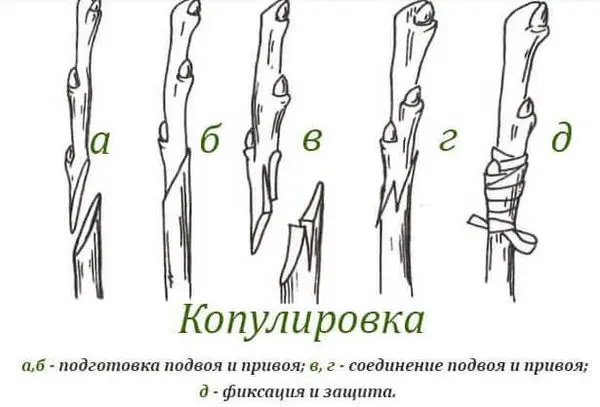
The term comes from the Latin word copulare, which means “to bind” or “to join”. Copulation is simple and improved, it is a kind of cuttings, for which a graft and stock of the same diameter are taken.
It is necessary to make oblique cuts on the stem of the mother culture, as well as on the handle, wrapping it tightly with tape or bandage, but carefully so as not to damage the plants. The dressing material can be removed after the revived stalk sprouts after a while.
Budding
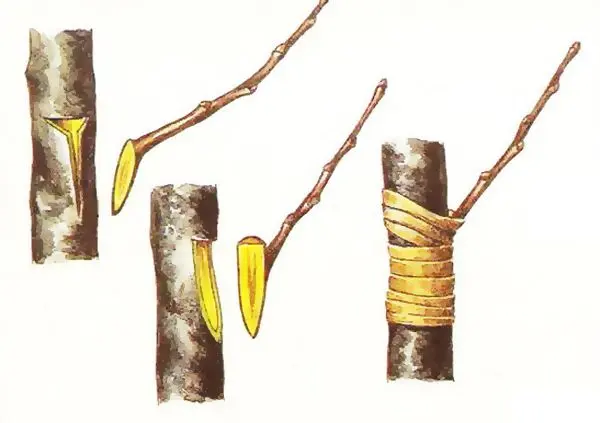

The method owes its name to the Latin word oculus, which means “eye”. The procedure is the introduction of a kidney, covered with a small layer of wood and obtained from a branch, into the bark of a rootstock.
To graft with an eye on the bark of a previously cleaned stock, an incision is made in the shape of the letter “T”, a scion is inserted into the slot, and a tape is fixed so that the kidney is open. The surface is treated with garden pitch, the culture is closed with a plastic bag or plastic bottle. It turns out a mini-greenhouse with a suitable microclimate.
For good fusion, airing and removal of excess shoots is required.
Grafting with a cutting
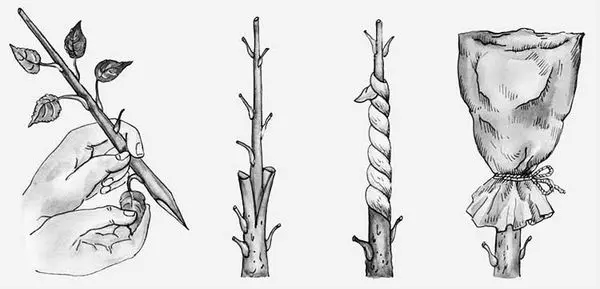
The grafting of citrus by cuttings involves such steps as cleaning the rootstock from dust and its horizontal pruning at a height of 5 cm from the soil surface. Next, a vertical split of the main stem is carried out by no more than 2 cm. A process with a kidney is inserted into the incision made obliquely on the handle, after which it is carefully pressed against the stem. The graft with the stock is securely fastened with tape, the cut is smeared with garden pitch.
In addition to this method of cuttings “for the bark”, it is also known to engraft the cuttings “into a split”. When carrying out work, the stem is removed from the bark at a height of 7 cm, the stock is divided with a scalpel or knife to a depth of no more than 4 cm. The plant is placed in a warm room where ventilation is carried out, the bandage is slightly loosened when the yellowed cuttings begin to fall off, and removed when the kidneys develop.
Vaccination by any of the methods requires certain skills, but if survival did not occur the first time, there is no need to be upset, you can try again.









