Contents
Every owner of cattle should be able to give an injection to a calf or cow, since it is not always possible to contact a veterinarian. Of course, this is not easy – there are some features of the introduction of medicinal substances to cows and calves. But you can cope with this task by observing certain rules and precautions.
Features of the introduction of cattle injections
The introduction of cattle injections has a number of features. Ignoring them is not recommended, as cows are large animals and can sometimes be dangerous to humans.
The main task facing the breeder is to limit the mobility of the cow. To do this, there are various methods of fixation, in particular, special machines that significantly minimize the movements of the animal, and for humans, facilitate the injection procedure.
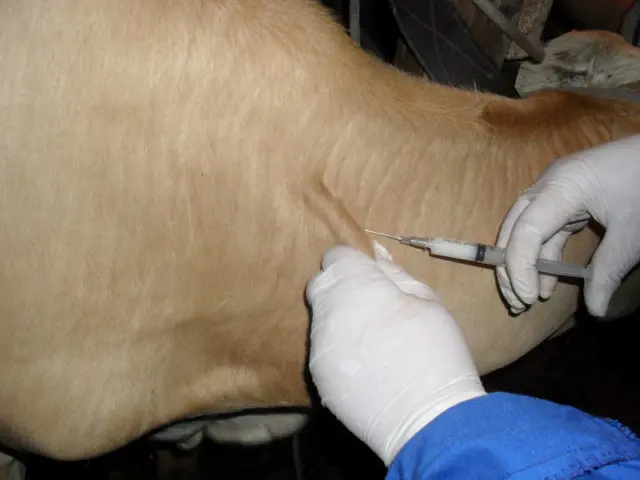
The owners of cattle know how gentle and sensitive animals they wards are. Therefore, during the procedure, the owner needs to behave as calmly and confidently as possible. You should not raise your voice at a cow, let alone beat her. It is better to act quickly and not worry the animal in vain. Before the introduction of the drug, you can stroke the cow, talk in a calm voice, try to calm her down with a word. All medicines must be administered in a warm form, so as not to shock the animal once again. Cold fluid should not enter the blood vessels.
It is desirable for the owner of cattle to have in his arsenal a supply of syringes, automatic syringes, a set of sterile cannulas of various sizes. The choice of cannulas depends on the weight of the animal, on the site of administration and on the form of injection. For example, injections to calves can be given using a 20-25 mm cannula. Often, an elongated form of an automatic syringe is used for injections. This is more comfortable and allows the person to keep a safe distance from the cow.
How to inject a calf or cow
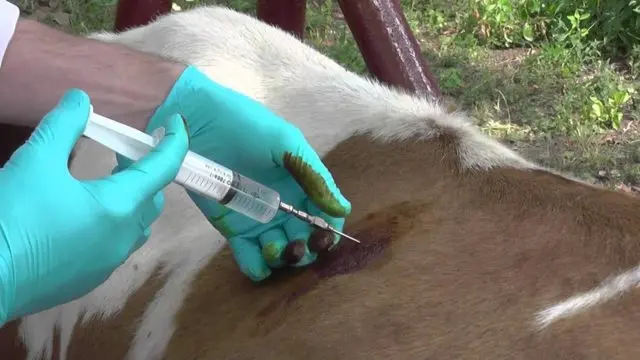
The introduction of drugs to a cow involves strict adherence to all basic precautions against infection in the area of injection.
If the animal’s skin is heavily contaminated, it is first washed with warm water, dried, then treated with alcohol or iodine. You should also wash and sanitize your hands. Injections are carried out only with a sterile instrument, observing the requirements for drugs. At the time of the manipulation, the cow must be carefully fixed.
When preparing a cow for an injection, you should read the instructions, which indicate how the drug should be administered, that is, subcutaneously, intramuscularly or intravenously. As a rule, the injection site is the neck of the animal or the pelvic region.
How to make an injection intramuscularly
Intramuscularly administered drugs in the form of solutions. With this method of administration, the drug quickly spreads through the blood throughout the body. It is important to choose the right injection site. Usually choose the area where the muscle tissue is most dense. This is the gluteal muscle, the triceps muscle of the shoulder, the dewlap area. It is better to carry out intramuscular injections in the cervical region. This will keep the quality of the meat.
The needle for intramuscular injection should be with a pointed end, 40 mm in size. Blunt needles give cows unnecessary discomfort. Often with a poor-quality needle, pieces of skin get into the wound, and this causes inflammation. Syringes for injection should be disposable. A good option for the procedure is automatic syringes with extension cords. They are often used to give injections to bulls.
First, the intended injection site is lightly hit with a fist, the syringe should be brought to the cow’s skin at an angle of 45 degrees. Then the needle is inserted deep into the muscle. After the injection of the solution, the needle is removed, and the injection site is treated. In the event that it is necessary to add another drug, the piston with the next drug should be attached to the cannula and injected into the muscle. If the cow becomes agitated during the introduction of the drug, you should stop for a while and calm the animal, and then continue. After the procedure, you can rub the injection site to relieve discomfort.
How to give an intravenous injection
Solutions for intravenous administration should be clear, without precipitation. Injections are made into the jugular vein, which is located in the neck at the border of the upper and middle thirds. To see it, raise the cow’s head and slightly push the skin fold. A large blood vessel, the jugular vein, will be visible there. If it is poorly visible, which happens with overfed, over-fed cows, then the head should be raised even higher. First, the skin is punctured, and then the vein itself is pierced. If the needle is clogged, and the blood does not flow, then you need to make an injection again, while the place is chosen just above the first puncture. The drug must be administered very slowly, strictly observing the dosage. The drug immediately enters the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body.
Intravenous injection technique:
- the jugular vein is clamped with a finger or a bandage;
- the injection site is treated with alcohol;
- in the place where the vein has expanded, a needle is inserted at an angle of 45 degrees;
- if necessary, if the blood is weak, the position of the needle is corrected;
- remove the bandage (or finger) from the vein and inject the medicine;
- after the injection, pressing the vein, the needle is removed and the injection site is treated again.
Intravenous injections are not recommended for an inexperienced person to do on their own. The procedure should be carried out by a veterinarian.
How to make a subcutaneous injection

Subcutaneous injections are less painful for animals than all the others. As a rule, alcohol, oily and aqueous solutions should be placed subcutaneously. With this method of administration, drugs are absorbed better. The agent begins to act in 5-10 minutes. Any parts of the body with the greatest number of folds will serve as an injection site. The skin folds are slightly pulled back and an injection is made. For a cattle injection, a 25-30 mm needle is used; for calves, a 10 mm needle is suitable. You can not do subcutaneous injections near the joints, tendons and cartilage tissue.
Subcutaneous injection technique:
- the neck area, where the deepest folds, wipe the cow’s skin with an alcohol solution;
- pull with hands;
- the syringe should be held at an angle of 30 degrees;
- slowly inject the drug;
- treat the injection site.
With subcutaneous injections, the needle penetrates the subcutaneous adipose tissue, where the nerve endings are in a minimal amount. Therefore, the pain effect is practically not observed and the fixation of the cow in the machine is not required.
Sometimes nasal injections are used. When carrying out, the animal also needs to be fixed, especially the head of a cow. Prepare a syringe with a plastic tip and a solution of the drug inside. The syringe is first injected into one nostril of the cow and the drug is injected sharply, and then the same is repeated from the second nostril.
Safety measures
The main precautions are related to human safety during various procedures.
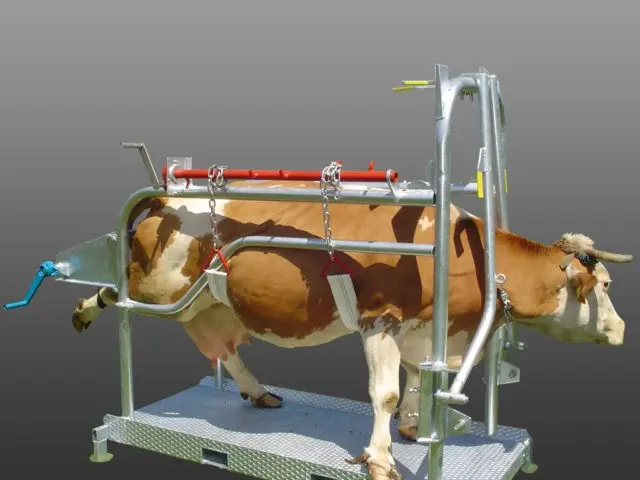

Fixation of the cow can be carried out by fixing the head or limbs of the animal. Sometimes a reflexive method is used, when the skin is squeezed over the spinous processes with a hand and pulled up. In this case, the cow freezes and cannot move actively. Also, cows are fixed with straps to the fence, wall, blocking the hind limbs with a pillar.
Today, combined machines are widely used, which can be used both in the standing position and in the prone position, during various surgical interventions. At the same time, it is strictly forbidden to enter the machine to the cow or stick your head in there. All procedures for the cow are carried out outside the machine. Violations of this requirement sometimes result in the death of the livestock breeder.
Before giving injections, livestock keepers should take care of sterile injection instruments. If syringes or cannulas are dirty, then at best there may not be a therapeutic effect. At worst, you can infect the entire livestock with yeast infections. A competent and caring owner should have a set of disposable syringes, cannulas, and needles to protect themselves from more significant expenses in the future if the animal gets sick.
Medicines should be stored in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations. Preparations lose their qualities if exposed to moisture or heat. Under such unfavorable conditions, bacteria can penetrate into the solutions. It is necessary to store medicines in the cold at a certain temperature. The expiration date should be checked regularly for medications. The use of expired products is strongly discouraged.
Conclusion
Giving a shot to a calf is as easy as giving a cow, but you need to have the necessary knowledge and experience. And yet it is undesirable to do injections on your own. Due to some tightness among cows, infectious diseases can spread quite quickly. Therefore, injections are carried out both for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes. In order to avoid many problems, the owners of cattle in the treatment of animals and routine vaccination of the livestock need to control the work of the staff. It is especially important to comply with and comply with all sanitary norms and rules.









