Contents
Potato is an unpretentious vegetable crop, which is easy to grow and does not require specific knowledge. Unfortunately, the whole idyll is broken by pests – insects that eat potatoes and spoil its tubers and greens. The fight against the wireworm among gardeners is in second place after the “battles” with the Colorado potato beetle. And, if the Colorado potato beetle shows itself well outwardly – its adults, larvae and eggs are on the surface and dot the green part of the bush, then the wireworm lurks underground and does not betray its presence in any way. You can find out that potato tubers are affected only after digging up the potatoes – and this is already too late.

How to protect your garden from a secret pest, how to rid a potato plot of a wireworm so as to cause minimal damage to plantings and soil – this will be an article.
Wireworm in potatoes
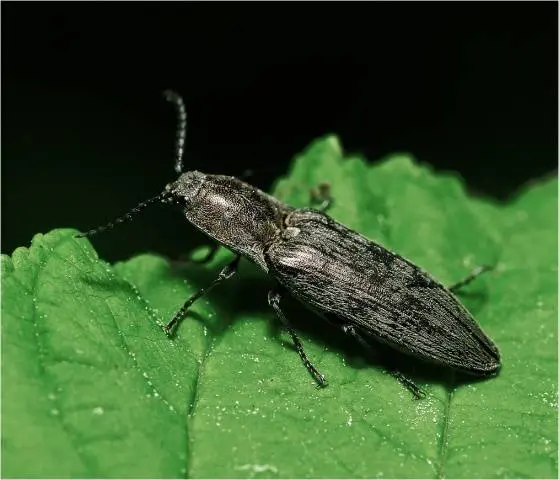
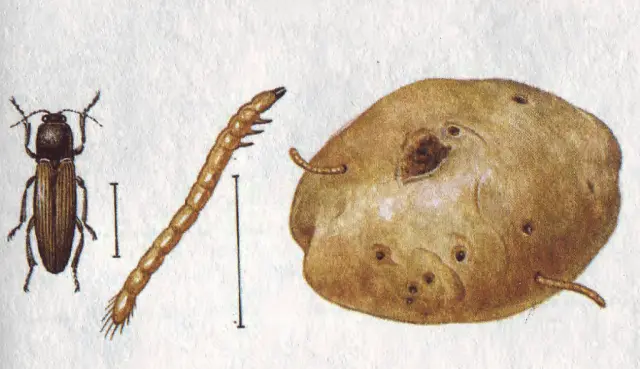
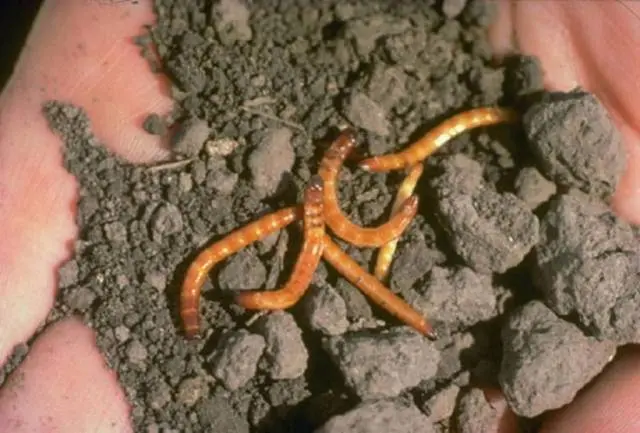
The notorious potato pest is the larva of the click beetle. The larva looks like a small worm, up to three centimeters long, it is colored yellow, orange or brown.

Imago of the pest is a black beetle with an elongated body, the length of which can reach five centimeters. The nutcracker got its name due to the characteristic sound that it makes when trying to roll over from its back to its abdomen.
The life cycle of click beetles is 3-5 years. Adults hibernate in the ground, where they are saved from frost. With the first warmth (usually in April), the beetles crawl to the surface, and their females begin to lay eggs – oval white granules and about 1,5 mm in diameter.
In one season, the female can lay up to a hundred eggs – click beetles are quite prolific. After some time, small larvae appear from the eggs – in the first year of life, such wireworms do not harm potatoes or other cultural plantings.. And already from the second year of life, the larva actively spoils potatoes, roots and tubers of other garden crops, cereals and perennial herbs.

To develop the correct tactics for getting rid of the wireworm in potatoes, you need to know the features and “habits” of this pest:
- Imago and click beetle larvae love high humidity and shade. That is why the wireworms rush to the potato field – they lack moisture, the lack of which they make up for together with the pulp of the potato.
- The beetle hibernates, as well as its larva, at a depth of 15-20 cm. If individuals or their eggs are above the ground in the autumn-winter period, they will die.
- Nutcracker eggs need shade and moisture, the sun is detrimental to them.
- For several years in a row, wireworms can eat only one type of food, the larvae do not get used to new food well – up to 90% of individuals die during this period.
- The favorite and natural food of the larvae is the roots of young shoots of weed grass – creeping wheatgrass.
- Dense thickets and earth entangled with plant roots are attractive to the wireworm.
- The pest loves acidic soils.
Knowing these features of the pest, you can easily draw up a plan to deal with it. But it should be remembered that the most effective are complex measures to combat the wireworm.

Potatoes damaged by a wireworm are dotted with multiple passages of complex shape (shown in the photo below). Such potatoes are very difficult to peel and cut, removing damaged areas, so most often they are simply thrown away.
All this is badly reflected in the presentation and quality of potatoes. Besides a passage gnawed by a wireworm in the pulp of a potato is an “open wound” through which infections, fungal spores or rot easily penetrate. Affected tubers often disappear soon after exposure to the pest.

And the worst thing is that next year the larvae will continue their “activities” and will harm the new potato crop.
How to deal with wireworm on potatoes
For many years, gardeners and farmers have been fighting this pest, so today the most effective wireworm remedies are used. Gardeners protect their fields in different ways, but All activities can be divided into four groups:
- Agrotechnical ways to save the crop.
- Chemical methods of dealing with larvae on potatoes.
- Luring larvae with baits and traps.
- Folk (or safe) means.

How to remove the wireworm, which method is better to use, must be decided depending on the complexity of the infection, as well as taking into account the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbthe plot planted with potatoes.
Agrotechnical events
Some agricultural practices developed taking into account the characteristics and lifestyle of this pest will help to destroy most of the larvae and adults on potatoes.

So, to remove the annoying wireworm from the potato field will help:
- Late autumn plowing land on a plot with potatoes. This should be done no earlier than the end of October, when the first frosts have already begun and serious frosts are already coming. The earth is dug up or plowed to a depth of at least 25 cm, trying to turn over each layer of soil. This way you can kill most of the adults and larvae that have descended deep into the soil for wintering – they will simply freeze.
- In the spring, the garden or field is dug up again, now you can not go so deep, since the goal is the nutcracker eggs, located 50-10 cm from the surface. A suitable period for such an event is May, when the sun will already bake well. Eggs with larvae will die. Along the way, you can remove the roots of wheatgrass and other weeds – adult wireworms can accumulate there. It’s better to burn the grass.
- As a rule, moist soils are highly acidic, and this is a suitable environment for wireworms. It is easy to find out about the acidity of the soil in the area with potatoes, you need to inspect the weeds growing there. Horse sorrel, plantain, mint and horsetail grow where it is damp and the earth is sour. By reducing the acidity, you can make the potato field unattractive to the wireworm. This can be done in several ways, the traditional one is the introduction of fluffy lime into the soil. It should be remembered that this method can also harm the potatoes, causing the appearance of scab on the tubers. More gentle ways: dolomite flour, chalk, wood ash, crushed egg shells.

- You need to clean the area with potatoes regularly and very carefully.. In the spring, all last year’s grass, tops and greens must be collected and burned, because under the dry grass, female clickers most often lay their eggs. Throughout the season, you need to pull out the weeds, trying to pull the entire root out of the ground. You can not leave torn or weeded weeds next to the potatoes – they should be taken away from the garden and better – burned.
- It has been noticed that the constant cultivation of potatoes in one place not only depletes the soil, but also leads to a multiple increase in wireworm individuals. The wireworm cannot switch to a new food in one year, therefore crop rotation in potato planting is especially important. It is best to do this: divide the site into 3-4 zones and every year sow one of the parts with a different crop, and the rest of the area with potatoes. Alternately, such areas change places – potatoes grow in place of green manure and so on. You can use both siderates, such as vetch, mustard, rapeseed, and crops that bring crops (legumes, corn, buckwheat). Crop rotation helps to improve the soil, saturate it with biological nitrogen, and increase the yield of potatoes. And yet, in a few seasons, you can completely cope with the wireworm.

- During dry periods, wireworms eat potatoes even more intensively, as they need moisture. If you water your potatoes more often, you can reduce the number of damaged tubers.
- If weed grass grows on the border with the garden, you need to separate it with several rows of lettuce. Weed wireworms will go to the potatoes, but they will meet more juicy lettuce roots on the way and remain there until the end of the season.
Fighting chemicals
The most aggressive measures to control wireworm on potatoes are insecticidal preparations and the use of mineral additives. If compared, then a more gentle way is to fertilize potatoes with nitrogen and ammonia, you can use:
- ammonium sulfate;
- ammonium chloride;
- ammonium nitrate.

Insecticides are used both for the treatment of potato tubers before planting, and at all stages of crop development. The most effective such preparations from the wireworm:
- “Aktara” is used during the sowing of potatoes, it is one hundred percent effective – the wireworm does not touch the processed potato bushes.
- “Prestige” also refers to insecticides applied to potato tubers before planting.
- “Bazudin” is recommended to be used only when other means against wireworm are ineffective. The drug is a real poison not only for the wireworm, but also for humans and mammals. Therefore, only those potatoes that have not yet tied tubers can be processed.

If possible, it is better to postpone the treatment of potatoes with insecticides and try to cope with the wireworm with biological means. The essence of the action of such drugs is based on the fact that in nature every living creature has an enemy. For the wireworm, such a natural enemy is predatory nematode – a microscopic worm that penetrates the body of a wireworm and eats it from the inside.
A biological agent must be applied to the soil in which potatoes grow. It is best to do this locally – in each hole before laying the tubers. Biological products are sold in the form of a suspension (“Nemabakt”) or as part of a special primer (“Protection”).
Traps and lures
Compared to other means of controlling wireworm on potatoes, such methods are the least effective, but they are safe and do not require material investments. In a small area with potatoes, traps can really cope with the wireworm, destroying up to 80% of individuals.
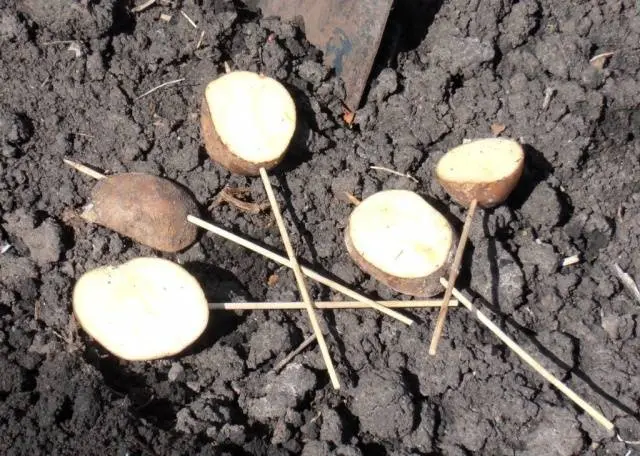

You can lure the wireworm, given his “culinary” addictions and cravings for warm, humid places:
- after harvesting potatoes, heaps of tops, straw or manure are left, and on a frosty day they turn them over – the wireworms accumulated in a warm place die.
- In the spring, such traps can be dug in or covered with foil. After a couple of days, dig it out with wireworms and burn it.
- In May or early June, cereals or corn are sown between potato rows, throwing a handful of seeds into the hole. After a couple of weeks, the cereals will sprout, their tender roots will attract the wireworm – the pest can be removed by simply digging up the bait plants.
- Pieces of potatoes, carrots, beets are strung on a stick and added dropwise to the ground. The next day, the baits can be removed and the wireworms removed from them, and then placed again in the ground.

Folk remedies

Attack in the form of a wireworm, destroying the planting of potatoes and other crops, has long been known. During this time, the people learned to deal with the pest and developed several effective tactics:
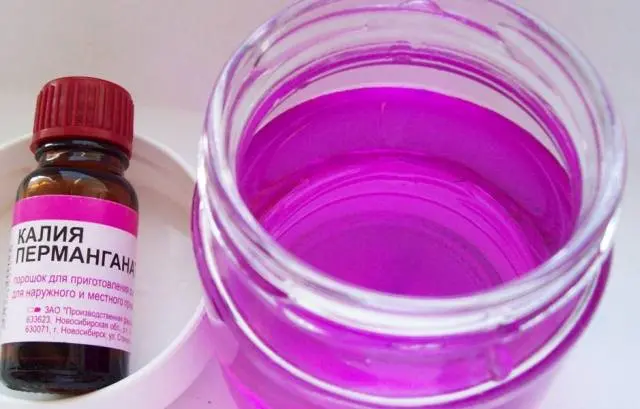
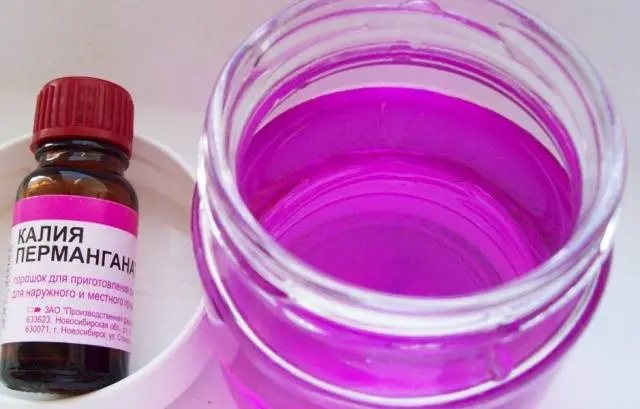
- During planting, half a liter of pink potassium permanganate is poured into each hole under the potatoes.
- Potato tubers are treated with dark purple potassium permanganate before planting – the wireworm will not eat such potatoes.
- Potatoes are watered with an infusion of field herbs such as nettle, dandelion, celandine, coltsfoot.
- A handful of onion peel is placed in each hole with potatoes – neither wireworms nor Colorado beetles can tolerate the smell of rotting onions.
- Since autumn, pine or spruce needles have been added to the potato plot – the wireworm does not like the smell of pine needles.
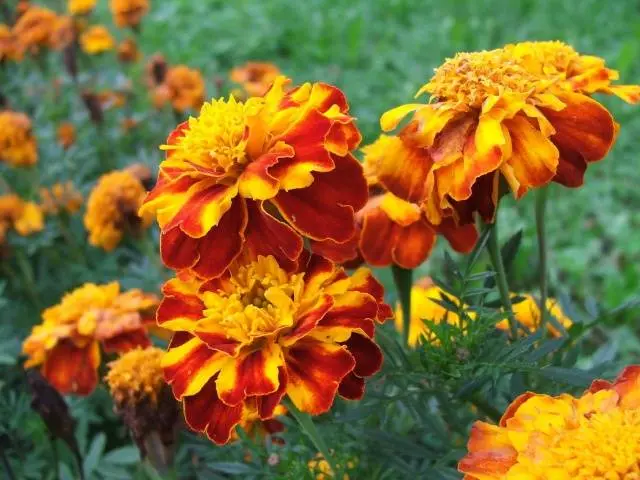
- Marigolds can be planted between rows of potatoes.

Results
How to get rid of the wireworm in potatoes, each gardener decides for himself. Experienced farmers recommend delaying the use of toxic drugs and trying other, safer methods.

For those who grow natural products, only the biological method and the installation of baits and traps are available, because even such gardeners do not use mineral fertilizers for their potatoes.
In any case, do not forget about agricultural practices, because their effectiveness has been proven by years of practice and clean crops of beautiful potatoes, without moves and damage.











