Contents
Hoof rot in cows is a common cause of lameness and a sign of poor-quality livestock management. The disease is very difficult to treat, since the pathogen feels great in a dirty bedding, and an ill animal is a carrier of the bacterium for 4 years. As soon as the microorganisms “feel the slack”, the infection not only resumes, but also infects previously healthy livestock.
Causes of foot rot in cattle
The causative agent of the disease is the anaerobic bacterium Fusiformis nodosus. It enters the hoof through scratches, cracks or punctures. Well preserved in a humid environment:
- manure;
- dirty bedding;
- water-soaked pasture;
- littered paddock.
The pasture is infected by the animals themselves, carrying the bacteria. The factor provoking infection is a decrease in immunity.
In fact, the real cause of foot rot in cows is an unbalanced diet and poor housing conditions. It is necessary for the protective functions of the body to weaken due to a lack of vitamins, micro- or macroelements for the bacterium to become more active.
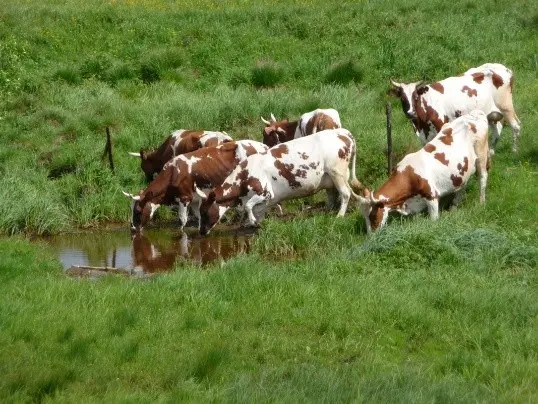

Grazing on a waterlogged pasture often leads to the disease of cows with hoof rot
Symptoms of foot rot in cows
Most owners do not pay enough attention to training a cow to show its hooves. Although the trimming of the hoof horn is required for animals every 6 weeks. If the cattle is accustomed to the fact that the owner takes care of the hooves, he does not resist inspection of the soles. Due to this, the appearance of foot rot can be noticed in the early stages. But in most cases, the owner knows about the problem when the cow has already begun to limp.
Early symptoms of foot rot in cows:
- softening of the sole;
- detachment of the side walls of the horn shoe;
- foci of wet erosion on the skin of the corolla;
- inflammation of the interdigital gap;
- characteristic unpleasant smell from the hoof.
Sometimes you can notice the initial stage of hoof rot only during the circumcision of an overgrown horn shoe.
With moderate severity, the shoe begins to flake off from the heel side. On a significant part of the sole, the skin comes off. At the last stage, the hoof shoe is completely separated from the base of the skin on the side of the front wall and on the sole.
Lameness begins as soon as the rot reaches the living part of the hoof. However, sometimes outwardly the disease can be invisible. Only a small hole with a discharge of fetid exudate indicates the site of infection.
In the photo below, a severe stage of foot rot in a cow:
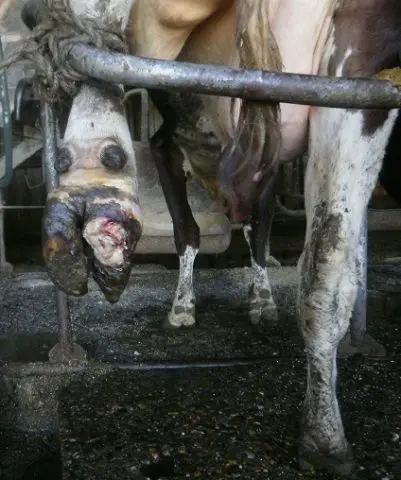

At an advanced stage of the disease, the animal actually walks on live meat.
Diagnosis of the disease
The symptoms of foot rot are similar to other hoof diseases:
- necrobacteriosis;
- pododermatitis;
- inflammation of the interhoof gap;
- a hint;
- aseptic dermatitis;
- foot and mouth disease.
Foot rot wounds often become infected with other bacteria. In this case, the disease proceeds as a mixed infection.
Diagnosis is carried out in the laboratory by inoculation of samples. Only a presumptive diagnosis can be made on the spot. But many hoof infections are treated with similar methods, so the fight against foot rot can be started without waiting for the results of the tests. Later therapy can always be adjusted.
How to cure foot rot in a cow
Using the old “folk” methods to treat hoof rot in cows is long and tedious. But even today these methods are popular because of the low cost of medicinal ingredients:
- tar;
- creolin;
- potassium permanganate;
- copper sulphate;
- iodoform;
- sulfate copper;
- formalin;
- zinc sulfate.
All these drugs have not only antibacterial action. They dry the weeping areas of the hoof. The use of these drugs and their mixtures is justified, since new effective drugs most often represent a complex composition of these ingredients. Sometimes with the addition of antibiotics. When using “pure” preparations of the “old” therapy, cows must be kept exclusively on dry bedding, which is technically impossible. And this is a minus of this method of treatment.
Antibiotics are recommended for use. But injections or oral administration of drugs only work on secondary infection. The bacterium that causes foot rot is anaerobic. This means that it does not come into contact with the blood that carries oxygen and antibiotics. Fusiformis nodosus habitat is already dead. It is possible to influence the causative agent of the disease only “outside”. Most often, foot rot is cured even without the use of antibacterial agents.
Hoof preparation for treatment
Before applying any preparation, the dead parts of the hoof are cut off as much as possible. Sometimes you have to cut before bleeding occurs. To clear the hooves of a cow, use:
- hoof knife;
- pincers;
- sometimes Bulgarian.
To use the latter, you need to have experience and a special circle.
The skin between the fingers is well washed with soap and water. The scabs are removed.
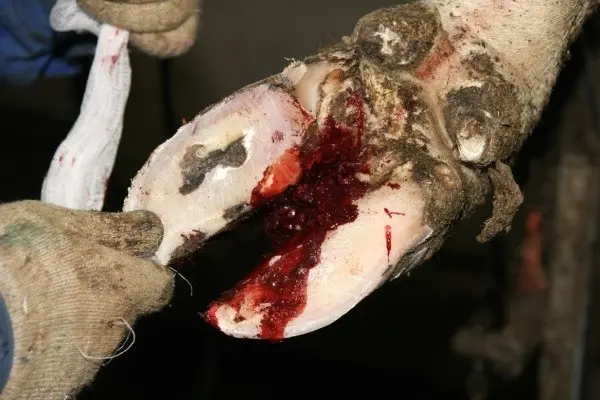
Bleeding is not uncommon in the treatment of foot rot in cows.
The use of old means
For treatment, almost all drugs are used undiluted. Tar and creolin are liquid fractions. They lubricate all the affected areas. The main effect of these substances is drying. They don’t kill bacteria.
Copper sulfate is poisonous, so the powder is used in case of deep holes in the hoof. It is impossible to apply pure copper sulfate to the bloody areas of the hoof. The same applies to zinc sulfate and formalin. For the treatment of skin and wound surfaces, 10% solutions are used.
A tampon is placed between the fingers. If there is a deep wound in the hoof that needs to be filled, it is also plugged. All hooves are covered with a tight bandage.
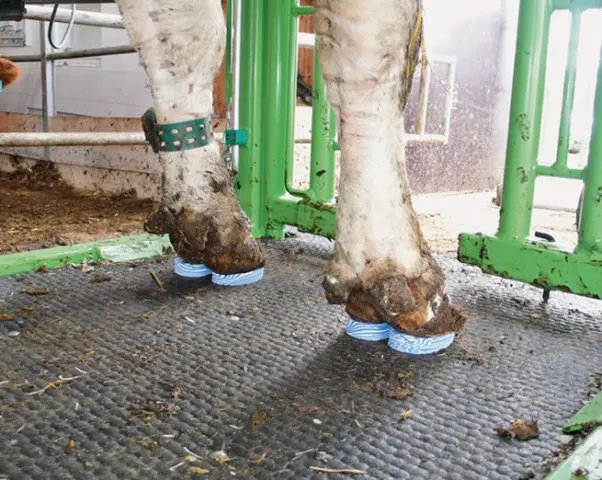

Advanced version of the bandage: insulating plastic “horseshoes”, not suitable if the skin above the sole is also damaged
New drugs
Technically, their use is the same as in the treatment of hooves with “folk” means. But in the composition of new drugs all the same ingredients. They can be in different concentrations and forms.
Fuzolin is produced in the form of a suspension. Its composition:
- probiotic based on hay bacillus Bacillus subtilis;
- probiotic based on soil mesophilic bacteria Bacillus licheniformis;
- glycerol;
- phenol;
- tar;
- methylene blue.
The last ingredients of Fuzolin are among the usual means of combating hoof rot, which have been used “from time immemorial”. The effectiveness of the drug can be provided by aerobic bacteria competing with anaerobic ones.
Suspension concentrated. To use it must be diluted according to the instructions. Fuzolin is also recommended for prophylactic use.

It is not known why, on most sites you cannot find the composition of the drug Fuzolin, the manufacturer himself does not hide it
In the video below, a cow owner demonstrates the effects of Intra Top-Hufs gel. Compound:
- aloe vera 5%;
- copper 4%;
- zinc 4%;
- substances that bind the whole complex into a single whole.
The manufacturer claims that the gel has a good wound healing ability. Preparations of copper and zinc are “traditional”, that is, in a different form they have also been used for a long time to treat rot and necrobacteriosis in ungulates.
Use of antibiotics
Effective for secondary infection of the hooves with bacteria susceptible to antibacterial drugs. Since drugs are administered by injection, the secondary microflora must be aerobic.
With hoof rot apply:
- Bicillin-5 intramuscularly, once at a dose of 40-50 thousand units per 1 kg of body weight.
- Biomycin subcutaneously in the form of a 10% emulsion at a dose of 0,6 ml per 1 kg of body weight. The drug is diluted on semi-liquid sterile agar, 3% sterile glycerol solution or normal horse serum. The dose required by the cow is administered in 6 ml at several points.
- Oxytetracycline.
In severe foot rot, oxytetracycline and bicillin-5 are most effective. They have not only antibacterial action. These drugs stimulate the regeneration of the soft tissues of the hoof.
Prognosis and prevention
With the initial form of foot rot, the prognosis is favorable. The severe form often results in the loss of the cow’s hoof shoe. Theoretically, it can be cured, but it will take about a year to grow a new horn. Economically it is unprofitable. If an infection gets on the exposed bone, it will lead to sepsis. The second option to save the cow is surgery. Cut off the affected finger. But surgery is only possible if the second hoof of the cow is healthy. With a severe form of rot, this is impossible. Conclusion: if the disease is running, the animal is handed over for meat. Losses can be avoided by taking preventive measures.
Prevention
Cows are bought only from prosperous farms. Before access to the general herd, the hooves are treated with a 10% solution of formalin or vitriol. If a sick animal is received, it is immediately isolated and treated until complete recovery.
At the entrance to the barn, a disinfection bath is arranged. For filling use 10% solutions of copper sulphate, formalin or Fuzolin. It should be remembered that such baths do not cure foot rot. They serve only for prevention. For private owners, this method may not be suitable.
Keeping a barn clean and dry is a must for any cattle owner. The task is not easy, but doable.
To maintain good immunity, cows are provided with a balanced diet and high-quality feed.
Another preventive measure available only to large farms is pasture reclamation. The rot bacterium cannot survive in relatively dry ground, and grazing becomes safe in the spring.
Conclusion
Hoof rot in cows is ubiquitous. Many livestock owners even consider it a necessary evil. But the disease can be successfully dealt with if you pay enough attention to the legs and the conditions of the cow.









