Contents
The sprawling and lush-flowering spirea shrub enjoys special attention of gardeners. This ornamental culture is unpretentious to growing conditions, but requires special care in preparation for wintering. Today we will tell you whether it is necessary to cover the spirea for the winter.
Pruning plants in the fall
Due to the variety of shapes, colors and sizes, spirea shrubs are widely used in landscape design. A decorative bush can act as an independent or composite element. This culture easily and quickly adapts to various growing conditions, therefore it is grown in almost every region of Our Country.
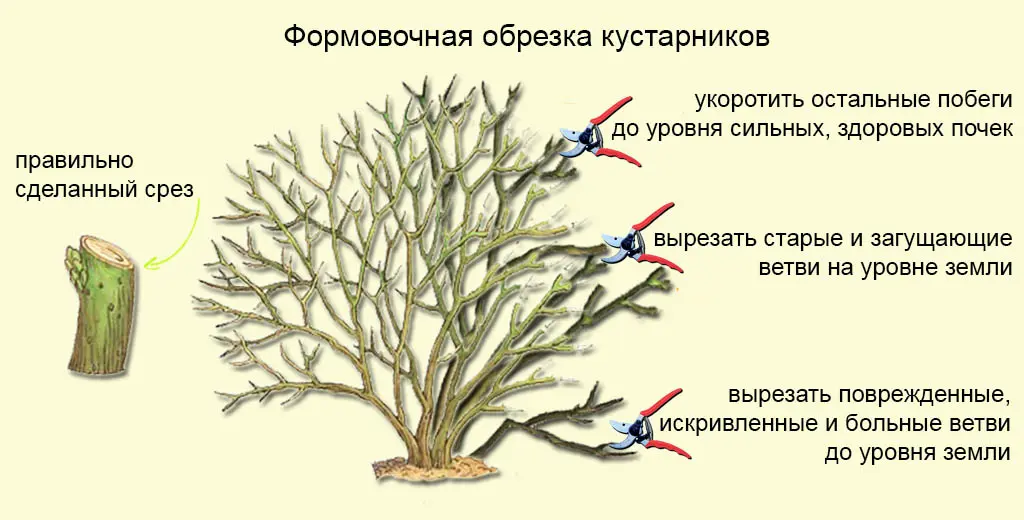
Pruning the crown of a shrub is an important step in caring for this ornamental crop. Please note that there is no single spirea pruning scheme. The technique depends on the flowering period of the shrub.
Video: “Autumn pruning of Japanese spirea”
From this video you will learn how to prepare an ornamental shrub for wintering.
blooming in summer
Early-flowering varieties include oak-leaved, nippon, sharp-toothed, medium and other spireas blooming in May. In early spring – at the end of March and beginning of April – pruning of frozen and withered shoots is carried out. Then you should select several mature branches to be deleted. Pruning powerful branches helps maintain the shape of the shrub and helps stimulate flowering. Remove adult and strong shoots should be 1 time in 2-3 years. Branches aged 6 years and older are cut at the very base. This procedure is necessary to build a new vegetative mass.
If the shoots are not removed, the plant loses its attractiveness, becomes weak, painful and unstable to various natural phenomena. Winter hardiness and endurance are reduced.
blooming in spring
Late-flowering or summer-flowering varieties of spirea are cut according to a different pattern:
- During the period of bud formation, which falls in mid-April, frozen and weather-damaged branches are removed.
- Most of last year’s shoots are shortened to healthy and most developed buds.
- On heavily overgrown bushes, all thin and short shoots are cut. Thus, the endurance of stronger and stronger branches increases.
- When the spirea reaches the age of 4 years, all shoots (young and old) are cut off at a height of 30 cm from the ground.
The brightest and most widespread representatives of the late-flowering group in our area are the varieties of Douglas, Billiard, Bumald, as well as Japanese, willow-leaved and birch-leaved spirea.
Pruning varieties
There are several techniques for pruning an overgrown spirea shrub. We bring to your attention some of the most common options.
Formative pruning is carried out in order to increase the aesthetic appeal of the bush. This procedure can be carried out both in spring and autumn. With the help of a sharp garden pruner, all old shoots are shortened. The bush takes on a new shape, which stimulates the growth of young shoots.
Anti-aging pruning is considered one of the stages in preparing spirea for winter. The shoots of young shrubs are shortened so that the plant can successfully overwinter and quickly recover with the advent of spring. As for spirea bushes aged 6 years and older, it is recommended to cut off all shoots almost under the stump. For further development, several branches with mature and healthy buds are left. It is necessary to rejuvenate ornamental crops in early autumn, so that the bush has time to “heal the wounds” and restore strength before winter.
Preventive pruning helps to strengthen endurance and increases resistance to various diseases and attacks of parasitic individuals. All old shoots injured by diseases, insects and rodents, as well as branches damaged by winds and other natural phenomena, are subject to removal.
Other preparatory work
Autumn care for plants growing in the garden begins with cleaning the area. First you need to harvest from fruit crops, inspect all vegetation for the presence of harmful insects and symptoms of various diseases, remove weeds and remove fallen leaves.
Spirea is characterized by high drought tolerance. Shrubs are watered only in the absence of precipitation. On average, one adult bush requires 15–17 liters of water. Do not forget to feed ornamental crops with potassium-phosphorus additives. Mineral fertilizers increase the endurance of plants and increase their resistance to diseases and precipitation.

After loosening the soil, watering and fertilizing the shrub with fertilizers, you can proceed to the mulching procedure. Dry oak leaves, tree bark, sawdust, hay, straw, peat, pieces of thick cardboard and scraps of non-woven fabric are used as mulch. The average height of the mulching layer is 10–15 cm.
Winter covering events
Now let’s figure out how to properly cover the spirea for the winter. The root neck and the bases of the branches are mulched, but the crown can be left intact or insulated with covering material. So that the wind does not break thin shoots, it is recommended to collect all the branches in a bundle and tie them with twine. The formed bundle is insulated with dry fallen leaves or pine spruce branches, the bushes are covered with burlap, white polypropylene bags, agrofiber, lutrasil or geofabric on top.

Nuances of shelter in different areas
The territory of the Federation covers several climatic zones. Accordingly, the features of autumn care and shelter of plants for the winter should be different. For example, spirea bushes growing in the south of the country do not cover at all. In order for the decorative culture to successfully winter, it is necessary to mulch the near-trunk circle and the base of the bush.

The central zone of Our Country, the Leningrad region and the Volga region are characterized by sharp temperature changes. If the winter is snowy, you can not cover the spirea. Snowy and unstable winters require more careful care of the plants in the garden. The crown is covered with any non-woven fabric or pine spruce branches.
In Siberia and the Urals, only frost-resistant varieties of Billard, Douglas, gray, crenate, medium, willow and birch-leaved spirea are grown. The mulching layer is increased to 20–25 cm, the bush itself is covered with “non-woven fabric”, fallen leaves and pine branches.
In order not to injure the decorative bush on the eve of the winter cold snap, it is recommended to abandon the autumn pruning.
Common rookie mistakes
The main reason for the death of an ornamental shrub in the winter is considered to be ignorance or violation of the technology for caring for spirea in the fall. The most common mistakes that negatively affect the endurance and winter hardiness of a crop are excessive soil moisture, the application of nitrogen-containing mineral fertilizers, and late pruning of shoots.
Many novice gardeners choose the wrong covering material for warming spirea. Ruberoid and polyethylene film do not allow plants to “breathe”. The lack of normal air exchange leads to the formation of mold on the shoots and rotting of the root collar.









