Contents
Good day, dear readers! We are glad to welcome you to the blog. Today I want to touch on the topic of management. We face the problem of leadership every day, be it at work, courses, school, etc. In the article, I want to briefly talk about the effectiveness of managers, I will specifically consider the Fiedler leadership model.
Who is F. Fiedler?
Fred Fiedler, a psychologist from the United States of America, has long studied the topic of organization and leadership in society. In this area, he is considered one of the leading experts. On his account, a number of studies and experiments on the topic of leadership problems. The result of his work was the conclusion that there are no ideal leaders, but their presence in society is necessary.
Fiedler’s ideas had a very noticeable impact on management both in the West and in the USSR. One of his most popular achievements is the creation of a model of effective leadership.
What is the essence of the Fiedler model?
F. Fiedler developed his model for 4 years (1954-1958). He was the first to reveal the dependence of management effectiveness on certain factors and circumstances.
He outlined 3 aspects or variables that shape the situation in the team:
- The state of the “manager-subordinate” relationship is the manifestation of loyalty to employees, the presence of trust in the manager, acceptance of his personality.
- The structure of tasks for each employee is the familiarity of the tasks set, their clarity and structure.
- The power (authority) of the manager is the scope of the manager’s powers, based on which he makes decisions about remuneration and support for employees.
8 options for situations in a team
Based on these 3 variables, the psychologist identified 8 standard situations that are characterized by their management style. But he also noticed that the leader basically acts in the same way in any team. Therefore, it makes sense to place a certain leader in a certain team. This creates the conditions for the most efficient and productive work.
Fiedler’s leadership style was determined by surveys of employees. He asked to describe the least preferred colleague (NPC) with whom the person does not want to deal. Based on the results of the survey, he made the following conclusions:
- A restrained description of the NPC is an indicator that the person is compliant, attentive, worried about human relations within the team. Managers with a high NPC rating prefer to build relationships with colleagues, led by an individual and mutual understanding (non-directive management with a relationship orientation) plays a key role.
- A person who talks about CPD in a negative way, i.e. has a low CPD rating, is a powerful leader who closely controls the process, quality and timing of tasks. Such managers usually do not worry about relationships with colleagues while doing work (directive, autocratic management).
Relationship between management style and situation
Below is a table that was developed by F. Fiedler. Here are the optimal management styles for each situation, which are ideal for a particular team. Situations are marked horizontally, and leadership styles are evaluated vertically according to the CPD criterion.
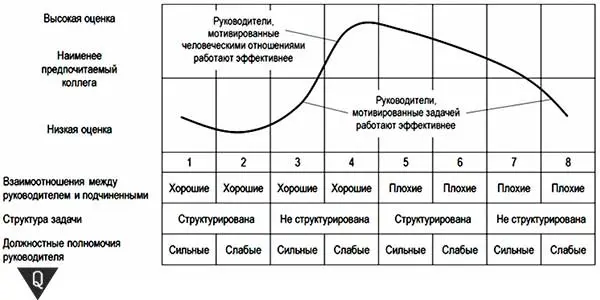
The table has pre-set parameters for determining 8 possible situations in which the manager is located. Based on this, the preferred management style for each of them is studied:
- Situations 1, 2, 3, and 8 require executives with the lowest possible CPD who prefer task orientation.
- In situations 4, 5, and 6, leaders with a favorable relationship orientation and a high NPC rating are most likely to take root.
- For situation 7, both management styles are suitable.
What criteria is used to evaluate the compliance of the leader with the team?
Below I will discuss how management style is related to team performance.
The 1 situation
The most favorable for the manager, as it is characterized by structured tasks, great powers and favorable relations with colleagues. It is in such conditions that it is possible to have maximum influence on subordinates. But she almost never occurs.
By the way, you can take a cohesion test in your team.
The 8 situation
The least favorable, since the leader has minimal authority, poor relations with colleagues, there is no clear structure in the tasks.
But F. Fiedler says that despite the colossal difference in situations 1 and 8, an autocratic management style is equally effective in such teams.
In a team that is interested in effectively performing tasks, high speed of productivity and decision-making in combination with strict process control. Therefore, the autocratic style is successful where the performers listen to their manager.
If the leader has little to no power and authority, in such cases, the authoritarian style is best suited. With its help, it is possible to organize direct control of subordinates and correct their actions if necessary.
Situations 1, 2, 3
In situation 1-3, initially good relations between the manager and subordinates, so there is no need to build and maintain them. Also, the success of these situations is predetermined by the routine of tasks and the authoritativeness of the leader, so the duty of colleagues is typical here.
Adherents of a non-directive style passively lead the team, although employees are not averse to taking on new assignments. Managers do not fully use all their influence opportunities, have good relationships in the team.
The leader should be clear that there is a big difference between being task-oriented and putting your colleagues down. As a dictator, he runs the risk of having an indignant team that does not want to negotiate, joins informal groups whose goals go at the expense of the organization’s strategy. This is followed by loss of management efficiency.
Situation 4, 5, 6

The leader prefers to focus on the person. This allows you to build trusting relationships with employees and thereby increase their desire to interact. For example, he may begin to show concern for subordinates. Uses high-level motivational methods, motivates colleagues to perform specific tasks. This reduces the need for strict supervision and minimizes the risk of loss of control over workers.
Under the same conditions, an autocratic leader has much less chance of success in organizing productive work in this team.
Disadvantages of F. Fiedler’s theory
Of the main shortcomings of F. Fiedler’s theory, I identified the following:
- It is difficult to specifically establish the correspondence of the characteristics of the situation to the style of management.
- Evaluation variables are not stable: the structure of the tasks and goals of the company is changing, the relationship between the manager and employees is improving or worsening, the authority of the manager is also increasing or decreasing.
- Not all aspects of the situation are characterized: time to complete tasks, work experience of team members, company size, corporate culture, etc. are not taken into account.
- There is no assessment of the character and personality traits of both the leader and his subordinates.
Conclusions
According to F. Fiedler, a certain situation in the team is suitable for each contingent of leaders. Hence the theory has another name — the contingent theory. It serves as the basis of the situational approach in management.
Thanks to the Fiedler model, the importance of interaction between the company manager, performers and the current situation was revealed. The main conclusion of this approach is that there is no universal and correct leadership style that can be effectively applied in any organization. At the head of everything is the situation in the team, from which it is necessary to build on the analysis of relations, the fulfillment of tasks and the productivity of production as a whole. The situational approach makes it much easier to select the right staff and appoint managers.
We also recommend reading an article about the principle of Peter Lawrence. It’s about why a person gets stuck in career growth and stays in the same position.
I really hope that the information provided was useful and interesting for you. Subscribe to the site, share useful posts with friends.
All the best!









