Contents
Any pig breeder will sooner or later want to breed offspring from his wards. And the viability of the offspring and the further fate of the sow depend on how correctly the pigs are cared for during pregnancy and how competently the farrowing process itself goes. The farrowing of pigs for the first time is especially important, as it lays the foundation for their entire future as sows.

Pig preparation for first pregnancy
When preparing a pig for its first pregnancy, it is very important to understand:
- which individuals are best suited for breeding;
- When do animals reach puberty?
- how to determine that the pregnancy has come.
Not every pig is able to bring healthy and high-quality offspring. First of all, only zoned breeds should be bred, they are more hardy and unpretentious. Particular attention should be paid to the constitution and body structure of the pig:
- the body must be strong and healthy;
- the animal must have a powerful skeleton with a wide back;
- the abdomen should not sag;
- in the pig’s udder there should be at least 12 well-formed teats, located at a decent distance from each other;
- the lower teats should not be blocked by the upper ones so that all piglets have free access to them.
It is also very important that the breeding pig has a calm and docile nature. At the same time, she showed healthy activity, excellent appetite and moved a lot.
It should be recognized that young pigs already at a fairly early age (5-6 months) experience a craving for mating. But a serious pig breeder should not allow his charges to mate at this age. Otherwise, the offspring may be very weak or completely lifeless. It is best to wait until the young pigs are 9-10 months old. Usually at this age they reach 100 kg in weight and their body is already more prepared for bearing piglets. In some late-ripening breeds, the time of the first mating comes after a year.
Since pigs come to hunt after the onset of puberty throughout the year, through certain cycles of 18-24 days, the time for the first mating must be selected the most convenient for the owner. This is best done in such a way that farrowing does not occur in the coldest, and also not in the hottest months of the year.
Signs of the onset of hunting or estrus are as follows:
- pigs refuse food for no reason;
- their behavior becomes restless, they begin to jump on other animals;
- the genitals swell and redden, mucus begins to stand out from them;
- when a boar appears, the pigs first seem to fall into a stupor, and then behave quite actively.
The estrus usually lasts from 2 to 4 days. But the boar must be allowed to approach the pig in the first two days, otherwise mating may not work.
When a pig carries a pregnancy, her behavior usually changes dramatically.
- animals express calmness and indifference to the world around them and even lose interest in food;
- despite some indifference to food, the mass of the pig begins to increase;
- from the genitals, there is a release of curdled formations;
- the nipples of the pig begin to redden and swell, preparing for feeding;
- During the next hunt, all signs completely disappear.
True, there is such a thing as a false pregnancy of pigs, in which all of the above signs also take place.

There are several simple folk ways to determine whether pigs have become pregnant or not.
Method 1 – the pig breeder calms the animal and, in a standing position, strokes it on the back from the shoulder blades to the back. In the normal state, the pig will definitely bend, but the pregnant female will stand evenly and calmly. This method gives a guarantee of pregnancy from 80 to 90%.
Method 2 is based on the fact that in the next period of hunting (that is, after about 20 days), a boar is again launched to the pig. A pregnant animal will not pay any attention to him, while an ordinary female will behave quite actively with him.
However, if after 2-3 weeks the signs of early pregnancy in the pig did not disappear, then most likely the process began to actively develop.
How long does pregnancy last in pigs
It has been calculated that the average gestation period for pigs is 3 months + 3 weeks + 114 days. Which together is exactly 110 days after mating. But this rule only makes it easy to remember the numbers. In fact, the gestation period for pigs can easily fall between 125 and 25 days. According to statistics, only 114% of sows farrow in exactly 30 days. 45% of animals bring offspring at an earlier date, and XNUMX% at a later date.
It is only important that the gestation period is at least 110 days. When farrowing before this period, the life of newborn piglets is at risk.
How many days a pig bears piglets depends on several factors:
- The age of the sows. The gestation period before the first or even the second farrowing can increase by 5-7 days. Conversely, mature pigs are able to farrow 7-10 days earlier than the average data.
- Climatic conditions and seasons. In summer, the gestation period is slightly longer than in winter.
- The number of born piglets. Oddly enough, but a larger number of offspring obtained requires a shorter gestation period.
- Animal breed. Generally, the smaller the animals, the shorter their gestation period. For example, Vietnamese bellied pigs have calves from 114 to 118 days, while large white sows have a pregnancy of 114 to 122 days.
- The conditions of detention also have an impact, the better they are, the longer a pig can carry its cubs.
Farrowing table of sows
For a more accurate determination of the sow’s farrowing time, experienced farmers advise using a special calendar.
It is usually created in the form of a table that allows you to determine the earliest date from which you need to be ready for farrowing at any time.
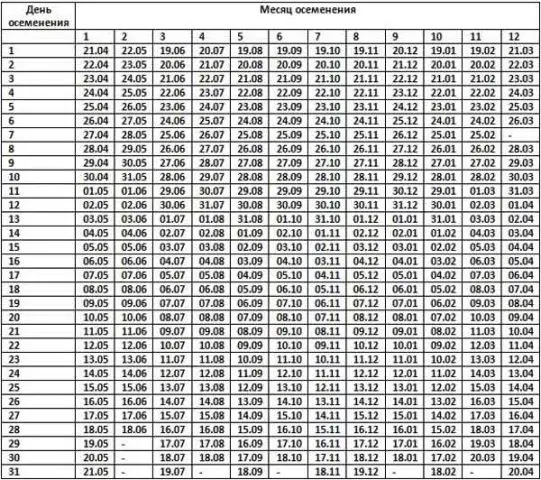
This spreadsheet pig calendar is quite easy to use.
In the first vertical column, you need to find the number when the actual mating of the pig occurred, and in the topmost horizontal line is the month when this event occurred. In the cell where the found row and column intersect, the date is written, starting from which it is necessary to expect farrowing every day.
How many times does a pig give birth per year
Most domestic animals bring offspring only once a year or even less often. But a feature of the sow is the fact that she is quite capable of farrowing twice a year when favorable conditions are created. At the same time to bring perfectly healthy and viable offspring.
How many piglets can a pig bring at a time?
It is not in vain that a pig is considered a prolific animal – it can bring about a dozen or more piglets at a time.
It is rather difficult to determine their exact number in advance. The fact is that the number of piglets in the litter is influenced by several factors:
- pig breed;
- her age;
- number of previous farrowings;
- health status;
- food;
- hereditary productivity.
At the first farrowing of pigs, the number of cubs usually does not exceed 6-8 pieces. In subsequent years, a good sow should gradually increase the number of piglets with each farrowing. A mature pig at the age of 2-3 years can give birth to 10-12 piglets. The most prolific individuals bring from 15 to 20 cubs.
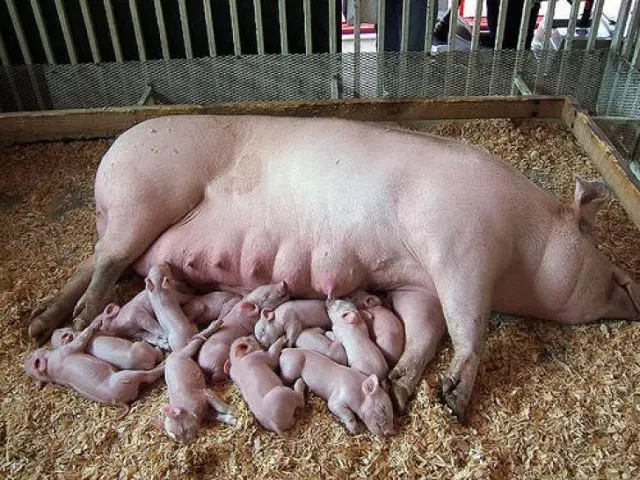

Much determines the breed of animals. If Chinese pigs, on average, are able to bring about 20 piglets, then representatives of the usual large white breed – only about 12-14 heads.
Preparing for farrowing
Only with a properly organized process of feeding and caring for pigs during pregnancy, it is possible to avoid most problems during farrowing at home, especially for the first time. There is a difference in feeding during gestation between young (primiparous) and mature sows
Young pigs are still growing and developing intensively, so they need a lot of protein feed. For the entire period of gestation, a primiparous pig should gain 45-55 kg of live weight.
Older pigs no longer need so much protein food, since they only need to maintain their own weight to bear piglets. Their weight is carefully monitored during the entire period of pregnancy. They should not gain more than 40-45 kg.
The last month is especially important, during which the pig can gain two-thirds of the total weight assigned to it. In the last weeks before giving birth, the pig is transferred to a diet of high-quality hay, liquid bran and flaxseed meal. To prevent constipation, beet pulp should be regularly added to food.
Food must be fed 3 times a day. And in the drinkers there should be fresh drinking water around the clock.
Pregnant pigs are not allowed to include in the diet:
- hard cake;
- chaff;
- sunflower husk;
- frozen and rotten food.
Signs of an upcoming farrowing
In order not to miss the exciting moment of childbirth, when pigs may need additional human assistance, every pig breeder should be aware of the main signs of the impending event.
The farrowing signs of a sow giving birth for the first time are practically the same as those of a mature pig, except that they are slightly less pronounced.
Approximately 4-5 days before farrowing, the sow clearly turns pink and begins to swell the vulva or loop, which is located at the prenatal opening. If this has not already been done before, the pig from now on must be placed separately, in a special farrowing pen. This is necessary so that during farrowing and in the future, a voluminous and massive animal has less opportunity to accidentally crush its newborn babies.
Approximately 2 days before farrowing, udder friability can be observed in the pig, as the process of colostrum production begins. Also, the belly sags quite strongly and the spine bends.

A day before the expected birth, the behavior of the pig changes: it behaves restlessly, often jumps up, lies down, grabs the bedding with its mouth, and makes a nest for itself. You need to make sure that she has enough sawdust, quality straw or corn husks in her pen. After some time, colostrum may already appear from the nipples when pressed, and mucus begins to be released from the genitals. By these signs, you can easily find out that the pig will farrow soon.
It should be understood that the first birth is usually the most difficult and may well take place with some delay. This is completely normal. Just before the start of labor, the pig usually calms down and lies on its side in some secluded corner. The beginning of contractions and wagging of the tail indicate the first contractions.
Preparing the machine, tools and disinfectants
All walls of the room in which farrowing will take place are whitewashed with slaked lime. The machine itself is also treated with a disinfectant solution (for 0,5 liters of hot water, 100 g of alkali). The litter is completely changed to fresh.
For piglets, it is necessary to prepare a separate warm corner with a fixed infrared lamp. The room should be free of drafts, but should not be too hot. The optimum temperature is about + 18-20 ° С. If farrowing occurs in the summer, on hot days it is necessary to spray the mother with cool water.
The pig itself is washed with soapy water a few days before farrowing, and then treated with an antimicrobial agent (1% creolin solution). Be sure to place a drinking bowl, preferably metal, in which the water is changed at least 2-3 times a day. At least 25-30 liters of water should go per day per pig.
At the ready should be a bag with tools and materials to assist in childbirth:
- scissors for cutting the umbilical cord;
- strong thread for tying it;
- 5% iodine or brilliant green for the treatment of the umbilical cord;
- clean soft diapers with which piglets are wiped;
- disposable sterile gloves;
- freshly prepared solution of potassium permanganate.
A container of warm water and soap should also be prepared.
Farrowing pigs at home
For sows that are going to farrow for the first time, it is especially important to create a calm atmosphere during childbirth. Unfamiliar noises and the presence of strangers are undesirable. It will be good if a person who cares for them will constantly be with young pigs. On average, depending on the strength of the efforts, farrowing in pigs giving birth for the first time lasts about 6 hours. With a favorable outcome, everything can be completed in 2-4 hours, and if the attempts are weak, then farrowing can continue up to 9 hours.
With an interval between attempts of 4 minutes, amniotic fluid usually begins to drain. Most often, the first piglet is the largest and therefore it comes out longer than the rest. Other piglets are usually born every 20-25 minutes.
Before the onset of childbirth, the pig’s nipples are wiped with a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
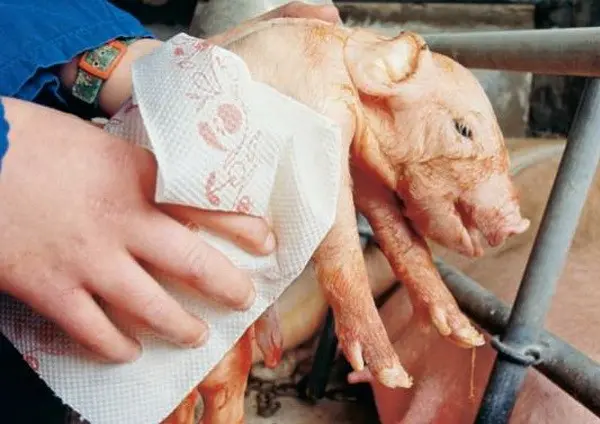
The born piglets are wiped with a clean diaper, if necessary, the airways are cleaned.
Having measured about 5 cm from the baby’s body, the umbilical cord is cut, and the cut site is treated with brilliant green or iodine. In cold weather, piglets must be dried under an infrared lamp. Then the piglets are applied to the mother’s nipples.
Pig colostrum contains the most valuable substances for the immature immunity of babies, so it is vital for them in the very first hour of their life. If this is not done, then the piglets most likely will not survive. The nipples that are closer to the sow’s head are usually fuller. It is to them that the weakest piglets should be applied, so that it is easier for them to suck out the portion of colostrum they need.
Before each birth of the next piglet, the pig’s hind leg begins to twitch and its tail wag. If all these movements stop, then, most likely, the birth process has ended.
But after the birth of piglets, after 3-6 hours, the afterbirth usually comes out. It is very important to wait for it to come out and immediately remove it so that the pig would not have the opportunity to eat it. If after 8 hours after the end of farrowing the placenta has not come out, it is urgent to call a veterinarian.
After the end of childbirth, the back of the pig’s torso is washed with warm water and the old litter is completely replaced with a new one.
It is allowed to feed the sow after farrowing no earlier than 2 hours after the end of the process. But water with sugar to restore strength can be given immediately. It is better if, after the placenta comes out, the pig itself will stand up and drink, and even eat a little.
Complicated farrowing
The first thing that can alert you during farrowing is if the contractions are weak or rare. In this case, you can try to get the pig to stand up and move around, give her a stomach massage or drink sweet water.
With premature withdrawal of amniotic fluid into the birth canal of a pig, you can inject a decoction of flaxseed or pre-boiled and cooled sunflower oil.
With prolonged non-disclosure of the cervix, hot (+ 45 ° C) boiled water can be poured into the birth canal.
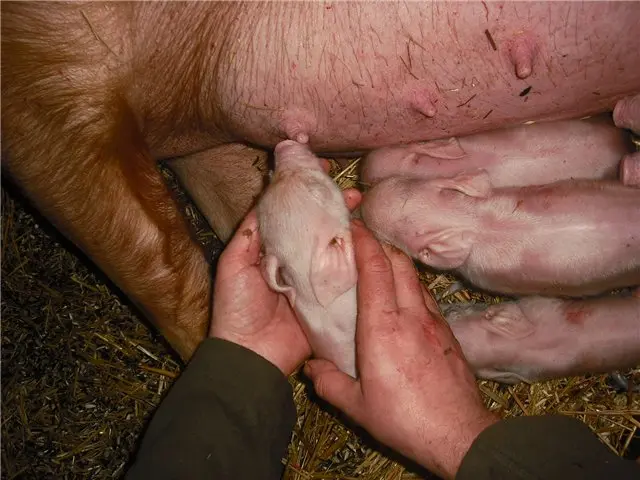
What to do if the pig cannot farrow
In the case of the first farrowing, the birth canal may be too narrow, and the process itself may be painful for the pig. In this case, you can use an antispasmodic for the uterus with the main active ingredient Vetrabutin hydrochloride. This drug is injected into the uterus of the pig, resulting in relaxation and pain relief. The use of oxytocin can stimulate labor activity, and calcium can support the contraction of the pig’s uterus.
If the fetus is not positioned correctly or is too large, the farrowing process may also be delayed. And if there is no veterinarian nearby, then you will have to act on your own.
This requires that the examiner’s hand be small and narrow. A glove lubricated with a special gel or petroleum jelly is put on the hand and inserted into the sow’s vagina. In the wrong position, they try to turn the piglet. In the case of a large cub, they try to take it by the legs and, at the time of the next fight, they pull it out.
So that the contractions during farrowing do not weaken, already born piglets are applied to the nipples. Since sucking stimulates labor activity.
If after birth the piglet does not breathe, then you can try to give him a heart massage, to do artificial respiration.
Rules for care after farrowing
After a successful farrowing, it is important that the pig is able to fully feed and raise all the born piglets.
What to feed a sow to have more milk
12 hours after farrowing, the pig can be given a liquid mixture of oat bran to produce milk. It is not recommended to give corn and rye, as they lead to a decrease in the amount of milk.
For the first 2 weeks, the sow’s food should be predominantly liquid. It is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:3.
Per day, one pig should receive:
- 1,5 kg of hay or fresh grass;
- 10 kg of succulent feed;
- 4 kg of concentrated feed.
How to care for a sow and piglets
Within 5 days after farrowing, the pig may experience bloody discharge from the birth canal. Gradually they become lighter and more transparent, and then stop. If this does not happen, you should contact your veterinarian.
While feeding babies, a pig may not let them near the udder, lie on its stomach. In this case, you need to examine the udder and if small wounds are found on it, then the milk fangs are blunted by 2 mm in piglets with the help of forceps.
Possible problems
Some of the possible problems have already been dealt with in the chapter describing the farrowing process.
What to do if the pig is walking
If the pig is farrowing for the first time, then the delay in childbirth is considered an almost normal process. The main thing is to provide the sow with at least some activity and fresh air.
Why does a pig eat its piglets
If a pig is allowed to swallow its afterbirth (placenta) during farrowing, then it will be able to eat its piglets in the future. Therefore, this cannot be allowed.
What to do if the sow does not eat and does not get up after farrowing
Often, especially in the case of prolonged or complicated births, excessive fatigue accumulates in the body of the pig. In this case, she needs to be offered sweet water and helped to get up. If all attempts are unsuccessful, then the problems may lie deeper. Perhaps the presence of inflammatory processes or problems with the gastrointestinal tract. In these cases, the pig needs urgent veterinary help.

After how many farrowings do they change the sow
The period of use of a sow in a subsidiary farm depends on its characteristics of multiple pregnancy, milk production, as well as the safety of piglets during the lactation period. If all these characteristics are high, then the pig is kept for at least 4-5 years to receive at least 6-7 farrowings from them. After all, the maintenance of a mature pig requires less feed than a young uterus. In addition, the maximum productivity of the sow is usually shown at the age of 2 to 5 years.
Conclusion
Farrowing pigs for the first time is too responsible, which, in the absence of the necessary knowledge and skills, may end and not very satisfactory. Therefore, it is necessary to evaluate your strengths and, if necessary, be sure to call a specialist for help.










Nashukulu sana kwa elim yen bora