Contents
Laryngotracheitis is a disease in which the larynx and trachea become inflamed. The cause of the development of the pathological process are viruses and bacteria. Laryngotracheitis can occur in both adults and children. The disease leads to a change in voice, accompanied by a wet cough, swollen lymph nodes, sore throat and chest. Laryngotracheitis can be an independent pathology, and can act as a complication of laryngitis, tracheitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis or rhinitis.
What is laryngotracheitis?
Laryngotracheitis – this is an inflammation of the larynx and the initial sections of the trachea. It leads to narrowing of the airways. Often, pathology develops as a complication of ARI. The disease is diagnosed mainly in childhood.
The mechanism of origin and development of laryngotracheitis is associated with the pathogenesis of SARS.
The lumen of the trachea and larynx narrows, which is due to a number of reasons:
Infiltration and swelling of tissues.
Increased mucus production. It is produced by the inflamed trachea and bronchi.
Spasm of the muscles of the respiratory tract.
Accumulation of thick sputum.
These pathological causes lead to the fact that air cannot pass normally through the respiratory tract. The person develops a barking cough. Due to inflammation of the vocal cords, a change in voice occurs. He becomes hoarse.
Causes of the disease
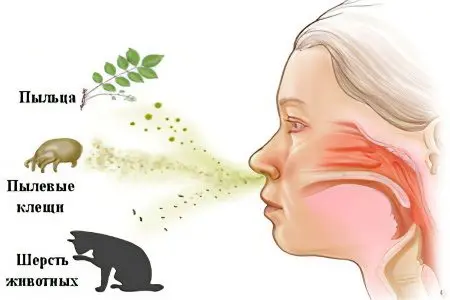
Viruses and bacteria lead to laryngotracheitis. They enter the respiratory system by airborne droplets.
The causes of laryngotracheitis are as follows:
Infection with a viral infection. Laryngotracheitis can occur with rubella, SARS, adenovirus infection, parainfluenza, measles, smallpox, scarlet fever.
Infection with bacteria. The culprits of laryngotracheitis can be staphylococci, streptococci, pneumococci. Less commonly, mycobacterium tuberculosis leads to the disease (a person develops tuberculosis of the larynx), pale treponema (causes tertiary syphilis), mycoplasmas and chlamydia.
Damage by chemicals.
Effects on the body of allergens.
Risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing laryngotracheitis:
Alcohol abuse, smoking.
Excessive stress on the vocal cords. Loud singing and screaming can provoke the development of laryngotracheitis.
Tendency to allergies.
Subcooling the body.
Eating foods that are too hot or too cold.
Infection with syphilis, tuberculosis and other infections. Laryngotracheitis in this case will act as a complication.
Bronchial asthma, pulmonary emphysema, pneumosclerosis, bronchiectasis.
Diabetes.
Diseases of the central nervous system.
Diseases of the heart and blood vessels.
Chronic laryngotracheitis is most often the result of a decrease in immunity. It can also occur due to the lack of treatment of an acute disease.
Classification

There are several classifications of laryngotracheitis. Each of them is based on various factors: the severity of the pathological process, the causes of the disease, the features of the clinical picture, etc.
Depending on the characteristics of the course of laryngotracheitis, it is divided into 2 forms:
Chronic laryngotracheitis. It can last for months or even years. From time to time, a person experiences exacerbations.
Acute laryngotracheitis. The duration of the inflammatory process is 7-20 days. If a person receives adequate therapy, then a full recovery will come.
Depending on the characteristics of the lesions of the mucous membranes of the trachea and larynx, there are such types of laryngotracheitis as:
Catarrhal laryngotracheitis. It proceeds acutely, the throat of a person becomes very red, the mucous membranes of the larynx and vocal cords swell. Infiltration of tissues with inflammatory exudate leads to their thickening. Due to malnutrition, the mucous membranes may become bluish. The permeability of the vascular wall increases, which is why pinpoint bruising appears on the mucous membranes.
Hypertrophic laryngotracheitis. The patient has a significant proliferation of mucous membranes. The trachea, larynx and vocal cords suffer. This negatively affects breathing, it becomes difficult. The voice of a person changes. When examining the affected structures, the doctor visualizes the so-called “singing nodules”. Most often, people with increased voice load suffer from this form of the disease: announcers, singers, teachers, actors, etc.
Atrophic laryngotracheitis. With this type of disease, normal tissues of the larynx and trachea are replaced by squamous stratified epithelium. There is atrophy of the vocal cords and surrounding structures. The glands that produce the normal secretion die off. Because of this, the inside of the throat is covered with dry crusts, which cause a lot of inconvenience to a person.
Depending on the cause of laryngotracheitis, the following forms are distinguished:
Viral.
Bacterial.
Combined.
Depending on the place of concentration of the inflammatory process, there are such types of diseases as:
Subfold laryngotracheitis, in which the larynx swells strongly. The cause of this form of the disease is often an allergic reaction of the body.
Acute laryngotracheitis. The larynx and trachea are swollen. The cause of the acute form of the disease are viruses and bacteria.
Obturating laryngotracheitis, which is characterized by a significant narrowing of the airway lumen. This form is the most dangerous, as it can cause suffocation.
The symptom is laryngotracheitis

Symptoms of laryngotracheitis in an adult are as follows:
An increase in body temperature to high levels.
The appearance of noisy breathing and wheezing. Such breathing is called stenotic.
Hoarseness of voice, sore throat.
Barking cough.
Pain when swallowing food.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck. When they are palpated, a person experiences pain.
In children, laryngotracheitis often manifests itself in the form of a false croup. The child coughs heavily, may begin to choke. Seizures happen at night. They last about 30 minutes and can be repeated regularly.
With stenosing laryngotracheitis, stenosis of the larynx develops. Pathology has an acute course, attacks of coughing and suffocation occur at night. The person begins to wheeze, he has shortness of breath. The lack of oxygen is manifested in the blue of the nasolabial triangle and lips.
Leaving a person with such symptoms alone is dangerous. If there are signs of suffocation, you need to call an ambulance. Children from false croup can quickly suffocate.
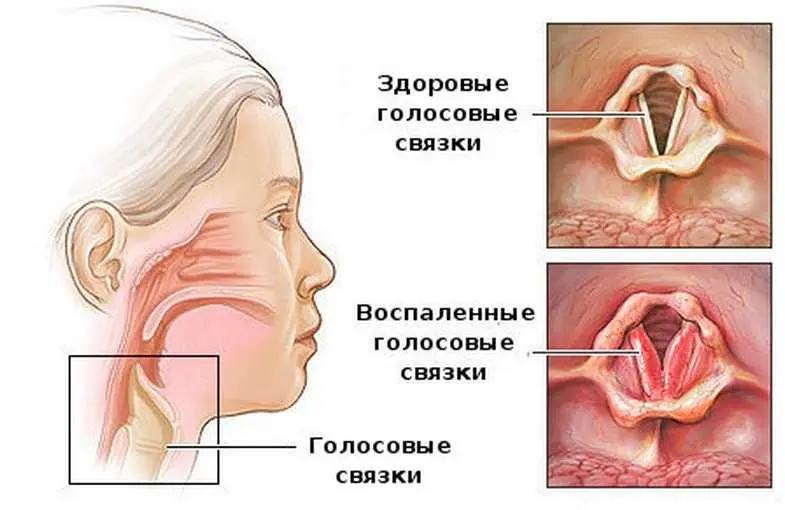
The acute form of the disease is characterized by pronounced symptoms, while the chronic course of laryngotracheitis gives meager symptoms. The difference lies in the fact that the acute form passes in a few days and its symptoms will not bother a person anymore. Chronic laryngotracheitis is accompanied by a constant cough and hoarseness.
Acute symptoms
The acute form of laryngotracheitis is accompanied by symptoms such as:
Burning and tickling sensation in the throat.
Chest pain. It is worse after coughing.
Isolation of viscous sputum.
Hoarseness of voice, hoarseness.
Inflammation of the lymph nodes, their soreness and increase in size.
Symptoms of the chronic form
Chronic laryngotracheitis is characterized by the following symptoms:
Cough with a small amount of sputum.
Sensation of a lump in the throat, which will be represented by tenacious mucus.
Voice change.
Feeling of fatigue in the region of the vocal cords after prolonged strain.
Interesting! Symptoms that were bright in the acute form of the disease, fade in people with chronic laryngotracheitis. A person after some improvement will feel bad again. A provoking factor can be pregnancy, menopause, menstruation, hypothermia, prolonged stress on the vocal cords.
Diagnostics
The doctor may suspect the disease based on the person’s complaints. Patients with laryngotracheitis indicate a dry cough, they have a hoarse voice, hard breathing.
To confirm the diagnosis, the patient is sent for the following tests:
General blood analysis.
General urine analysis.
Bacterial analysis of sputum.
Serological studies that allow you to establish the type of infectious agent.
Instrumental methods of examination include microlaryngoscopy and tracheoscopy. The ligaments and larynx are examined on special equipment. If necessary, the patient is referred for an X-ray examination or a CT scan of the larynx and trachea. Be sure to perform a chest x-ray for patients who have wheezing. This study will rule out bronchitis and pneumonia.
If a person suffers from laryngotracheitis, then a biopsy is performed on him. The doctor takes tissue from the affected area. In the future, the resulting material is carefully studied to exclude the presence of cancer cells in it.
When diagnosing laryngotracheitis, it is necessary to distinguish it from such diseases as: abscess, diphtheria, pneumonia, bronchial asthma.
Treatment of laryngotracheitis

It is possible to cope with laryngotracheitis without hospitalization, but only on condition that treatment is started in the early stages of the disease.
Recommendations to be followed:
Stick to bed rest.
Talk as little as possible and strain the inflamed structures.
Drink enough water.
Treat the throat with antiseptic agents.
Auxiliary measures that allow you to speed up recovery include:
Regular ventilation of the room.
Air humidification.
Complete voice rest.
Gargling with medicinal herbs, inhalation with them.
Eating soups, cereals with vegetables and fruits, dairy products. You need to eat in small portions.
Medication
If the disease does not lead to the development of complications, then you can cope with it on an outpatient basis.
Drugs that can be prescribed to the patient:
Antibacterial agents. They are prescribed for developing bronchitis or pneumonia. Most often, drugs with a wide spectrum of action are used: Ciprofloxacin, Suprax, Ampicillin, Azithromycin.
Antipyretics. It is advisable to take them only if the body temperature is very high. You can use preparations containing ibuprofen or paracetamol, such as Nurofen or Panadol.
Antihistamines. They are used to eliminate swelling of tissues. Preference should be given to the latest generation of drugs that have a minimal set of side effects, for example, Cetrin, Zirtek, Zilola.
Sputum thinners (mucolytics) and antitussives. If the sputum is viscous and difficult to separate, then the patient is prescribed mucolytics, for example, Lazolvan or marshmallow syrup. With a dry debilitating cough, the doctor prescribes Stoptussin and Sinekod. They are aimed at suppressing the cough reflex.
Inhalations with mineral water, oil solutions. They can be performed only after the body temperature returns to normal.
Vasoconstrictor drugs: Lazorin, Nazivin. These drugs will restore nasal breathing.
Antiseptics for the throat. They are forbidden to be used during the acute phase of the disease, as they can cause laryngospasm. The most popular drugs include Oracept and Ingalipt.
Antispasmodics. They are prescribed for spasm of the larynx to facilitate breathing. It can be No-shpa and Eufillin.
Immunomodulators: Immunal, Likopid. Their reception is indicated for patients with a chronic form of the disease.
Surgery
In chronic laryngotracheitis, the patient may be referred for surgery. Also, the help of a surgeon is required for people who have not been helped to cope with the problem by drug treatment. Without fail, altered tissues are removed from those patients who have a risk of developing a cancerous tumor. The doctor excised the overgrown tissue of the larynx and vocal cords. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
Modern surgery involves the use of a laser or radio wave equipment. After the operation, the symptoms of the disease become less intense. The recovery period takes about a week. At this time, a person should observe speech peace and not play sports. If there is a risk of thrombosis, surgery is not performed.









