In line with its mission, the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony makes every effort to provide reliable medical content supported by the latest scientific knowledge. The additional flag “Checked Content” indicates that the article has been reviewed by or written directly by a physician. This two-step verification: a medical journalist and a doctor allows us to provide the highest quality content in line with current medical knowledge.
Our commitment in this area has been appreciated, among others, by by the Association of Journalists for Health, which awarded the Editorial Board of MedTvoiLokony with the honorary title of the Great Educator.
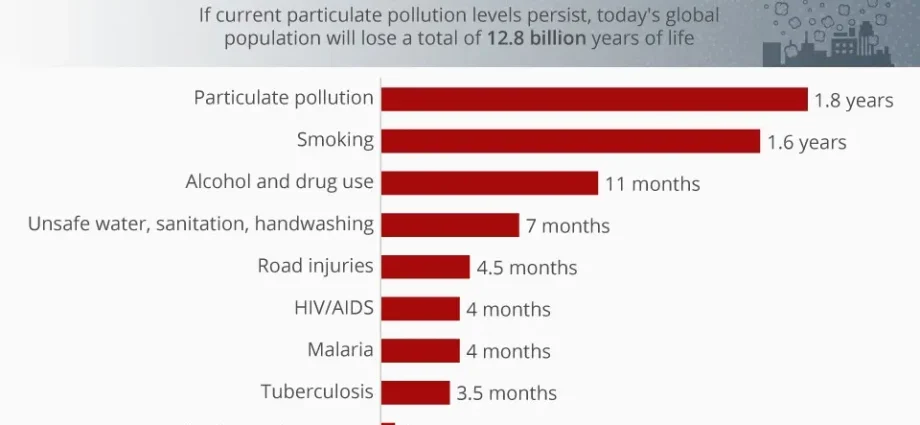
Almost everyone has heard that smog contributes to lung diseases and cardiovascular diseases. Unfortunately, few people realize that poor air quality in our homes can also have fatal consequences for health. Do we live shorter lives due to smog? What can each of us do to breathe better air? We asked prof. dr hab. n. med. Barbara Nieradko-Iwanicka from the Medical University of Lublin, who studies how air pollution affects health.
- – It is estimated that the number of COVID-19 cases increases by 100% when the concentration of dust pollution increases by 20%. – says prof. Nieadko-Iwanicka
- High concentrations of dust are present wherever solid fuel stoves and stoves are used, including indoors
- The scientist also talks about the “sick building syndrome”, which consists of malaise, headaches, respiratory infections. This is because windows cannot be opened in many places
- On November 14, we celebrated Clean Air Day. This article was published as part of the TvoiLokony and Airly #OddychajPolsko campaign, which aims to spread knowledge about the problem of smog in Poland
- You can find more such texts on the TvoiLokony home page
Sylwia Stachura, Medonet: You analyzed the influence of air pollution on life expectancy. How many years can breathing bad air shorten our lives?
Prof. dr hab. n. med. Barbara Nieradko-Iwanicka, Chair and Department of Hygiene, Medical University of Lublin: According to the data of the Central Statistical Office, in 2017, the average life expectancy for men was 74,0 years and for women 81,8 years. Breathing polluted air and smoking can shorten life expectancy. The risk of cardiovascular and respiratory diseases increases. Scientific research shows that quitting smoking and improving the quality of the air you breathe in can extend your life by an average of 8 years.
It’s a lot.
Making people aware of this fact, campaigns to encourage air quality, smoking cessation, and undergoing diagnostic tests and treatment also have a huge impact on survival time. This is evidenced by the statistical data: the life expectancy of the inhabitants of Poland has been systematically increasing after 1991 and by 2017 it had increased for men by 8,1 years, and for women by 6,5 years.
- READ: Minister of Climate: a civilization challenge ahead [INTERVIEW]
Recently, at the Department and Institute of Hygiene of the Medical University of Lublin, the doctoral student conducted research on the health effects of air pollution in Lublin. She found a significant increase in air dust pollution from mid-October to the end of the heating season. A negative correlation was observed between air temperature and dust concentrations (i.e. the colder, the greater the dustiness due to the combustion of solid fuels). However, she noted a positive correlation between air humidity and the number of hospitalizations due to exacerbation of lung diseases. This means that in the autumn and winter period, patients were hospitalized more often due to the exacerbation of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Both women and men were significantly more likely to be hospitalized due to exacerbations of heart disease than due to lung disease.
Can it be said that due to air pollution, people die prematurely?
According to the report “The health situation of the Polish population and its conditions”, edited by Bogdan Wojtyniak and Paweł Goryński published by the National Institute of Public Health – National Institute of Hygiene in Warsaw in 2018, the number of premature deaths resulting from short-term exposure to PM2,5 in 12 agglomerations and The 14 largest Polish cities in 2005-2017 is on average less than 4 in year.
In situations of smog episodes that last longer than a few days in winter, one should expect an increase in the number of deaths per month at the level of over 2. additional cases nationwide.
Scientists have also already noticed a link between air pollution and the risk of infection with the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. What is the relationship?
In the current situation, it is estimated that the number of COVID-19 cases increases by 100%, while the concentration of dust pollution increases by 20%. Increased air humidity also promotes longer survival of viruses in water droplets from nasal or mouth discharge, carried by air currents when sneezing and coughing.
- Editors recommend: Pulmonologist explains how smog affects the risk of coronavirus infection
There is a lot of talk about smog and air pollution, but in the scientific research you co-authored, it was pointed out that the air in homes and offices can also be contaminated.
We spend 90% in closed rooms. our life, that is, a woman 73,62 years, and a man 66,6 years. Often we cannot (or do not want to) ventilate them. It is not always possible to install air purifiers, even air conditioning systems cannot clean this air.
What pollutants are most common in indoor air?
Indoor air (in buildings) contains most of the same components as outdoor (atmospheric) air, i.e. 78%. nitrogen and 21 percent. oxygen. However, in the composition of the remaining 1 percent. there can be big differences.
Outside, it is 0,03-0,04 percent. carbon dioxide (correct chemical name: carbon monoxide IV), water vapor and noble gases. There may be pollen of plants, regional volcanic ash, particles of sand. Due to human activity, the content of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increases, as do oxides of nitrogen, sulfur, ozone and dust with a diameter of 2,5 and 10 micrometers (PM2,5, PM10).
Internal air, according to Pttenkoffer’s standard, may contain up to 0,1%. carbon dioxide.
In addition, it can contain vapors of paints, adhesives, solvents, pesticides used to protect carpets and upholstery against pests, and in old buildings, crumbling paint contains lead (fortunately, modern paints do not contain lead).
House dust is also collected in the rooms, including animal hair, flaky skin of people and pets, dust from clothes, bedding, wall paint crumbs, mites and fungal spores.
Carbon monoxide may also be present in the rooms.
Wherever combustion takes place: in gas stoves, hot water stoves, fireplaces, kitchens and solid fuel stoves, carbon monoxide (carbon monoxide II) can be produced in case of insufficient ventilation. It is a very toxic gas. At a concentration of 1 percent. several breaths in the air may be fatal. Exposure to even traces of it can cause headaches, memory loss and symptoms suggesting heart disease. This is due to the hypoxia of the most important organs: the brain and the heart. Therefore, it is worth investing in a carbon monoxide detector that effectively warns you with a loud sound signal when this gas is detected in the room.
High concentrations of dust are present wherever solid fuel stoves and stoves are used, including indoors. It has been proven that in poor regions of the world where open hearths are used, these pollutants cause changes in the structure of the lungs, temporary and permanent disruption of breathing, and premature death, especially in women who prepare meals.
What ailments may indicate that the air in the home or office is harmful to us? What should be worrying?
Sometimes sick building syndrome is diagnosed, which consists of malaise, headaches, respiratory tract infections. This is due to the fact that in many places it is impossible to open the windows and you breathe dry air, circulating in closed rooms.
People who often fly on airplanes, where dry, artificially heated air circulates, feel similarly badly. They suffer from dry eyes, mouth and skin.
Do we make mistakes ourselves that make the air in our homes harmful to us?
It happens that we move too quickly into newly built flats or premises after renovation without sufficient ventilation. Not all floors are wet. Remember that this method removes most of the dust falling to the floor. Vacuuming and dry sweeping make the dust fall under the force of gravity again.
The use of air fresheners can have a negative impact on air quality. It is not advisable if we have a person with asthma or an allergy to inhaled allergens at home.
What else?
Remember that bedding is home to mites that feed on feathers and flaky skin of the household members. That is why it is worth changing bedding regularly and in the case of allergy sufferers use only synthetic (washable) fillings for pillows and quilts.
On sunny, dry and frosty days, it is advisable to hang bedding outside. Low temperatures and ultraviolet sunlight reduce the number of bacteria and mites in bedding.
Carpets and rugs are also a reservoir of dust and mites. In addition, the new ones are soaked in pyrethroids. They are insecticides used to prevent the development of insects and arachnids in these products. People also inhale them.
- See also: How to get rid of dust mites?
What can all of us do to improve the air quality at home?
I encourage you to open your windows, as long as the air outside the building is clean. If we cannot ventilate, it is worth taking care of the proper functioning of ventilation systems (both gravity ones, i.e. grilles in the walls of buildings, and air conditioning systems). The chimney sweep, in addition to cleaning the smoke exhaust pipes, can check the airflow of the ventilation ducts. It is also worth disinfecting air conditioning systems in cars. They may contain the dangerous Legionella bacteria.
Is it true that plants help filter the air in our homes?
It is worth growing plants in your apartments that remove air pollutants. According to scientists, there should be at least one plant per ten square meters of an apartment.
A list of 18 plants has been compiled that have a beneficial effect on indoor air quality. These are: anthurium, aglaonema, ivy, multiflorous chrysanthemum, dieffenbachia, low date palm, inverted dracaena, epipremnum, ficus, gerbera, croton, liripe, nephrolepis, pteroflower, sansevieria, phoenix, herbaceous, ginine rapis and sensewiria.
- READ ALSO: «Since March, we have lived in one plague. Now we’re facing three ». A pulmonologist explains how smog affects the risk of COVID-19
A graduate of the Medical Academy in Lublin. Employee of the Chair and Department of Hygiene at the Medical University of Lublin. Internal medicine specialist, rheumatologist, science promoter
This may interest you:
- How does smog kill?
- Smog destroys not only the lungs. Here’s how it affects the body
- Every year it kills 45. Poles
The content of the medTvoiLokony website is intended to improve, not replace, the contact between the Website User and their doctor. The website is intended for informational and educational purposes only. Before following the specialist knowledge, in particular medical advice, contained on our Website, you must consult a doctor. The Administrator does not bear any consequences resulting from the use of information contained on the Website. Do you need a medical consultation or an e-prescription? Go to halodoctor.pl, where you will get online help – quickly, safely and without leaving your home.