Contents
Innovation is usually seen as the key to solving environmental problems. At the same time, it remains behind the scenes that many new and seemingly “green” technologies not only solve, but create problems that the planet suffers from.
Bulat Kaliev, Sustainability Services Group Manager, Deloitte CIS:
“At first glance, IT companies and data centers produce few emissions, but this is not the case. Back in 2016, it was reported that the world’s data centers in total use more electricity than, for example, the UK generates.
According to forecasts, by 2020 up to 3,5% of carbon dioxide emissions will come from the processing and transmission of information. There are no updated figures, but the forecasts most likely turned out to be correct. We are talking only about direct emissions: the announced data does not take into account the electricity used by IT firms: energy companies most often use non-renewable sources and also pollute the atmosphere.”
Some tech companies are already aware of the problem
Elza Ganeeva, Microsoft Government Relations Manager in our country:
“Scientists distinguish three categories of emissions. And this pattern is observed in most companies.


IT is a sector “where CO2 are getting out of control,” Philippe Zaouati, chief executive officer of Mirova, a large Parisian company, told Bloomberg.
And the problem will get worse as the amount of data that companies store and send increases. At the end of 2018, the American hard drive manufacturer Seagate predicted that by 2030 the global volume of world data would grow more than five times (from 33 to 175 zettabytes, or 175 trillion gigabytes).


By 2025, every person whose devices are connected to the Internet will interact with external data at least once every 17 seconds.
Another example: now data centers consume about 2% of the electricity generated in the world, and by 2030 this figure could reach 8%. According to Hewlett Packard Enterprise, only 6% of the data ever created is used today. Accordingly, 94% of the data is dead weight on servers that consume huge amounts of energy.
“You may be wrong if you think you are completely deleting an email when you empty the trash in an email. Servers all over the world store many copies of ten-year-old and older emails,” says Kirk Bresniker, Hewlett Packard Labs.
“Storing data that we don’t even use is costing us as much as maintaining the entire air transport industry,” said Andrew Choi, senior research analyst at US green investment firm Parnassus Investments.
Cryptocurrency miners consume a huge amount of electricity
Ivan Oseledets, Head of the Scientific Computing Group at the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology:
“The technology itself is designed in such a way that even more calculations are required to produce each new coin, which means that more and more energy is needed. We’re just warming up the planet.
As researchers at the Technical University of Munich have calculated, the electricity consumption and carbon footprint associated with bitcoin alone is comparable to the power consumption and emissions of countries like Jordan and Sri Lanka.”
Cryptocurrencies are considered by many as a whim, in a number of countries their use is generally considered illegal. But there is another technology that is evaluated more positively, but it leads to the same disastrous effect. Scientists from the University of Massachusetts Amherst have calculated that training a single artificial intelligence (AI) model can release as much carbon dioxide as five cars produce during their entire life (including even that CO2that the factories emitted during their production). The same amount of greenhouse gas emissions will be created, for example, by 300 flights from New York to San Francisco and back.
We are talking about teaching AI the ability to recognize human language and compose meaningful phrases in it. This direction is now developing rapidly: thanks to it, Amazon Alexa voice speakers have appeared (according to the company itself, several hundred million units have already been sold by now) and digital assistants like Siri.
Around 2012, the so-called deep learning revolution took place – AI models began to be taught not on processors, but on video cards: due to the architecture of their core, they are better able to cope with the task. Any research group or company could buy 5-10 graphics cards and train models that achieve world-class results. The more data such a model receives, the better the result. Training with the help of video cards made it possible to solve many problems more efficiently: image recognition, face search, machine translation, sound processing, work with medical data, etc.
Companies began to develop AI systems more often for different purposes, and this required more and more computing resources – especially when it was about AI, which, for example, beats a person in Go. It no longer needs ten graphics cards, but thousands. These are huge computing resources that consume a lot of energy and generate a lot of heat.
Artificial intelligence is one of the key technologies of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. As ex-president of Google China Li Kaifu previously predicted in an interview, in the next decade, AI will turn into the new electricity – it will be applied everywhere. According to the research company IDC, in 2023 the total value of AI systems sold in the world will reach $98 billion (compared to $37,5 billion in 2019). The main buyers of such systems will be retail and the banking sector.


Elza Ganeeva, Microsoft Government Relations Manager in our country:
“Companies are putting forward various initiatives to cope with carbon emissions. Microsoft will drastically reduce its own carbon footprint and invest $1 billion in research to help remove carbon from the atmosphere through a new Climate Innovation Fund. By 2030, Microsoft intends to be completely carbon negative (that is, the company’s environmental projects will remove exhaust from the atmosphere faster than the company’s activities will create it. – ), and by 2050, completely eliminate the consequences of emissions since the founding of the company in 1975.
By 2025, Microsoft plans to completely switch to renewable energy sources for all data centers, buildings and campuses and electrify the internal vehicle fleet. To remove its carbon footprint, the company promises to reforest and work on innovative technologies: sequestration (soil carbon capture), bioenergy with carbon sequestration and storage (BECCS), and direct air capture for purification (DAC).”
Bulat Kaliev, Sustainability Services Group Manager, Deloitte CIS:
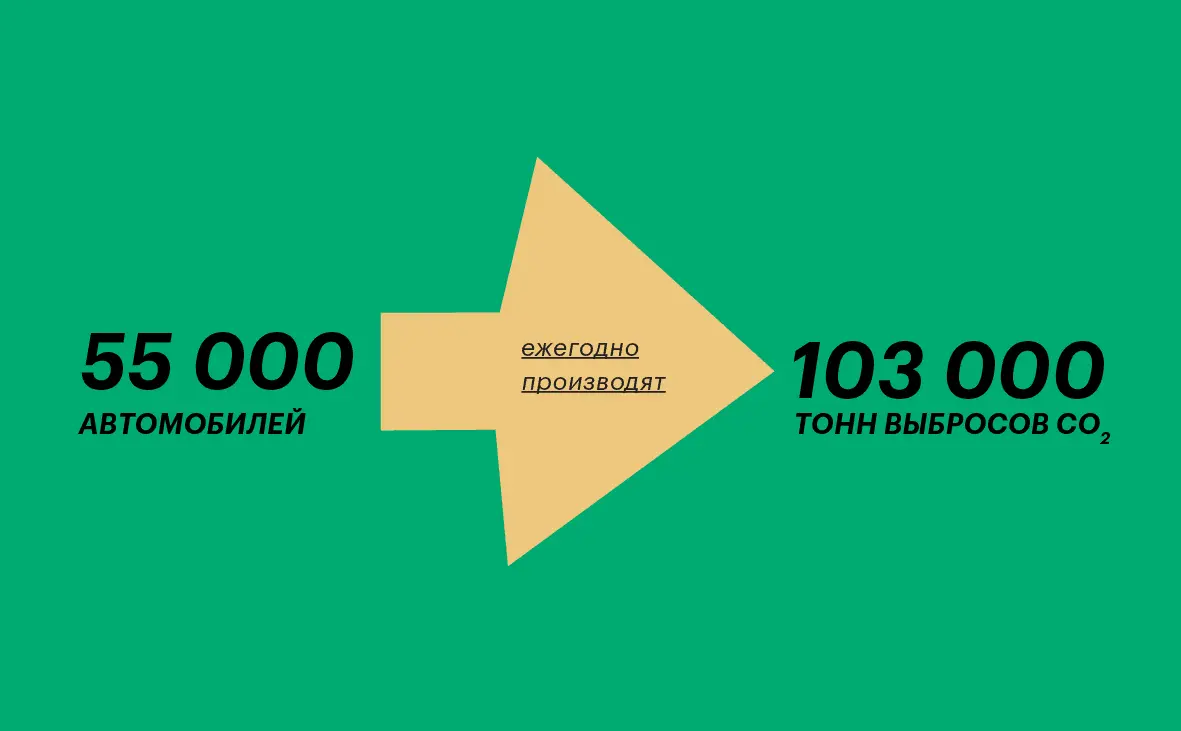
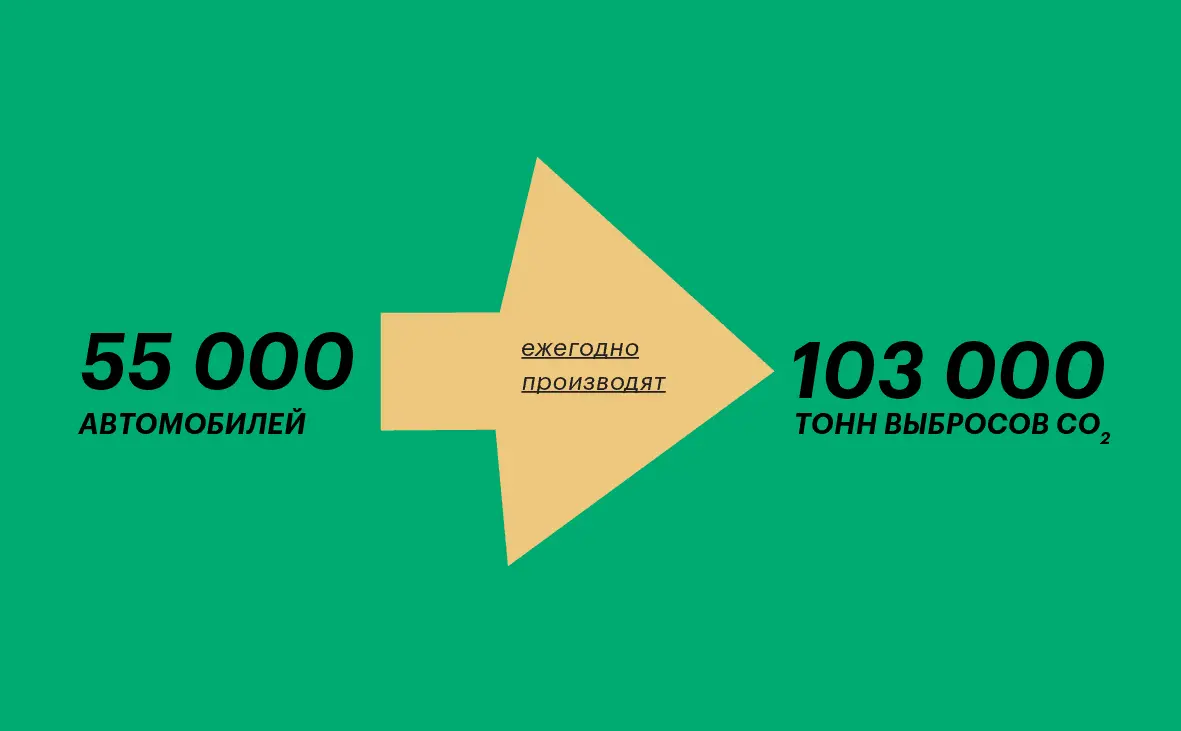
“There are projects to use harm for good. For example, in Finland, the largest data center will heat houses. So they will reduce 103 thousand tons of CO emissions2. The same amount of emissions, according to Fortum itself, is produced annually by 55 cars. The data center plans to heat 25 households.”
Ivan Oseledets, Head of the Scientific Computing Group at the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology:
“To really solve the problem, you need to develop new algorithms and create new computing systems. We will not be able to increase the power of a classical computer in the near future. Moore’s law of constantly increasing the capacity of computer memory elements no longer works. Progress has slowed down. Looking for other possibilities. The solution could be quantum or neuromorphic computers. Research in these areas is underway. There is already a machine that has achieved what is called quantum supremacy: one of the experimental problems can be solved more efficiently on a quantum rather than a classical computer. There is progress, big investments”.
Alexey Fedorov, Head of the Quantum Information Technologies Group of the Russian Quantum Center:
“Solving problems faster than classic supercomputers without multiplying power consumption is not their only benefit. Quantum computers will also be able to help model more energy-efficient materials, which will prove useful for the development of computer technology. So far, there are prototypes of quantum computers with dozens of qubits – elements for storing information (there are about 50 of them in the largest quantum processors). To increase computing power, it is necessary to increase the number of qubits and reduce the level of errors when working with them. The effect of the introduction of quantum computers can become tangible on the horizon of 3–5 years.”
How much does the “Yarovaya package” weigh?
Since July 2018, the Yarovaya Package, a set of laws on combating terrorism and protecting personal data of our country, has been fully operational in our country. Telecom operators must store information about calls, messages and Internet traffic of citizens for three years and provide access to it to law enforcement agencies upon request. In the spring of 2016, when the bill was still under discussion in parliament, experts from the Giprosvyaz Institute (a subsidiary of Rostelecom) calculated that the amount of data stored in accordance with the requirements of the law for three years would exceed 157 exabytes, or 157 billion GB. According to the authors of the report, this is 100 thousand times more than the amount of data on the facts of the provision of services that the operators kept at that time.
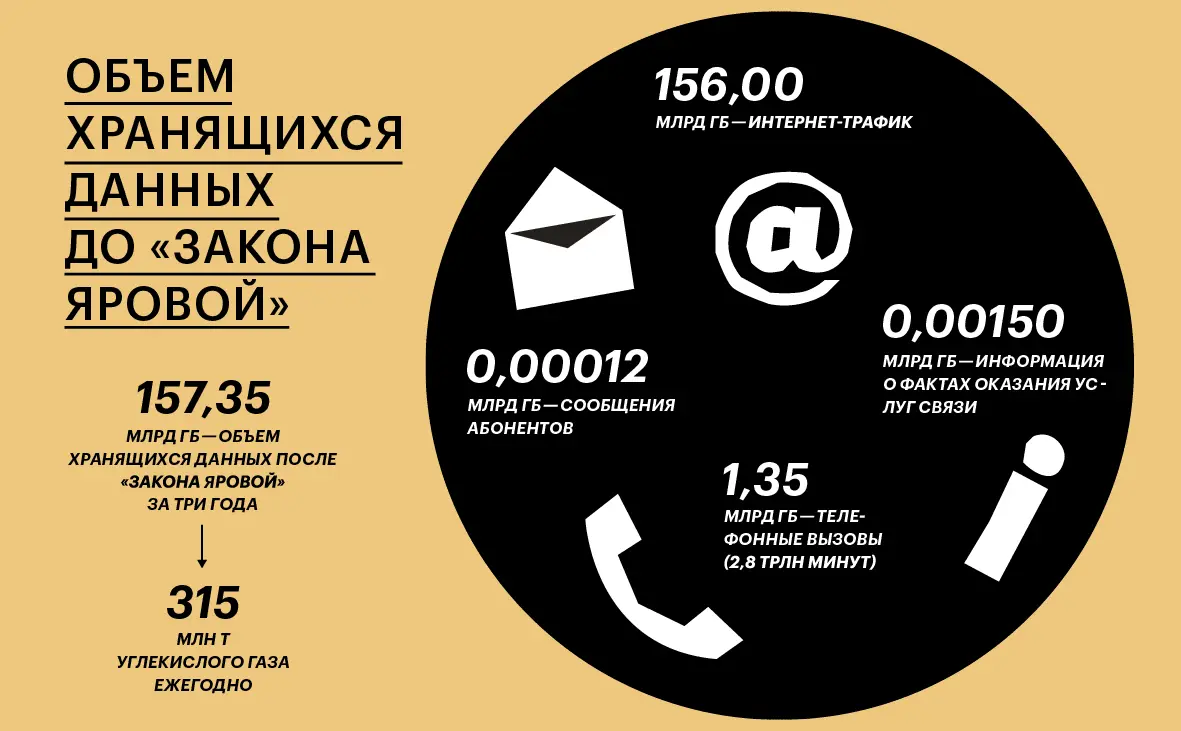
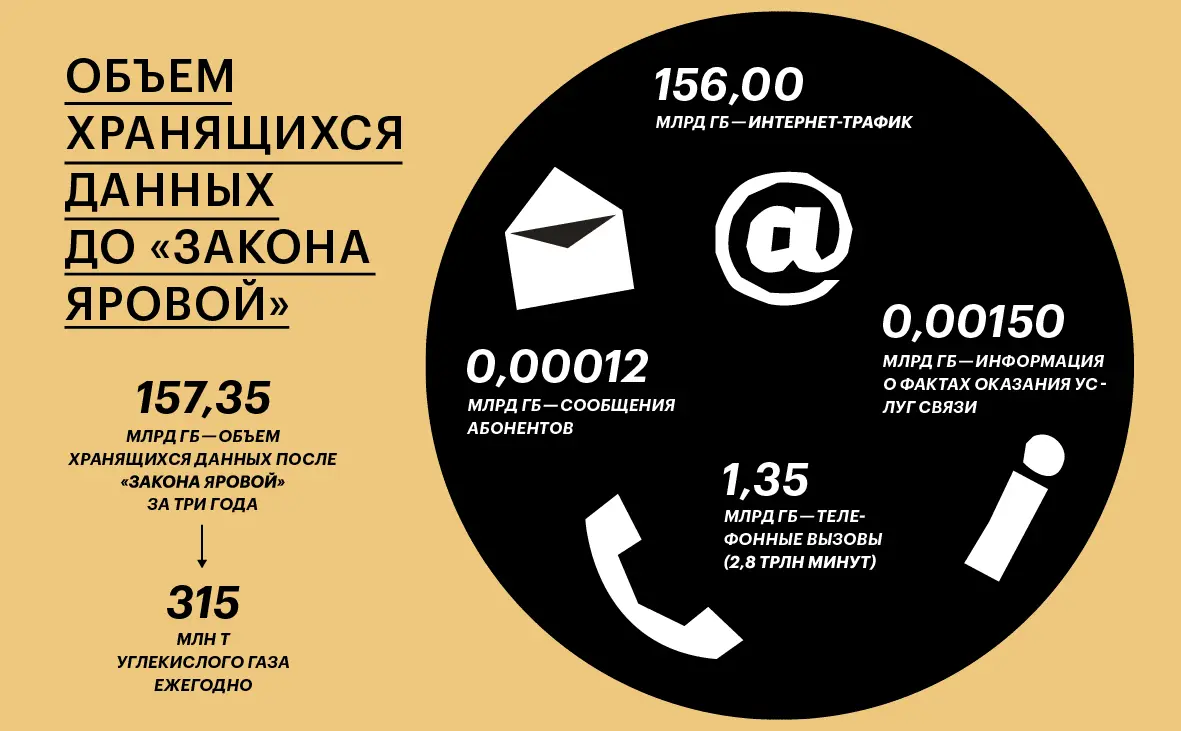
Creating data centers for such volumes of information is not only tens of billions of dollars, but also huge energy costs, and hence carbon dioxide emissions. According to Stanford Magazine, 100 GB of cloud storage is equivalent to 200 kg of CO emissions annually.2. This means that if all 157 billion GB of our country’s data were uploaded to servers, supplying them with electricity would add about 315 million tons of carbon dioxide annually. For comparison: about the same amount of CO2 for 2018 (separately) produced by France, Thailand and Kazakhstan.
Subscribe and follow us on Yandex.Zen — technology, innovation, economics, education and sharing in one channel.










