Contents
- Mechanism of the effects of alcohol on the brain and central nervous system
- The effect of alcohol on parts of the brain
- The effect of alcohol on the central nervous system – stages of intoxication
- Hangover and brain
- How is alcohol addiction formed?
- Symptoms of the destructive effect of alcohol
- Alcohol related brain disease
- Other Effects of Alcohol on the Brain
- Prenatal alcohol exposure
- Does the brain recover after quitting alcohol?
- How to quickly restore the brain after alcohol
- General recommendations
- Latest scientific research
Hello readers! Alcohol is actually a drug that is widely available. Moreover, society – and especially in our country in Mother Russia – is not only loyal to it, but sometimes even imposes its consumption.
And this despite the fact that alcoholic beverages have a detrimental effect on brain cells. Let’s take a closer look at how alcohol affects the brain.
Mechanism of the effects of alcohol on the brain and central nervous system
Ethanol (the main active ingredient in all alcoholic beverages) affects the brain and the nervous system as a whole. Alcohol makes a person temporarily cheerful, carefree and distracted – this effect is explained by an increase in the production of dopamine in the brain.
In addition to the increased work of dopamine receptors, during the period of intoxication, a lot of peptides are released that inhibit brain activity and negatively affect the central nervous system.

The constant use of alcohol, albeit moderate, inhibits the activity of neurons. This is manifested by a decrease in the sharpness of mental activity, it becomes difficult to remember facts and even names. Often in chronic alcoholics under the influence of alcohol, concentration is disturbed.
Long-term use of alcoholic beverages affects not only mental activity, but also health in general. People who drink alcohol often die from a stroke or heart attack – local hemorrhages, accompanied by necrosis of the brain and heart muscle.
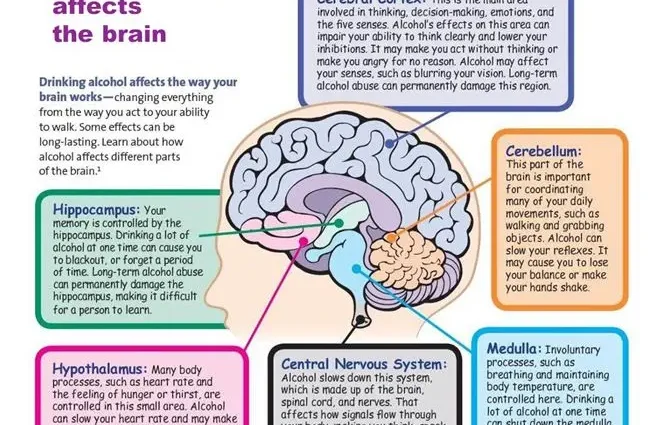
The effect of alcohol on parts of the brain
Alcoholic drinks affect, though different parts of the brain, but equally detrimental. Let’s look at exactly what damage they cause.
mesolimbic pathway
The mesolimbic pathway contains areas responsible for feelings of pleasure, deep satisfaction, and happiness. Drinking alcohol depresses the activity of these receptors in the brain.
A person under the influence of booze literally becomes dumber for a while, less coordinated and more unhappy.
Hippocampus
The section of the hippocampus in the brain is responsible for memory and the formation of correct memories. If it is damaged, and this is inevitable as a result of prolonged use of alcohol, there is a chance to permanently lose the correct perception of space and the ability to control your memories.

The regeneration of brain cells under the constant influence of alcohol will also stop. This is how alcohol adversely affects cognitive functions.
Cortex
The cerebral cortex is a kind of crown of the whole organ, and alcohol also affects it in a far from good way. A person’s ability to analyze deteriorates, the reaction slows down, a feeling of false freedom appears, but is it worth saying that this is just a short-term illusion born under the influence of a green serpent?
Frontal left and prefrontal cortex
These parts of the brain consist of a large number of neurons, extensive neural networks are located here. Alcohol negatively affects them and hits the structure of neurons, which causes structural failures in the brain.

Outwardly, this is manifested by behavioral disorders at the level of reaction and will. Alcoholics often become lethargic, lack goals and motivation in life, become depressed, and fall under the influence of bad company.
The pituitary and hypothalamus
These two sections of the brain are responsible for the production of hormones. For the body, they are no less important than, for example, the thyroid gland. Alcohol damages them, causing irreversible changes – some hormones either cease to be produced in the required amount, or too much of them is thrown out.
Cerebellum
The cerebellum influences the motor activity of the body and regulates blood flow. Regular drinking of alcohol can lead to partial or complete loss of coordination in space, strokes.
Amygdala
The amygdala in the brain is responsible for the emotional component in the body. Thanks to him, we are able to feel a sense of impending danger, thereby gaining time to make the necessary decision.

Alcohol negatively affects these receptors, and a person becomes fearless, as a result of which he can commit many bad and thoughtless acts, for which he will then have to bear responsibility (at least blush).
Medulla
Alcohol, affecting the medulla oblongata, worsens the processes of blood circulation and respiration. For this reason, a drunk often wants to sleep, he feels seriously tired.
This effect of alcohol on the brain is very dangerous, because it can easily provoke respiratory depression. There is a real opportunity to die under the influence of a drunken frenzy from an overdose of ethyl alcohol.
The effect of alcohol on the central nervous system – stages of intoxication
Alcohol intoxication according to the degree of influence on the body can be mild, moderate and severe:
- If the level of ethanol in the blood does not exceed 0,05-0,20 / 00, then we are talking about a subclinical, mild stage. It has no visual effect and appears when a person is already sober. However, alcohol already has a noticeable effect on the brain, inhibiting the processes in the central nervous system. It is already destroying neurons and the connections between them. A person usually does not smell of alcohol, although the tester is able to determine a low level of ethanol in the blood.
- The hypomanic phase (moderate intoxication) occurs when a person has drunk a total of 50-150 ml of alcohol, if we are talking about strong drinks with a powerful effect, for example, vodka, or several liters of beer. There is a noticeable motor-motor excitation, an aggressive state, emotional instability. At this stage, the brain already ceases to function properly – it begins to give false signals to the receptors. The reaction is dulled, the coordination of movements when walking is disturbed.
- A severe degree of alcohol influence on the brain is characterized by severe intoxication of the whole organism. Consciousness is clouded, the drinker feels muscle hypotension. Motor activity is practically reduced to nothing – most often a person falls, crawls, stumbles, performing chaotic, incoherent movements with his hands and feet. This is a typical effect of ethyl alcohol on the body. Speech is difficult, the drunk is not able to pronounce articulate words.

If a lethal dose of alcohol was taken, then its consequences will be appropriate: a person will fall under the action of a hypertoxic phase, which is characterized by massive damage to the bulbar centers and general intoxication of the brain. In this state, a coma quickly develops, then death occurs from respiratory arrest.
Dopamine
Analyzing each phase in a little more detail, you should start with dopamine. It is characterized by a sharp improvement in mood, which is caused by drinking alcohol, the amount of which is still small. This phase does not last so long and is quickly replaced by the next.
AMC stage
Arteriomesenteric compression is the stage following the dopamine one. To achieve it, you need to drink more alcohol. The effect on the brain here is much more pronounced – depression of the central nervous system, cardiovascular and motor systems begins.
The person may experience dizziness, nausea, and diarrhea.
strong stage
A strong stage of alcoholic intoxication is characterized by a pre-coma state, when a person, due to the influence of alcohol on the brain, is no longer able to report on his actions. At this stage, he is driven mainly by reflexes, and critical thinking is not discussed at all.

This condition can be extremely dangerous, if possible, it is necessary to provide first aid to the drunk – to be taken to the hospital in order to minimize the harmful effects of ethanol and, possibly, save a life.
Hangover and brain
After drinking a lot of alcohol, a hangover inevitably comes in the morning. It occurs for the reason that ethanol, having damaged brain cells and having a negative effect on the central nervous system, breaks down and is excreted from the body.
Common hangover symptoms include:
- headache;
- nausea;
- abdominal pain;
- spasm of blood vessels;
- high or low pressure.

Alcohol also affects the liver, having a hepatoxic effect, so it is possible that there will be a feeling of bitterness in the mouth and pain in the right hypochondrium. This is caused by acetaldehyde, a substance that appears during the breakdown of ethanol.
A man suffers a hangover harder than a woman.
How is alcohol addiction formed?
Dependence on the influence of alcohol is formed gradually in several stages. At first, a person simply begins to systematically consume alcohol. The turning point is the moment when the withdrawal syndrome occurs – the alcoholic becomes physically ill without a dose of alcohol.
At this stage, internal organs are irreversibly damaged: the heart, liver, kidneys, brain. If you do not have time to help the alcoholic at this stage of the disease, then the addiction will become chronic. It is almost impossible to get rid of not on your own without extraneous influence.

At this stage, in addition to brain damage, cirrhosis of the liver can begin. She will cease to cope with her work, and hepatocytes are reborn into fibrous or adipose tissue. Some people believe that if you “snack” alcohol, then nothing will happen.
To do this, they recommend fatty foods, such as lard. This is a big misconception. The influence of alcohol occurs at the level of tissues and cells. This is too complex a process to be controlled by food.
Symptoms of the destructive effect of alcohol
Alcohol is extremely detrimental to the brain, and the whole body as a whole:
- A person suffering from alcoholism loses the ability to think adequately, brain neurons are gradually destroyed, and the personality degrades. Problems also begin at the level of peripheral nerves – trembling hands, sweating, loss of sensation in the limbs – all these are the “first” signs of irreversible brain damage.
- An alcoholic has a need for constant use of doping – this greatly affects his character. He can become withdrawn, aggressive, quick-tempered. There are problems in communicating with others – a person can steal, lie, go to blackmail or cause physical injury.
- Alcoholics have a high risk of developing a variety of diseases – problems can begin with the heart, blood vessels, liver or stomach. Due to the influence of alcohol, an oncological disease can occur – alcohol is the main risk factor for developing cancer of the esophagus, stomach, intestines (all departments), pancreas and mammary glands.

The main symptom of alcoholism is obsessive thoughts about drinking. Under their influence, you can do something strange for others – get drunk in the middle of a working day or pawn an engagement ring in a pawnshop.
So, we found out that the constant use of alcohol adversely affects the brain. For example, after a year of regular drinking, a person is diagnosed with alcoholic encephalopathy. Among the main symptoms:
- headache;
- asthenia;
- fatigue;
- sleep deprivation;
- trembling in limbs;
- fluctuating blood pressure.

The disease has a serious impact on the cognitive abilities of a person, depriving him of independence and self-sufficiency.
Other Effects of Alcohol on the Brain
Alcohol literally “smoothes” the brain convolutions, which leads to a decrease in the overall level of intelligence. But this will take years.
With the systematic consumption of alcoholic beverages, there is a high chance of cerebral hemorrhage. But this can lead to dire consequences up to paralysis and death.
Atrophy
Brain atrophy is the most common alcohol-related disease. This condition is also called alcoholic encephalopathy and has been discussed in more detail above. The reason is also ethanol, which affects the brain, its effect is really detrimental.
Wernicke-Korsakov syndrome
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome (abbreviated as WKS) is a complex disease that is characterized by a constant deterioration in the state of neurons, their gradual degradation due to the toxic effects of alcohol breakdown products.

The disease develops not so much because of the direct effect of alcohol on the brain, but because of a critical deficiency of certain B vitamins (primarily thiamine). It is customary to distinguish between several forms of the syndrome – chronic, residual and acute.
An alcoholic will experience many unpleasant symptoms:
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- fatigue;
- clouding of consciousness;
- visual disturbances.
Psychopathic states and motor seizures will begin.
It is difficult to treat CRS; an integrated approach is used. To accurately diagnose the syndrome, an MRI of the brain is performed.
Problems of neurogenesis
Neurogenesis is the regeneration and creation of neurons in the brain. As mentioned earlier, alcohol is the main provocateur and catalyst for their decay. It turns out that drinking alcohol entails problems with both the creation of new cells and neural connections, and the destruction of existing ones.
Because of this influence, health and mental status problems are snowballing.
Prenatal alcohol exposure
Alcohol is evil, which we have already figured out, but how much can it harm expectant mothers and what effect can it have on the fetus? And it can be colossal – in newborns whose parents abused alcohol, there are:
- heart defects;
- congenital anomalies of development, including genetic ones;
- hernia;
- epilepsy;
- underweight and IUGR (intrauterine growth retardation).

Drinking alcohol during pregnancy is strictly prohibited, because it threatens the fetus with fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS for short), because of which the child will have problems with cognitive and mental activity.
The child will be significantly behind in development from their peers and will not be able to fully integrate into the team. Due to FAS, not only the central nervous system suffers, but also facial features. Children with congenital alcohol syndrome, even in appearance, differ from healthy babies.
Does the brain recover after quitting alcohol?
Yes, the restoration of brain activity is quite real, but with some reservations. If an alcoholic has successfully “tied up” in the early stages, then there should not be critically irreversible consequences. The brain, of course, will not recover in full, but the remaining neurons will be enough for a normal life.
But if alcoholism has gone far, then the changes will be irreversible. A person, of course, will be able to live for a long time if he completely refuses alcohol, however, a powerful blow will be dealt to the nervous system.

A former alcoholic will need the help of neurologists and psychiatrists, and cognitive abilities will not be restored, unfortunately, never even under the influence of powerful psychotropic drugs.
How to quickly restore the brain after alcohol
Recovery of the brain from the effects of alcohol will depend on many factors. The most important thing is how many people have been under the influence of alcohol addiction. If the period is relatively short, then it will be possible to recover quickly. However, if a person goes into hard drinking for many years, then the situation is much more complicated.
The main factor in recovery is the complete rejection of alcohol!
General recommendations
I strongly do not recommend anyone to drink. As we found out in this article, this will not lead to anything good – believe me, the influence of ethyl alcohol is very large. If you or your loved one is addicted, do not hesitate to seek professional medical help.
Keeping falling into this abyss is not an option at all. The combination of alcohol with other neurotropic substances: energy drinks, cigarettes, drugs is also unacceptable. The harm from the negative influence will be increased many times over.
Latest scientific research
Many still believe that drinking in “moderate amounts” is not dangerous. I hasten to upset: it threatens and how.
In 2018, American scientists from the US Institute for Health Assessment analyzed several groups of people who drank alcohol. One group drank a small amount, and the other was made up of real alcoholics.
The negative consequences of alcoholism and the severity of diseases grew in accordance with the amount of alcohol consumed. Yes, in the case of the first group, the process of personality disintegration was much slower, but there was no talk of a positive or neutral effect of alcohol on the body.
Thank you for reading to the end. If you have a friend to hint that it’s time to tie, then share this article on social networks. Maybe this will be the saving straw?