Contents
Breeders have cultivated many wild plants so that gardeners have the opportunity to grow them on their site. One of these representatives is the forest beauty honeysuckle. The berry is saturated with trace elements and vitamins useful for humans. Among the many bred varieties, Kamchadalka stands out.
Inference history

The culture was bred by employees of the Siberian gardening at the Bakcharsky stronghold. The parent of the variety is the wild Kamchatka honeysuckle. The authors of Kamchadalka are breeders A. T. Tkacheva and I. K. Gidzyuk. The culture was bred by natural pollination of the wild form of the plant. The variety was sent for testing in 1984, and after 9 years honeysuckle was zoned in the regions.
Description and characteristics of the variety

In terms of ripening, honeysuckle of the Kamchadalka variety is considered a mid-ripening crop. The form of the plant is a shrub. Active fruiting usually begins 3 or 4 years after planting the seedling.

The bush of Kamchadalka brings berries of large and medium sizes. The length of the fruit varies from 2,2 to 2,7 cm. In diameter, the berry reaches 1 cm. The fruits are elongated oval in shape, tapering towards the top. The skin is smooth, strong, blue. Superficial white bloom gives the berry a light blue tint.
The pulp of Kamchadalka honeysuckle consists of many fibers, but they are not felt when chewing the fruit. The taste of the berry is sweet and sour with a pronounced forest aroma.
The composition of the berry includes:
- dry matter – no more than 14,2%;
- acid – from 2,5 to 2,6%;
- sugar – from 5,4 to 7,9%.
Additionally, 100 g of pulp contains 52 mg of vitamin C, as well as up to 40 mg of vitamin B1. The berries of Kamchadalka are saturated with minerals that help strengthen blood vessels. Fruits for medicinal purposes are used by people with high blood pressure. In folk medicine, honeysuckle is known as a tonic and diuretic.
The inflorescences of Kamchadalka consist of two small flowers with yellow petals. Flowering time lasts only one day. The bush of Kamchadalka is not sprawling of medium height. The dense crown forms the shape of a cone. The height of an adult bush is about 1,5 m. Young shoots are short and rather powerful green. The leaf shape is an elongated oval. Leaf color is pale green.
The video provides an overview of the Kamchadalka honeysuckle variety:
Pollinators
Cultural honeysuckle turned out to be self-fertile. In order for the bush to give birth, pollinators of other varieties are planted nearby. Great for:
- Parabelskaya;
- Cinderella;
- In memory of Gidzyuk;
- X.
A good pollinator variety is Roxana, as well as Tomichka. From the reviews of gardeners, good fruiting of Kamchadalka is observed if the Blue Spindle honeysuckle bush grows nearby.
Features of fruiting

Ripening of Kamchadalka berries begins in the third decade of June. The yield from one adult bush does not exceed 1,2–1,8 kg. Occasionally, a well-developed bush can bring up to 3,5 kg of fruit. The harvest of Kamchadalka lends itself to long-term storage. By destination, the berries are universal. Fruits are eaten fresh, jam, wine, juice are prepared, frozen.
A feature of the fruiting varieties of Kamchadalka is the uneven ripening of berries. Harvesting has to be done 2-3 times. Productivity does not depend on weather conditions. The bush will stably disfigure cold, hot and rainy summers.
Problems with the cultivation of the Kamchadalka variety are observed only among residents of the southern regions. The warm climate creates favorable conditions for repeated autumn flowering. Berries often have time to ripen before the onset of cold weather, but the quality of bud formation for the next season is greatly deteriorating. The second problem is winter thaws in the southern regions. Kamchadalka quickly reacts to the appearance of heat by awakening buds. The severe frosts that hit in a couple of days supercool the planted fruit buds, and in the summer the bush may not spoil at all.
Advantages and disadvantages

The variety of honeysuckle Kamchadalka is positively appreciated more by residents of cold regions, as an unpretentious and disease-resistant plant that brings tasty berries.
The following points are distinguished from the advantages of Kamchadalka:
- frost resistance;
- large fruits that do not crumble from the bush in a mature state;
- decorative bush;
- ripe berries do not fade, remaining juicy and fresh.
The disadvantage of the Kamchadalka variety is the average yield, uneven ripening of berries. From the stalks, the fruits come off badly. Pollination in inclement weather is of poor quality, due to which the yield is reduced. In the reviews there are tips from gardeners, which talk about the need to plant an X-honeysuckle bush almost right next to Kamchadalka.
Secrets of cultivation
Growing honeysuckle on your site is no more difficult than currants, but there are features and they need to be taken into account.
Terms of planting
You can plant honeysuckle seedlings in spring and autumn. However, Kamchadalka is characterized by early bud break. Autumn is still considered the optimal landing time, when the plant is in dormant stage. In the south, the planting of Kamchadalka begins in the third decade of September and ends in October. Gardeners in the northern regions individually determine the timing. It is optimal to plant a seedling of Kamchadalka 2-3 weeks before the onset of frost.
Site and soil selection

Variety Kamchadalka does not tolerate temperature fluctuations. Honeysuckle is best grown in areas where a temperate climate prevails. Bushes are planted in a bright area where the sun’s rays fall during the day. It is advisable to make protection from the wind by planting a plant near the fence or surrounding it with other berry bushes.
Kamchadalka is not suitable for a hill with dry soil. The bush may not bloom, but will constantly increase side shoots and foliage. Lowlands are optimally suited for the Kamchadalka variety, but the height of groundwater should not exceed 1 m from the surface of the earth.
The optimal indicator of soil acidity is from 5,5 to 6,5. If the soil is highly acidic, 30 days before planting the seedling, 200 g of chalk or lime is applied per 1 m2 plot.
Bush planting

Planting of honeysuckle seedlings of the Kamchadalka variety is carried out in the following order:
- The hole is dug at least 5 days before planting the seedling. Since one bush cannot bear fruit, at least three honeysuckles are located on the site nearby. A span of 2 m is made between the holes for each seedling. The depth and width of each hole is 40 cm.
- The bottom of the holes is covered with a drainage layer of fine stone or broken brick.
- Part of the hole is covered with black soil mixed with an equal amount of compost. About 1 kg of wood ash is added to the mixture. From mineral fertilizers, 50 g of superphosphate is mixed. If the soil is sandy, then larger holes are dug to fit a mixture of two buckets of black soil and three buckets of compost. 1 m2 plot even when digging, you can add 5 kg of clay.
- The hole filled with the mixture is abundantly filled with water.
- Before planting honeysuckle at the bottom of the hole, a hill is formed from the soil. The seedling is carefully placed on a hill, the root system is straightened along the slopes, covered with loose soil. The root neck cannot be buried. After backfilling, the honeysuckle seedling is watered with water at room temperature. When the soil settles, they make an addition, another watering and backfilling with mulch.
Immediately after planting, the Kamchadalka honeysuckle seedling is not pruned. The shrub can slow down in growth and throw out inflorescences. Only damaged shoots can be removed.
Care
You can get a good harvest of honeysuckle only by providing the shrub with proper care.
Watering

The first-year honeysuckle seedling Kamchadalka is watered regularly as the soil dries. The bush should take root well. Adult honeysuckle is watered a maximum of three times a month. The only exception is drought.
Additional fertilizing

Honeysuckle has enough organic matter for good development and fruiting. In the spring, the bush is fed by adding 1 bucket of humus. In autumn, 150 g of wood ash is added. From mineral dressings, nitrogen-containing preparations are used in early spring. During the melting of snow, honeysuckle is watered with 1 bucket of water, where 1 tbsp is dissolved. l. urea. Before flowering, foliar top dressing with the drug Mortar or Aquarin is useful.
Trimming
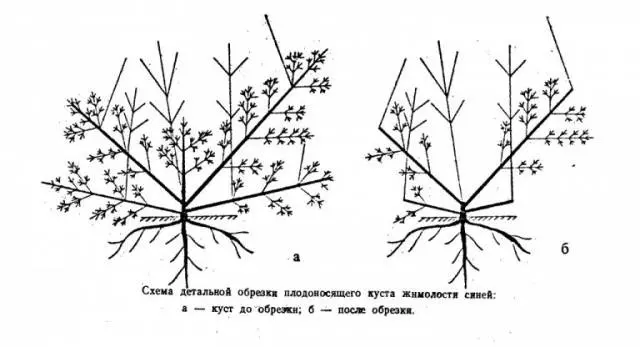
Pruned honeysuckle bushes in the fall after a complete drop of foliage. Adult plants are subject to pruning, starting from the sixth year of life. The first step is to remove all root shoots. Thick shoots with numerous flower buds are left on the bush. Cut only thin, damaged and elongated branches. A second pruning may be needed in the summer if diseased shoots with darkened foliage and dry flowers appear.
Protection against diseases and pests

Frost-resistant honeysuckle Kamchadalka is resistant to diseases. The main pests are aphids, as well as honeysuckle fly. Spraying insecticide helps to fight harmful insects. Rarely, foliage is affected by a fungal infection, as evidenced by dark spots on the foliage. A fungicide will come to the rescue, you just need to choose a drug that will have time to neutralize before the start of harvesting.
Blue honeysuckle berries often attract birds. Protect the crop from feathered guests with nets. The bush is covered as soon as the fruits begin to turn blue.
Reproduction

Honeysuckle is propagated by seedlings. During the purchase, it is optimal to give preference to the bushes of the second year of life. Such a honeysuckle seedling can be identified by a crown height of 30–40 cm and the presence of 2–3 branches.
The branches of a healthy seedling are flexible. Shoots should not be dried, but the bark can peel off. This is fine. For honeysuckle, peeling of the bark is considered a feature of the plant. Live buds must be present on the branches. A good honeysuckle seedling always has a developed root system.
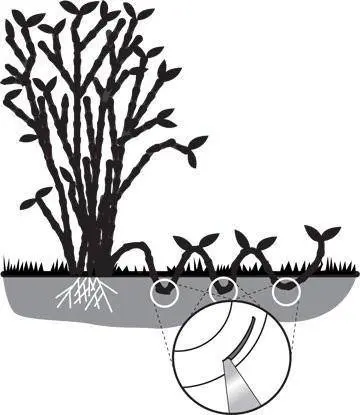
Gardeners independently propagate honeysuckle by layering if adult bushes are already growing on the site. It is enough to sprinkle part of the branch with moist soil and make an incision in the bark. When the cutting takes root, it is cut off from the mother bush, and a new seedling is obtained.
Conclusion

Honeysuckle Kamchadalka will truly please with a bountiful harvest, subject to the cultivation technology. It is better for residents of the southern regions to find other varieties, since the Siberian beauty may not live up to expectations in an unacceptable climate for her.









