Contents
Planting and caring for honeysuckle in the Leningrad region are practically no different from the procedures carried out in other regions. However, there are small nuances, and they are associated with a cool climate. Here, first of all, it is necessary to correctly select varieties adapted to weather conditions.
Features of growing honeysuckle in the Leningrad region
The cool climate of the Leningrad region does not prevent gardeners from successfully growing shrubs that bring tasty and healthy berries. Most varieties of honeysuckle are cold-resistant, survive without problems and bear fruit abundantly in the northern strip. A feature of agricultural technology is the right choice of a variety suitable for a cold area, the correct planting of a berry plant and caring for it.

Berry in the Leningrad cold region is optimally planted on the south side of the building
In order for honeysuckle to grow well in the Leningrad cold region, it is better to plant it in a site with bright lighting, where the sun hits most of the day. In the worst case, partial shade is allowed. Berry does not like drafts, clay and marshy soil. Under such conditions, honeysuckle will take root, but the plant will be weak, will bring little harvest.
The landing pattern for the Leningrad region is standard. In the rows between the seedlings, a span of 1,5-2 m is left. The aisles are made 2 to 3 m wide. The site is cleared of weeds before planting, dug up, leveled. The holes are dug up to a depth of 50 cm, a width of up to 60 cm. The size depends on the root system of the seedling. The root of the berry plant installed in the hole is covered with a soil mixture prepared from 50% soil and 50% humus. Water honeysuckle with three buckets of water. When the earth settles, the trunk circle is mulched with dry compost. Further care goes according to the standard scheme. The shrub is periodically watered, weeds are removed, the ground is loosened, and fed. In autumn they prepare for wintering.
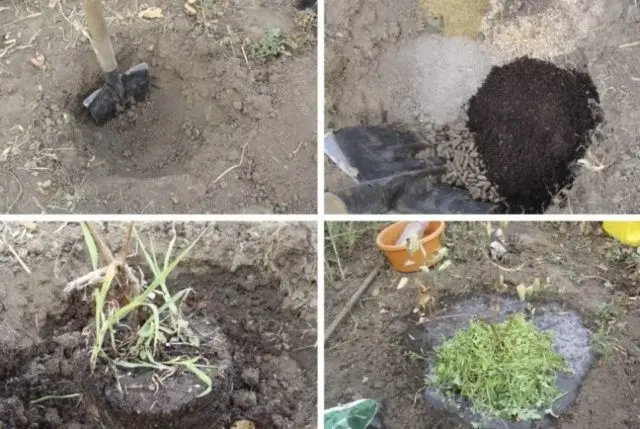

Honeysuckle will take root better if the seedling is carefully planted with a clod of earth, without disturbing the root system.
A feature of growing a berry crop is that it is rarely affected by common diseases in the Leningrad region. This is due to the cool climate. The fact is confirmed by the doctor of biological sciences F. Teterev. But with pests, the situation is more serious. Birds love honeysuckle. Birds eat not only berries, but also leaves.
Another feature of this crop is the fact that the chemical composition of berries grown in different regions is very different. For the Leningrad region, the sugar norm is 4,4-7,3%. Acid index 2-3,3%. The berries are abundantly saturated with vitamin C. The indicator reaches 87%. The listed substances are more than in the fruits of honeysuckle grown in Altai or even in Primorsky Krai.
Yield is also different. Honeysuckle actively bears fruit in the Far East. Despite the natural conditions for cultivation here, nevertheless, in the cool Leningrad region, the yield is 3-4 times higher.
The best varieties of honeysuckle for the Leningrad region
Not every variety of berry crop is able to bring a good harvest if the climate is not suitable for the plant. This fact must be taken into account when buying seedlings. To help gardeners, we offer an overview of honeysuckle varieties for the Leningrad region with photos that are optimally adapted to the conditions of the northern strip.
Dessert
The berry has a compact crown. Honeysuckle drives out branches up to 1,8 m long, but they are lowered to the ground. The total height of the bush does not exceed 1 m. In the Leningrad region, ripe berries are expected in June. The fruits are cylindrical, elongated, weighing a maximum of 1 g. The skin is blue with a light bloom. The pulp tastes sweet with a strongly perceptible sourness. The fruits do not ripen together, it is difficult to separate from the stalk. The yield of one bush reaches 2,5 kg.

Harvest requires proximity to pollinators
Pavlovskaya
An excellent variety for the Leningrad region with a yield of up to 2 kg per plant. Harvest maturity is average. Bushes usually form an unthickened crown. The maximum height is 1,4 m. Honeysuckle brings sweet and sour fruits of blue color, but this is the color of plaque. The skin itself is dark blue and very elastic. The harvest is transportable.

The berries are firmly attached to the stalk, do not spontaneously crumble
Amphora
Honeysuckle bushes grow low. In terms of ripening, the variety is considered medium. The fruits are shaped like small jugs. There is a bit of bitterness in the sweet and sour taste of the pulp. Fruit weight – up to 1 g. The skin is thickened, strong, blue in color with a light bloom. Productivity in the Leningrad region from one bush reaches 2 kg. Fruit ripening is friendly, but they do not spontaneously crumble.

Honeysuckle in the cold climate of the region does not get sick, but aphids or mites are often observed.
Tomichka
Honeysuckle of this variety in the Leningrad cool region grows in the form of a small bush. The leaves are green with a light tint. On the surface of the leaf plates there is a slight edge. Fruits with a dark blue skin are shaped like a drop of water. The taste of the pulp is sweet and sour with an attractive aroma. Bitterness is completely absent. Fruit weight maximum 0,9 g. One bush brings up to 2,5 kg of crop.

Fruits ripen quickly in the conditions of the Leningrad region
Violet
The variety of medium-late honeysuckle is distinguished by a sparse crown of a neat round shape. Bushes grow of medium height – about 1,5 m. The branches are strong, covered with dark green foliage. The fruits grow up to 1,1 g in weight. The berries are elongated, some have a slight bend. The skin is light blue, thin, but strong. The taste of the pulp is sweet and sour.

The yield from one bush reaches 1,8 kg
Viola
A tall variety in the conditions of the Leningrad cool region grows a bush up to 2 m. The crown stands out for its strong thickening. In shape, it resembles an oval. The color of the berries is dark blue with a characteristic light bloom. The fruits are elongated, the weight reaches 1 g. The variety is considered average in terms of ripening. The advantage is a high yield, reaching 4 kg of berries from one bush.

A distinctive feature is the absence of an edge on the surface of large foliage.
Moraine
For the Leningrad region, an excellent early variety. Bushes grow of medium height with an unthickened crown. The berries are large, weighing about 1 g. The skin is blue, but due to the light coating it is more blue. The shape of the fruit is elongated with visible irregularities. The pulp is fragrant. There is no bitterness in the taste, only sweetness and acidity. Productivity varies from 1,5 to 1,9 kg.

After ripening, the fruits do not crumble
Nymph
Vigorous honeysuckle grows up to 2,5 m high. The color of the berries is blue. The fruits are large, oval, slightly elongated. Weight reaches 1,1 g. The pulp has a pleasantly sweet taste with a bright aroma. Bitterness is absent. Harvest ripening begins in the last decade of June. The yield is high – up to 2 kg per plant.

Honeysuckle does not drop ripe fruits
Commonwealth
The variety is considered to be of old origin. Shrub tall. The branches are spreading, strong, hanging down. The total height of the bush is up to 2 m. A distinctive feature of honeysuckle is large berries weighing up to 1,5 g. The pulp tastes sweet and sour. When eaten, bitterness is felt. The value of the fruit in a thin skin. It is practically not felt during chewing. One bush in the conditions of the Leningrad region is able to bring 2,5 kg of crop.

In terms of ripening, honeysuckle is considered early
The Leningrad Giant
By the name of the variety, it is already possible to determine its regionalization. Tall bushes build up a powerful crown of medium density. The height of adult honeysuckle reaches 2 m. The branches grow even without bends. Large foliage has an elongated shape, there is an edge on the surface. The skin is dark blue with a light bloom, thin, but quite strong. There is no bitterness in the pulp, only acid and sweetness are felt. Up to 5 kg of crop is harvested from one bush in the Leningrad region.
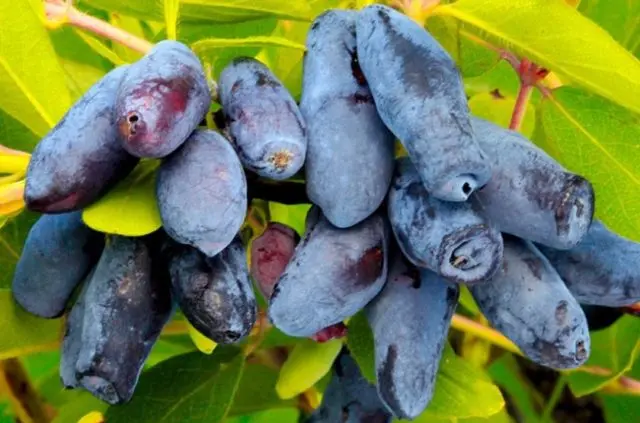

The mass of one berry reaches 4 g
The listed varieties of honeysuckle are suitable for the north-west of the Leningrad region and other regions with a similar climate. The culture is well adapted, brings a stable harvest with decent care.
Planting and care of honeysuckle in the Leningrad region
The culture takes root well and requires simple care. Even a novice gardener can grow honeysuckle. When there are clear definitions with the variety, the seedling is bought, they start planting.

Despite the cool climate of the Leningrad region, growing honeysuckle here is not difficult.
Terms of planting
The optimal time for planting is the period from August to November. At this time, honeysuckle is at rest. Spring plantings are not recommended. Culture wakes up early. In March, you can already observe swelling of the kidneys. If you do not have time to plant the shrub before this time, it may begin to hurt. It will be difficult to adapt to new conditions.
Selection and preparation of the landing site
About the choice of place is a little stipulated in the features of cultivation. In addition, it can be noted that honeysuckle grows well on fertile sandy loamy soil. Optimal neutral acidity. The plant does not like standing water. If the underground layers of water lie above 1,5 m, honeysuckle may not take root here.
Rules for planting honeysuckle in the Leningrad region
Pits for planting a berry plant are dug out in three weeks. At the bottom, it is optimal to organize drainage. The soil mixture for backfilling is made according to the above method: equal parts of earth and humus. However, experts advise a different composition. Add 30 g of superphosphate and potassium salt to a bucket of humus and chernozem.
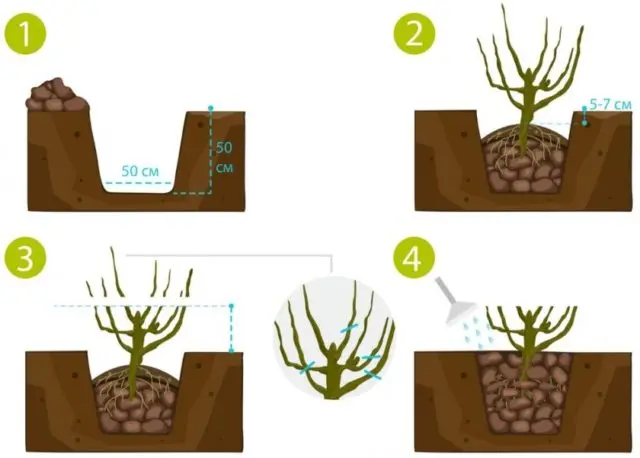
After planting, the seedling requires shortening of the branches and abundant watering.
A couple of hours before planting, honeysuckle is soaked with roots in water with the addition of any growth stimulant. The seedling is placed in the hole with the root system on a tubercle formed from the soil. After falling asleep, abundant watering and mulching of the trunk circle is required.
Watering and feeding
There will be no problems with watering honeysuckle. It is enough to do this five times per season. If a hot summer has turned out in the Leningrad Region, then the number of irrigations is increased. Warm water is poured directly under the root. Honeysuckle loves dousing the crown with sprinkling, but not during flowering. When watering under the root, a bucket of water is enough.
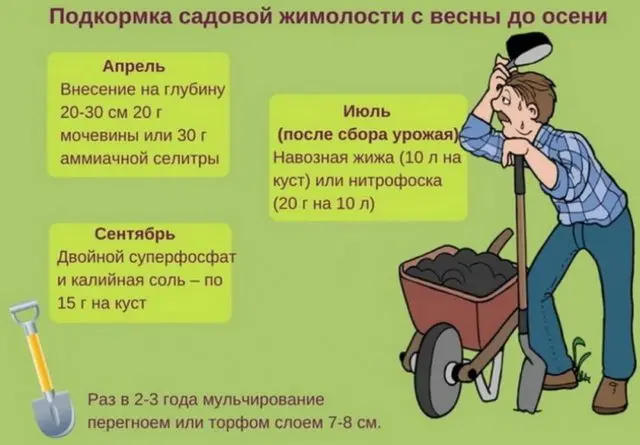
To obtain a good harvest, top dressing is applied throughout the growing season.
The first top dressing is carried out in the third year from the date of planting the seedling. In the spring, the bush is watered with a solution of 2 tbsp. l. urea in a bucket of water or add 10 kg of rotted humus. With the advent of buds and berries, the bush is watered with a bucket of water with 1 liter of water dissolved. The third time they feed the berry in the fall. The trunk circle is covered with a mixture of 5 kg of compost, 40 g of superphosphate with the addition of 100 g of wood ash.
Trimming
The first pruning is carried out immediately after planting the seedling. From the third year of life, the procedure is resorted to carefully. Remove all root shoots, cut off excess branches that thicken the crown. Leave only five strong shoots. Sanitary pruning is carried out annually in the spring. Get rid of damaged, frozen and thin branches. But the main pruning is best done in the fall. In spring, honeysuckle wakes up early, and this procedure injures it. Anti-aging pruning is carried out every 7-10 years. To do this, gradually remove the old branches, and leave the young shoots to develop.
On the video more about pruning the berry:
Wintering
In the climatic conditions of the Leningrad cool region, the culture winters without shelter. In autumn, it is enough to remove the leaves from under the bushes, fertilize and prune. For reliability, the trunk circle can be sprinkled with earth, forming a mound. The mound will protect the root system during severe frosts.
Reproduction of honeysuckle in the Leningrad region
If the neighbors have honeysuckle growing on the site, it is not necessary to buy seedlings somewhere. There are many ways to propagate the berry. It is enough to take cuttings, seeds from friends, ask them to make layering or separate the bush.
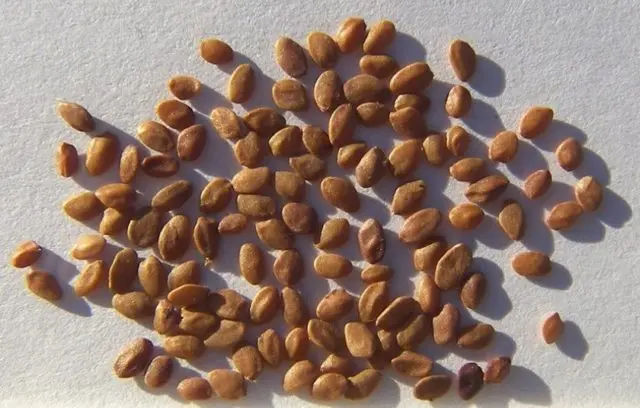

Propagation by seeds is considered a difficult and unpopular way.
To grow seedlings from seeds, prepare the soil mixture. Mix two parts of humus, earth and one part of sand. The soil mixture is poured into boxes, the seeds are planted to a depth of 1 cm. The crops are covered with a film, germinated like ordinary seedlings.
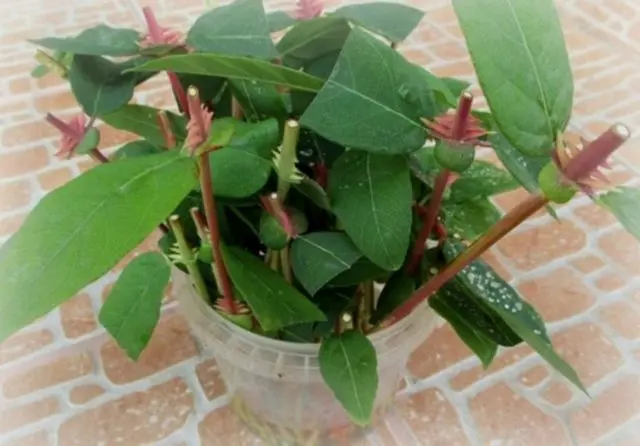

The easiest way to propagate honeysuckle is cuttings.
Lignified cuttings for propagation are cut in autumn or early spring. Regardless of the time of collection, rooting is performed in the spring in the ground. The blanks are stuck into the ground at an angle so that one kidney remains on the surface. Water regularly to maintain constant moisture.
Green cuttings germinate in water or soil. In the second option, a greenhouse is organized over the plantations. Remove it after the branches take root. There is another option for using combined cuttings, in which one or two shoots are green on the side, and the lower part is lignified, about 2 cm long. This breeding option is practiced in the summer.
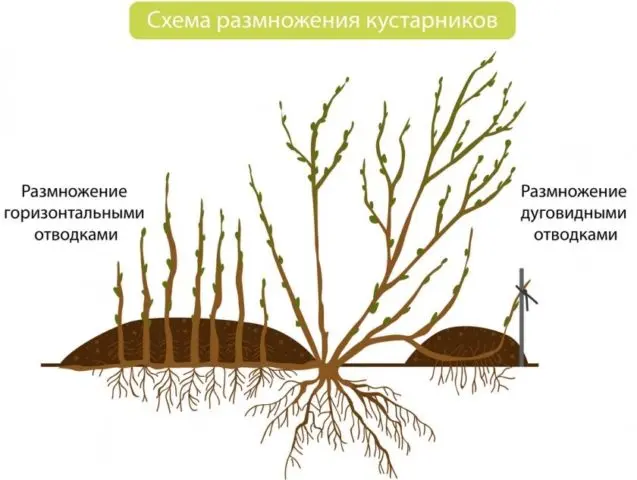
Layering allows you to get strong seedlings
To obtain layering, honeysuckle branches are bent to the ground, covered with soil and constantly watered. When rooting occurs, the lash is separated from the mother bush. The seedling is transplanted to a new place in the fall.
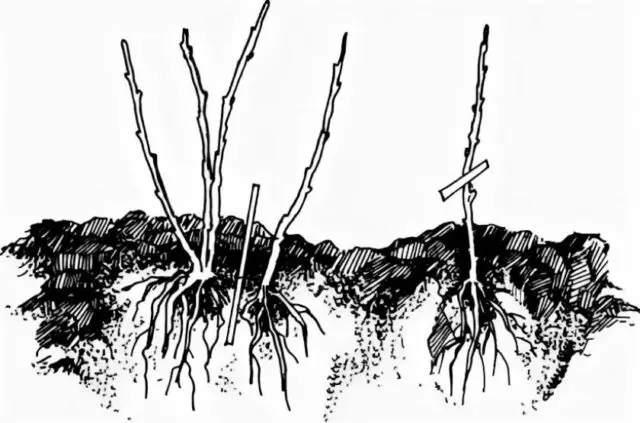
The division of the bush for the plant is painful
The method of propagation by division is based on digging up the entire five-year-old honeysuckle bush. Several shoots with full-fledged roots are separated from it and planted in permanent places of growth.
Diseases and pests
Of the diseases in honeysuckle, spotting is most common. You can recognize the disease by the spots on the leaves of red color with different shades. This is due to high humidity and strong thickening.
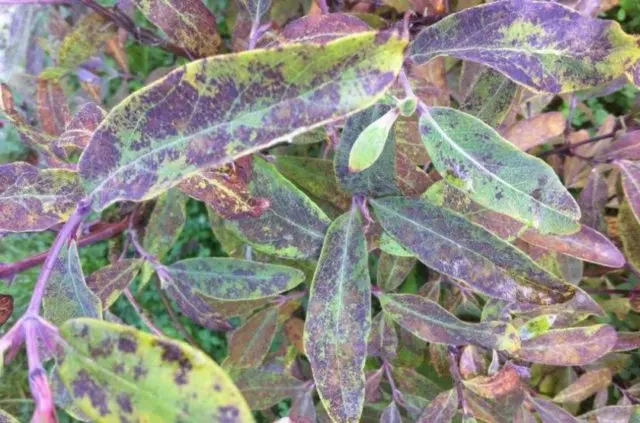

Spotting is most often seen in honeysuckle with improper care.
Of the other diseases, powdery mildew, sooty fungus, and tuberculosis are less common. On the branches of honeysuckle, aphids, honeysuckle fingerwings, and scale insects often appear. In order not to be left without a crop, it is recommended to carry out preventive spraying with drugs.
Conclusion
Planting and caring for honeysuckle in the Leningrad region is a simple procedure. From the gardener requires a minimum of labor. For this, the culture will thank with delicious berries that you can simply eat, cook jam, compotes.









