Contents
The creation of large-fruited honeysuckle by breeders contributed to the wide spread of cultivated shrubs. Hardy winter-hardy honeysuckle of the Amphora variety of medium-late ripening, the berries have a harmonious dessert taste. She was brought out at an experimental station in Pavlovsk near St. Petersburg.
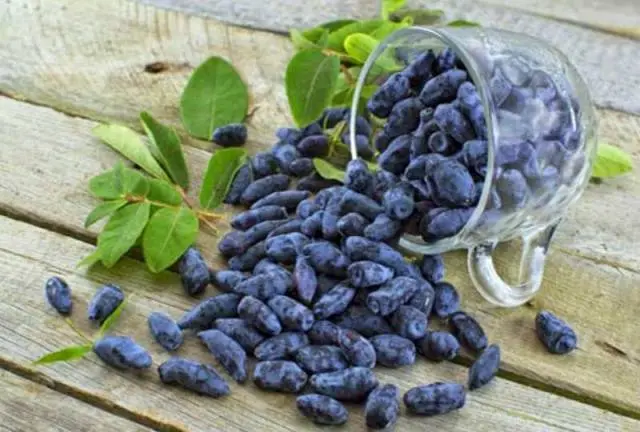

Description and characteristics of the variety
The Amphora variety was created on the basis of the cultivated honeysuckle Roxana and a wild variety from Kamchatka, it has been entered in the State Register since 1998. This unpretentious berry shrub is a real find for gardeners in cold regions. Honeysuckle buds Amphora withstand frosts up to -45-47 оC. The plant is also tolerant of return frosts: the flowers withstand without damage a long-term drop in temperature to -4, -6 оC, and short-term – up to 7 оC. The variety is also valuable because it is resistant to repeated flowering.
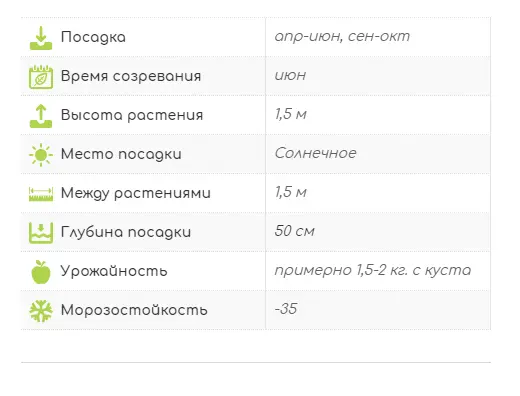
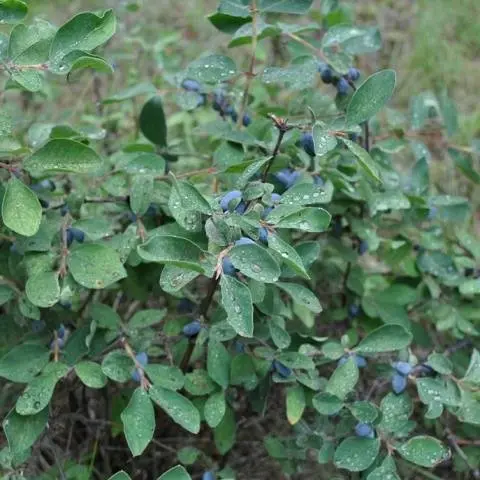
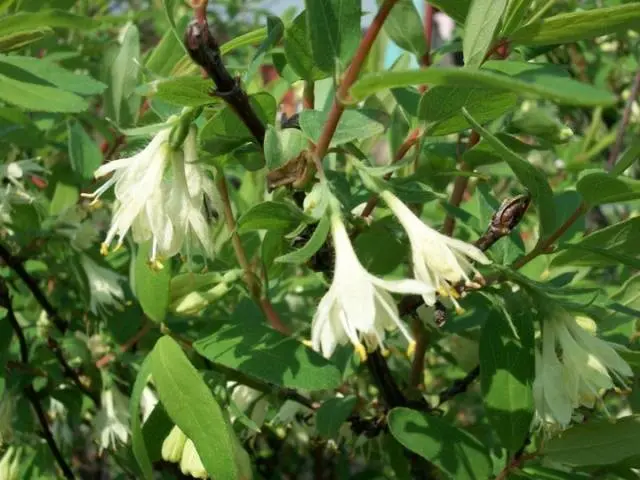
A bush of the Amphora variety with a rounded dense crown grows up to 1,5 m. The trunks are straight, strong, moving obliquely from the root. The bark of honeysuckle is brownish-red, the pubescent shoots are crimson. The leaves are oblong-oval, dense, fleecy. Flowers are pubescent, tubular-bell-shaped, yellow-green.

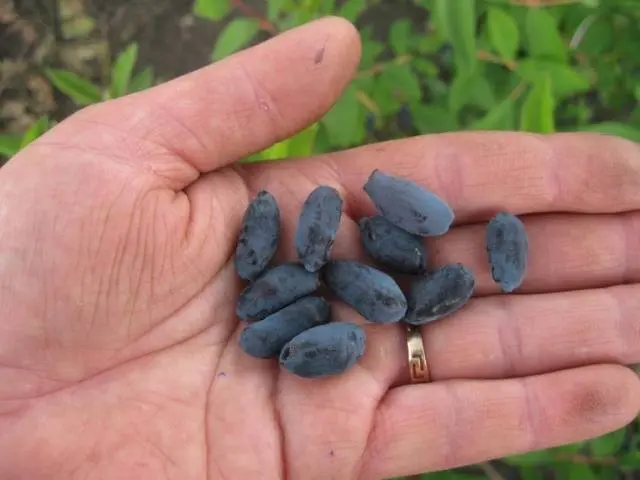
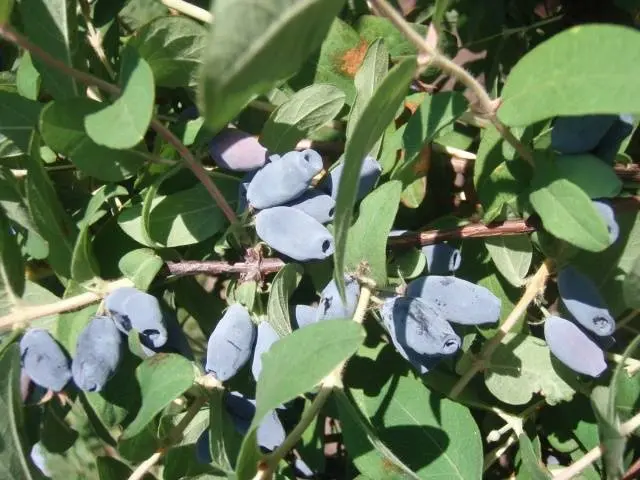
Amphora honeysuckle berries are elongated-jug-shaped, 2 cm long, weighing 1,2-1,5 g, in good conditions on fertile soils – 3 g. There is a strong wax coating on the dense blue skin. The dense, cartilaginous, sweet pulp of the Amphora honeysuckle berries has no aroma, the sourness is mild, there is a lingonberry flavor and a slight bitterness. Small seeds are invisible when eating. The berries are rich in ascorbic acid: 58 mg per 100 g, respectively, the percentage of acid, sugar and dry matter looks like this: 2,6: 7,6: 13,8. Amphora honeysuckle berries after the test, the tasters rated 4,5 points.
Honeysuckle bushes are interesting for their decorative effect, they are often used for hedges, they bear fruit well when cross-pollinated.

Pollinators Amphora
The Amphora variety, like all honeysuckle shrubs, does not bear fruit without cross-pollination. Other cultivars are planted nearby – up to 3-5 plants. The best pollinators for Amphora honeysuckle are:
- Violet;
- Pavlovskaya;
- Altair;
- Gzhelka;
- morena,
- Malvina.
Features of fruiting
On average, 1,3-1,5 kg of useful and healing berries are harvested from one plant. Agrofon corrects the yield of Amphora honeysuckle bushes within 0,8-2 kg. Often signal fruits appear in the first year of planting. The variety shows its full potential from the third year of growth. The fruits of honeysuckle hold firmly on the branches, do not crumble for a long time, and tolerate transportation perfectly. In the Moscow region, honeysuckle bears fruit from the beginning of June. In cold regions, the mid-late Amphora variety ripens from mid-June, a little earlier than strawberries and raspberries. The productivity of honeysuckle is long – more than 30 years, the yield is stable. Honeysuckle bushes bearing fruit for 80 years or more have been documented.

Amphora honeysuckle is universal, suitable for fresh consumption and in preparations. Gardeners who grow Amphora berry bushes assure that the jam tastes delicious, there is no bitterness. The fruits are also frozen and vitamin raw jam is prepared.
Secrets of cultivation
The bush begins spring awakening very early, so autumn planting, in September, is the best option. Only in the south, the culture can be transplanted until mid-March. You need to seriously approach the selection of a place for a seedling. Honeysuckle Amphora grows in any conditions, including in the shade. At the same time, the shrub is photophilous, it bears fruit better in warm and moderately rainy weather. In the sun, Amphora berries are tastier and sweeter. Honeysuckle bushes are planted at intervals of 1,5-2 m.
Site and soil selection
For honeysuckle, Amphora is chosen in a sunny place or with light partial shade if the bush is grown as a fruit-bearing one. In the shade, the plant will develop, but is unlikely to bloom. It can be planted in an open place, the honeysuckle is not afraid of the cold wind. Although this will also affect the quality of fruiting negatively. The plant is moisture-loving, but does not develop well on swampy soil and in areas where spring or rain water accumulates. It is impossible to place honeysuckle in the lowlands.
Light soils, slightly acidic and neutral, are suitable for shrubs. On heavy soils, a substrate is prepared in the hole from equal parts of local fertile soil, humus and sand. Experienced gardeners advise placing the bush in a light midday shade from an apple tree, which is considered a favorable neighbor for honeysuckle.

Bush planting
For a fruitful bush, 2-3-year-old seedlings of the Amphora variety with a root system diameter of up to 20 cm are chosen. A hole is prepared at the chosen place a week before planting.
- The size of the landing pit is 0,3 m x 0,3 m x 0,3 m;
- The drainage layer of ceramics, pebbles is at least 10 cm;
- The soil is mixed with humus, 1 liter of wood ash, 60 g of potassium sulfate and 150 g of superphosphate;
- Before planting, the hole is watered, a mound of fertile soil is poured and the roots of the seedling are carefully laid on it;
- When filling the hole, the root neck is deepened by 3 cm;
- The soil around the trunk is compacted, a circular groove is made along the edges of the hole for irrigation and filled with water;
- Then the soil is mulched with grass, old sawdust, compost, peat.
Care
The early ripening berry shrub of the Amphora variety is undemanding, but still the harvest will be much better if more attention is paid to the plants. The earth is slightly loosened, up to 5-6 cm, so as not to damage the surface root system, weeds are removed on which pests settle. They work especially carefully under bushes older than 5 years, in which the root system rises to the surface of the soil.
Watering
In the southern regions, honeysuckle must be watered every other day. In the middle lane, in dry weather, the shrub also requires regular watering, especially in the ovary formation phase and before fruiting. To saturate the bush with moisture, it is also watered after harvesting, in July and August.
- A groove 10-15 cm deep is dug along the crown line, and it is filled with water;
- When watering, the soil does not need to be heavily soaked, it should remain crumbly;
- In a drought, the Amphora bush is watered in the morning and in the evening by sprinkling through a fine nozzle to keep the delicate leaves from drying out.

Additional fertilizing
In the third year, the Amphora honeysuckle bush begins to bear fruit and requires nutrient support.
- In early spring, the bush is mulched with humus and compost;
- Before flowering and in the ovary phase, they are fed with mullein infusion in a ratio of 1:10;
- At the end of summer, a natural potash fertilizer is applied under the Amphora bush: 0,5 l of wood ash is dissolved in 10 l of water;
- If they are fed with minerals, a solution of urea is added in the spring: 20 g per 10 liters of water;
- Having collected the berries, water with a solution of 10 g of urea, 20 g of ammonium nitrate, 60 g of superphosphate per bucket of water;
- In August, 20 g of superphosphate and 60 g of potassium sulfate are diluted in 40 liters of water for one bush;
- Foliar top dressing with a ready-made mineral complex is given to young plants of the Amphora variety.
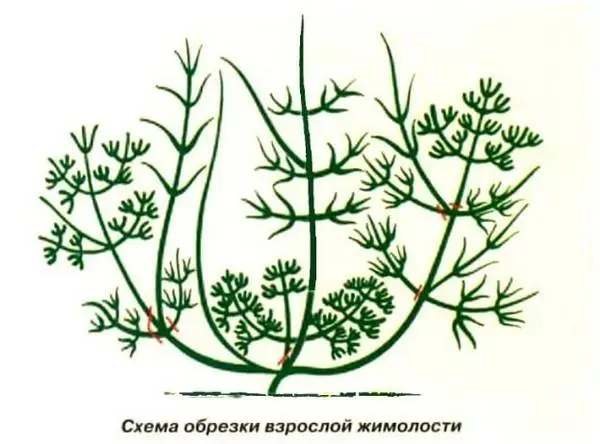
Trimming
Young Amphora honeysuckle plants are pruned only from dry, very low-lying or damaged branches.
- After 7 years of development, thinning pruning is carried out in the fall: old shoots and thickening ones are removed, leaving no more than 10 developed branches;
- Rejuvenating pruning is applied to honeysuckle bushes of 15 years of age, removing most of the branches. This procedure is repeated after 10 years.
Protection against diseases and pests
Amphora honeysuckle is susceptible to fungal diseases – downy mildew and rust only in years with rainy summers. In early spring, for prevention, the bushes of the gardener’s choice are treated with:
- 5% carbamide solution;
- 0,2% solution of preparations “Aktellik” or “Rogor”;
- In the summer, after picking berries, fungicides “Skor”, “Strobi”, “Flint”, “Topaz” are used to combat pathogens;
- They increase immunity by spraying with Epin or Zircon preparations, according to the instructions.

Aphids can settle on young shoots of the Amphora variety, sometimes whiteflies and scale insects attack the bushes.
- Aphid colonies are sprayed with tincture of hot pepper;
- Other pests are fought with insecticides “Iskra”, “Inta-Vir”, “Fitoverm”, “Aktellik”;
- If you have to protect honeysuckle with growing fruits, biological agents are used: Gliocladin, Fitosporin, Alirin-B, Gamair.
Reproduction
The Amphora variety is propagated by layering, bending the lower branch into the dug groove in the spring. The top is left on the surface. The shoot is constantly watered. Emerging sprouts are transplanted next spring or autumn. Amphora bushes can also be divided with a sharp shovel or cut into cuttings in the spring.
Conclusion
Growing honeysuckle will not bring big worries. The correct arrangement of several bushes for cross-pollination, timely top dressing and competent pruning will provide the family with useful berry preparations.









