Contents
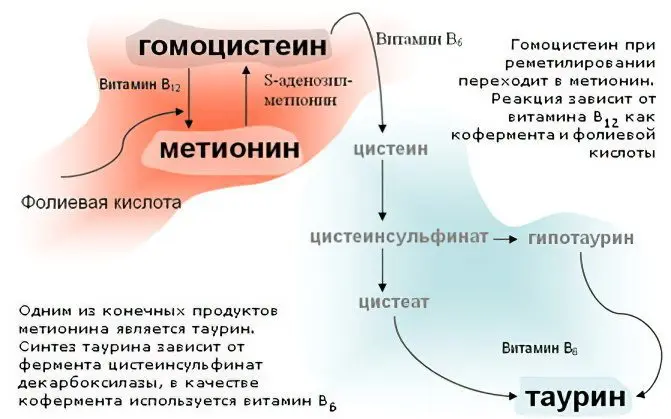
Homocysteine is an amino acid that does not contain protein inclusions. It does not enter the body with food, but is formed in it as a result of a series of biochemical reactions. Homocysteine is produced from another amino acid called methionine (it belongs to the essential amino acids). Her human body cannot produce on its own, so it takes methionine from food. This amino acid is found in eggs, cottage cheese, meat. If a person does not have a deficiency of folic acid and B vitamins, then homocysteine can go through a number of metabolic processes and again transform into methionine.
Methionine is important for the human body, but if it abuses food products in which this acid is contained, then its level begins to exceed the permissible limits. The benefits of acid are neutralized, so sometimes doctors strongly recommend that their patients review their diet. Otherwise, health problems can not be avoided.
Why does a person need homocysteine?
The normal level of homocysteine in the blood varies in the range of 10-11 µmol/l. Gender differences in this case do not matter. In children, the norm of homocysteine is 6 μmol / l. For girls who have entered puberty, this figure is equated to 6 µmol / l, and for boys to 7 µmol / l.
About 80% of all homocysteine in human blood is present in conjunction with albumin and other white fractions. With acquired diseases that provoke a deficiency of vitamins and enzymes, the production of homocysteine in the body will be disrupted. As a result, the amino acid will begin to accumulate in tissue cells, in the intercellular fluid, in the blood.
If the level of homocysteine exceeds the maximum permissible limits, then the body begins to suffer from a cytostatic effect. Tissue cells are destroyed, vascular walls suffer, becoming loose. In those places where there is damage, harmful cholesterol and calcium salts begin to accumulate, which lead to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. Also, an increase in the level of homocysteine in the blood entails the risk of developing thrombosis. Therefore, an analysis to determine the quantitative content of this amino acid is prescribed to patients who have risks of developing cardiovascular pathologies.
As a rule, during the dispensary observation of a patient, the doctor does not ask to donate his blood for homocysteine. However, during pregnancy, this analysis is always carried out.
If the level of the amino acid in the blood is increased in a woman who is expecting a baby, then this can provoke a miscarriage, premature birth, preeclampsia and eclampsia, abnormalities in the intrauterine development of the fetus against the background of hypoxia.
Video: homocysteine specialist:
Increase and decrease in the level of homocysteine in the blood

An increase in homocysteine is associated with a risk of developing various diseases, so an analysis can be prescribed in the following cases:
Diabetes. In this condition, high levels of homocysteine can cause retinopathy or nephropathy.
Alzheimer’s disease, in which high levels of homocysteine cause memory loss without the possibility of its recovery.
Homocystinuria. This disease is hereditary. In humans, a number of abnormal enzymes are produced in the body, so the exchange of homocysteine in the blood is disturbed.
Serious errors in nutrition, which can lead to an increase in the level of homocysteine in the body. The analysis is prescribed for people who consume a large number of meat dishes, or products containing phtholates and B vitamins.
Hypothyroidism.
Acute psoriasis.
Serious disorders in the work of the kidneys.
hyperproliferative processes.
Treatment with drugs such as: Penicillamine, Cyclosporine (suppress immunity), Phenytoin, Carbamazepine (drugs for the treatment of epilepsy), Methotrexate (suppresses the production of folic acid).
People who suffer from alcoholism, smokers, coffee lovers, as well as patients who lead a sedentary lifestyle.
A decrease in the level of homocysteine in the blood is extremely rare. This can happen against the background of multiple sclerosis. To confirm the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed a number of additional examinations that are of greater diagnostic value.
Homocystinuria – what is it?
Homocystinuria is a rare disease that is inherited. It is characterized by a deficiency in the body of synthease. This enzyme is involved in metabolic processes.
With homocystinuria, the internal organs of a sick person will be affected, which contributes to the occurrence of the following symptoms:
Mental retardation, lethargy.
Epileptic seizures.
Violations in the formation of the skeleton. A person suffers from scoliosis, is very tall, etc.
Blood clots form in the patient’s vessels.
Arterial pressure rises significantly.
The optic nerves atrophy, cataracts and glaucoma develop.
The cheeks of the patient always have a bright crimson color.
In addition to a blood test for homocysteine, patients are prescribed a urine test to determine the level of this amino acid. Normally, homocysteine should be absent in urine. If a person suffers from a hereditary pathology, then his traces in the urine will be detected.
So, an analysis to determine the level of homocysteine in the blood is a significant diagnostic study. It is widely used in obstetric medicine, both at the stage of pregnancy planning and after its onset.
An increase in homocysteine levels is dangerous for both pregnant women and ordinary people. Its limiting concentrations contribute to the development of cardiovascular pathologies.
A blood test is taken in the morning, on an empty stomach. If homocysteine is determined in the urine, then it should be investigated as soon as possible. In the urine, the amino acid is not stored for a long time. It oxidizes and transforms into homocysteine disulfide, which cannot be detected.









