Contents
Modern breeders work tirelessly and create new hybrids and varieties of tomatoes every year. They, and all of us, want new varieties to be tastier than the varieties that we plant. It would be good if they sang earlier and kept longer. But probably the most important thing is that they are resistant to the main diseases of tomatoes. Unfortunately, there are simply no varieties and hybrids that are resistant to them at the genetic level. If they try to sell you such a tomato, then the seller is simply disingenuous.
But there are varieties and hybrids of tomatoes that quite successfully resist the main scourge of nightshade – phytophthora. The gardener will only need a little help for the plant, for example, home processing a tomato. This will greatly reduce the risk of this dangerous disease. Hom also fights with Alternariosis of tomatoes.

The main signs and methods of distribution of phytophthora
Phytophthora or late blight is a disease of tomatoes and other crops from the nightshade family, including potatoes. Late blight is caused by pathogenic fungi. Weakened plants usually fall ill first. Brown-brown spots appear on the stems and leaves. If you look closely, you will see a delicate white fluff on the other side of the sheet. These are zoosporangia that are easily transferred from plant to plant. In a humid environment, spores of the pathogen come out of them, which enter the plant through stomata or germinate directly through the top layer of tissue.
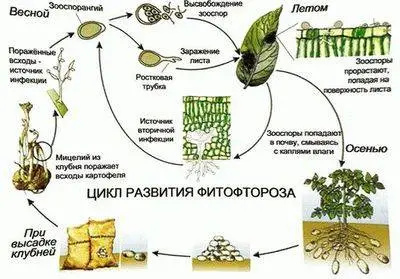
As a rule, potatoes are the first to fall ill with late blight. Spores of the fungus can be found on healthy-looking seed tubers and in the topsoil. From a diseased potato, the disease spreads to tomatoes. The time from potato disease to tomato disease is only a week, a maximum of ten days. In sunny weather, spores may die. Humid and cold summers with sudden changes in temperature and fog contribute to the rapid spread of phytophthora.
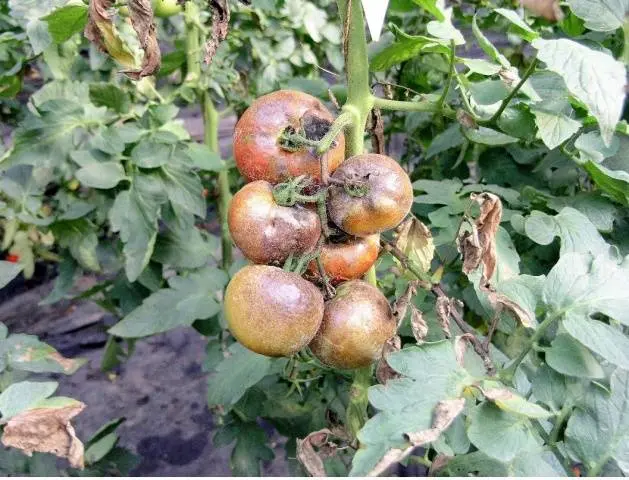

This will not only reduce the risk of disease for both crops, but also increase the growing season of the potato, and hence its yield. Homemade potatoes do not like the Colorado potato beetle.
In order to prevent phytophthora spores from infecting tomatoes, it is necessary to create a protective layer on the leaf surface of plants, and also to treat the tomatoes with a substance that, by infecting the spores of the pathogen, would destroy them. The drug hom meets each of these requirements.

Hom preparation and processing of tomatoes
Hom is a contact fungicide. What does it mean?
- Such a drug cannot cure already diseased plants, but it reliably protects them from infection, forming a protective film on the leaves and stems. Due to the peculiarities of the action of the drug, treatments should be of a prophylactic nature and begin before the appearance of phytophthora not only on tomatoes, but also on potatoes.
- It practically does not penetrate into tissues, concentrating on their surface.
- Copper oxychloride, which is the main active ingredient of the drug, destroys the cells of the causative agent of the disease, causing its death, but only on the surface of the plant.
- Pathogenic organisms do not get used to the action of the drug. Therefore, each treatment will be equally effective.
- Treatments can be carried out repeatedly, on average from three to five times, since the drug does not accumulate in the plant.
- The validity of each treatment is from ten to fourteen days.
- The drug completely decomposes in six months into components that are not dangerous to humans.
How to use hom
For standard treatment of plants according to the instructions, ten liters of water are added for every forty grams of the drug. First, a concentrated solution is prepared by dissolving copper chloride in a small amount of water, and then adding the rest of the water. Since the processing rate of tomatoes is not more than one liter per ten square meters, such an amount will clearly be superfluous. This solution is not intended for storage. Therefore, you need to focus on the area occupied by tomatoes, and, of course, tall varieties will require more solution consumption, as they have a large leaf mass.

Features of processing tomatoes with home
There are rules, the observance of which will help to make the treatment not only as effective as possible for plants, but also safe for humans.
- Each time prepare a fresh preparation.
- Observe the proportions in its preparation and processing standards.
- Process tomatoes on a clear and calm day. It is better to do this in the morning or late in the evening. The air temperature during processing should not exceed 30 degrees.
- When processing, pay attention to the underside of the leaves, as pathogens often settle on it.
- Be sure to wear special clothing, gloves and use a respirator. Do not smoke or eat.
- After treatment, you need to change clothes, wash yourself completely and even rinse your mouth.
- Keep the drug away from foodstuffs and use specially allocated utensils for its preparation.
- Do not use iron containers and utensils made of galvanized steel. Copper oxychloride reacts with iron, and the composition and properties of the solution change.
- Avoid contact of hom with alkalis, they decompose it.
- Do not store the drug at temperatures above thirty and below five degrees Celsius.
- The drug has a third hazard class. It is toxic to fish and should not be allowed to enter water bodies. In the first six hours after treatment, the drug is toxic to bees.
- Processing during flowering of tomatoes is undesirable.
- Hom is compatible with most modern pesticides and fungicides of other classes, except for those that have an alkaline reaction. It is possible to combine with some fertilizers and immunostimulants, for example, humates and epin.
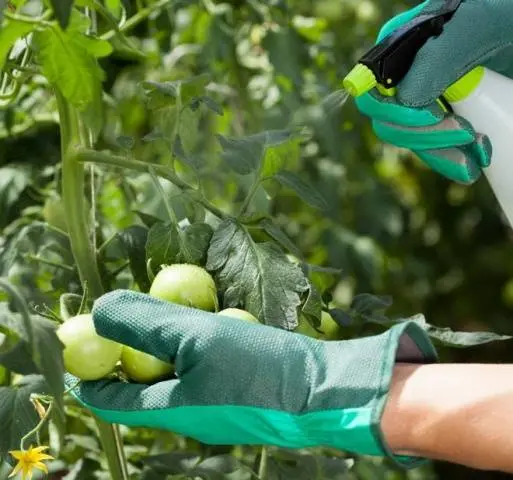

Given the peculiarities of processing tomatoes with hom, it is better to carry them out before flowering, as well as between the flowering of the first and second flower brushes. In other periods of the growing season of plants, it is possible to carry out treatments with formulations that do not have restrictions and a waiting period, that is, processed tomatoes can be eaten on the day it is carried out.
Phytophthora is an insidious and unpredictable disease. Preventing it is much easier than treating it.









