Contents
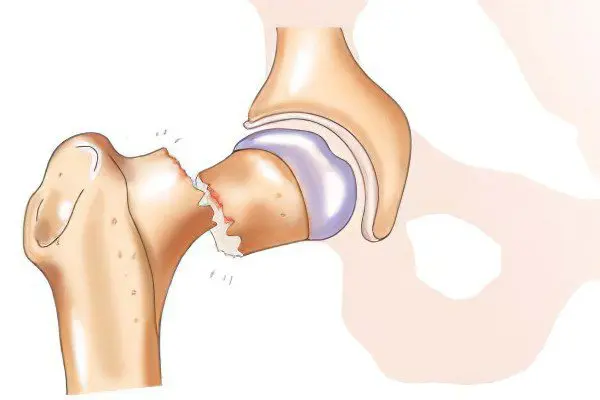
One of the largest joints in the human body is the hip. It performs important functions when moving, since it is on it that the main load falls when walking, running, jumping. In a hip fracture, the neck of the femur is damaged. It connects the head, located in the acetabulum, with the body of the bone. The hip joint is surrounded by large muscles. The friction of the articular surfaces against each other is eliminated with the help of cartilage covering the head.
Blood supply to the femoral neck occurs through a large number of vessels. They are located in the joint capsule, inside the bone and ligament of the head. A fracture leads to damage not only to the femur itself or the femoral neck, but also to the vessels. Due to impaired blood circulation, bone fragments disappear. This phenomenon in medicine is known as osteonecrosis.
Lack of normal blood circulation can lead to non-union of the fracture. Such cases are not uncommon among older patients. This is due to the fact that with age, the vessel inside the head of the joint becomes thin and eventually ceases to function. That is why a hip fracture is much more dangerous for older people than for young people.
Patients over 65 years of age have a hard time enduring the rehabilitation period. If surgery is not done in time, prolonged treatment and bed rest provoke an exacerbation of concomitant diseases and lead to death. Women are more susceptible to hip fractures than men.
Causes of hip fracture
In older people, damage to the femoral neck is associated with osteoporosis, that is, a decrease in bone strength. In women, this phenomenon is observed after the onset of menopause. For a fracture in osteoporosis, a normal fall is sufficient.
Damage to the hip joint also contributes to a lack of calcium, which is a consequence of an unbalanced diet, poor eyesight, malignant tumors, lack of physical activity.
For young people, the most common cause of this injury is car accidents and other situations in which there is too much stress on the femoral neck.
Symptoms of a hip fracture
A fracture of the femoral neck is accompanied by pain, which is most noticeable when you try to make any movement with your foot. At rest, the injured joint of the patient practically does not bother. You can determine a fracture of the femoral neck by tapping on the heel. In this case, pain should occur in the groin and directly in the area of the injured joint.
If during the fracture there was a displacement of bone fragments, the deformity of the leg will be outwardly noticeable. It shortens or lengthens. Most patients suffer from the “stuck heel” symptom or Girgolav’s symptom, that is, they cannot raise their legs on their own, tearing the foot off the surface of the bed, and keep it on weight.
If you do not help the victim in time, a hematoma will form at the site of the fracture of the hip joint in a few days. The outer edge of the foot is pressed against the surface when the patient lies on the bed. This position indicates damage to the femoral neck.
Types of hip fractures
In accordance with the anatomical features, the following types of hip fracture are distinguished:
Basiscervical. The site of damage to the femur removed from the head of the joint.
transcervical. In this type of fracture, the femoral neck is damaged.
Subcapital. The area around the head of the joint is injured.
Capital. It falls directly on the head of the femur.
Depending on whether the displacement of bone fragments occurs during damage, several degrees of fractures are distinguished.
Classification allows you to identify specific treatments for different cases. Considerable remoteness of the fracture site from the femoral head makes it possible to make a favorable prognosis. The chances that normal blood circulation will remain in the damaged area are quite high. If the head is affected, it can cause non-union or lead to serious complications. This situation is especially dangerous for elderly patients, whose blood circulation is often disturbed.
Diagnosis and treatment of a hip fracture
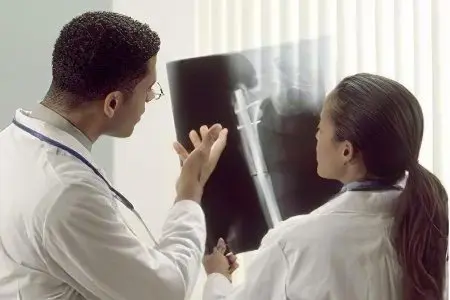
The presence of a hip fracture is determined by X-ray. This is the main diagnostic method. In some cases, resort to the help of computed tomography. It allows you to identify comorbidities.
Initially, the only way out for a fracture of the femoral neck was the immobilization of the limb, its fixation and conservative treatment. At the same time, the fusion of bones was difficult, accompanied by various complications. Over time, other methods of treatment began to be used, including surgery. This is the most effective way to help a patient with a hip fracture.
The conservative method is used in rare cases when, for some reason, it is impossible to perform an operation, for example, in people aged or after a heart attack. For elderly patients, bed rest often causes death, as the lack of movement exacerbates various diseases, and there are problems with digestion. Congestive pneumonia is one of the possible complications. It causes respiratory failure, which leads to death. Significant discomfort to patients who are forced to comply with bed rest is caused by bedsores. You can avoid their appearance by providing the patient with good care, constantly maintaining the cleanliness of the body and changing its position.
Young people also have a hard time with conservative treatment. Long-term immobilization of the joint can lead to disruption of its functions and subsequent disability. That is why surgery and a speedy recovery are so important. The patient should start walking independently as soon as possible. In this case, the rehabilitation period is of great importance, during which it is necessary to perform pull-ups with the help of special belts, do breathing exercises and follow a diet.









