Contents
Hip dysplasia in newborns – this is the underdevelopment of the largest joint in the human body (hip), as well as its segments. These segments include cartilage, ligaments, neural structures, muscles, and bony surfaces. Congenital dysplasia entails a dislocation or subluxation of the joint. Sometimes you can come across the concept of “congenital hip dislocation”, but you need to understand that in this case we are talking about a complication of dysplasia.
More often dislocations and subluxations are formed after the baby was born. It is extremely rare to find a dislocation of the hip joint, which occurs even in the prenatal period. Such a dislocation is called “tetralogical”. With it, the acetabulum, as well as the adjacent part of the femur bone, are in a developed state.
Children have suffered from such pathologies since ancient times. For the first time, the symptoms of dysplasia were described by Hippocrates, who began to straighten the legs of babies with the help of weights.
Having heard such a diagnosis from a pediatrician, you should not panic, because in most cases this pathology is perfectly treated. Moreover, in the world, hip dysplasia is quite common: out of 1000 newborns, about 25 babies are born with it. Moreover, mostly female infants are ill.
Forms of hip dysplasia in newborns
I distinguish three forms of dysplasia, depending on their complexity:
Predislocation, which is characterized by the fact that the head of the femoral bone is not fixed in the acetabulum, but is able to move freely. The ligaments that should hold it are in a relaxed state, due to which instability appears. Due to the fact that the changes are insignificant, it is almost impossible to detect this pathology on your own. The joint may even function normally, but there is a risk of transition to subluxation;
The next, more complex stage of dysplasia is called subluxation. In this case, the femoral head is slightly displaced upward and to the side. It can come out of the acetabulum and fall into place, it is at this moment that a characteristic click is heard;
The most dangerous and requiring serious treatment is the stage called “hip dislocation”. With it, the head will be located separately from the articular bag and move slightly back and up. The acetabulum is underdeveloped. It accumulates fatty and connective tissues.
Causes of hip dysplasia in newborns

The following factors are distinguished as the causes of hip dysplasia::
Hereditary predisposition determined by genetic characteristics. Doctors have established the fact that it is precisely those children whose mothers were also born with hip dislocation that suffer from dysplasia more often;
Unfavorable ecological situation in the area where the pregnant woman lives. According to statistics, children are more likely to be affected by this malformation if the mother’s body is affected by ionizing radiation, the accumulation of exhaust gases, and even passive inhalation of tobacco smoke;
The age of the woman giving birth. The later the baby is born, especially if this is the first child, the higher the risk that he will have dysplasia;
Some diseases of the woman in labor, such as fibroids and the presence of adhesions. Hormonal changes in the body, in particular, an increase in progesterone levels, can also affect;
Severe somatic diseases of the mother;
Toxicosis at an early and late stage of pregnancy;
Bad habits;
Taking certain medications;
Irrational nutrition of a pregnant woman, which causes a lack of vitamins and trace elements in the child’s body. We are talking about calcium, phosphorus, iron, iodine and vitamin E;
Incorrect position of the fetus in the womb: breech or breech presentation;
Some features of the development of the fetus: insufficient weight or short length of the umbilical cord;
Imbalance of water-salt metabolism of the fetus due to kidney pathology;
Entwining the newborn with the umbilical cord;
prematurity;
Trauma to the child during or after childbirth.
Swaddling for hip dysplasia
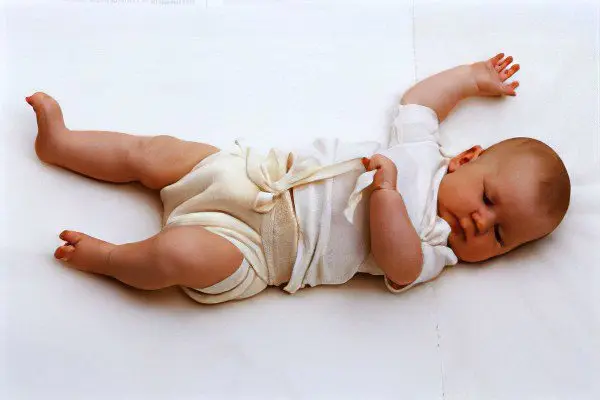

It is worth dwelling separately on swaddling children with hip dysplasia. At the moment, a link has been scientifically established between tight swaddling of babies and an increase in the incidence of dysplasia.
For example, in African and Asian countries, children practically do not suffer from this disease. Due to the fact that babies are carried on their backs, giving them freedom of movement, they rarely develop dysplasia.
Moreover, the important role of wide swaddling cannot be underestimated in order to prevent and treat existing dysplasia. This method gives very good results, especially if wide swaddling is used from birth. This contributes to the proper formation of joint tissues, normalization of blood circulation and reduction of the risk of subluxations and dislocations in children with dysplasia. Wide swaddling allows the baby not to be limited in freedom of movement, but at the same time somewhat restrains the limbs so that the baby smoothly adapts to the conditions of the big world. This not only calms the child, but also improves his sleep.
For wide swaddling, you can use both ordinary diapers and specialized devices. The latter include covers for wide swaddling and the Frejka pillow.
Symptoms of hip dysplasia in newborns
Symptoms that can help determine whether a newborn has dysplasia include:
Tension of the spinal muscles, expressed in increased tone;
Shortening of the leg, on the side of which there is a malformation, relative to a healthy limb;
The presence of an extra fold on the buttock;
Stop position. One or even both legs may be turned out unnaturally;
Asymmetry of folds on a healthy and diseased leg;
Inability to fully spread the limbs of the newborn to the sides. To do this, they first have to bend at the knees;
The child may be in an uncharacteristic position for a healthy baby. His back will be arched outward at the lumbar region, with his shoulder blades and legs elevated. This position of the body resembles the letter “C”;
The baby’s head is tilted to one side. The fingers on one of the hands are constantly compressed;
The so-called “slip” symptom. It is characterized by a click that will be heard when the legs of the crumbs are spread to the sides;
Secondary symptoms, which include atrophied muscles adjacent to the affected joint, as well as a low, barely audible pulse on the femoral artery.
You should not look for a combination of several signs to take the child to an orthopedic appointment. If there is at least one of these symptoms, then you should worry about the health of the baby in advance.
Diagnosis of hip dysplasia
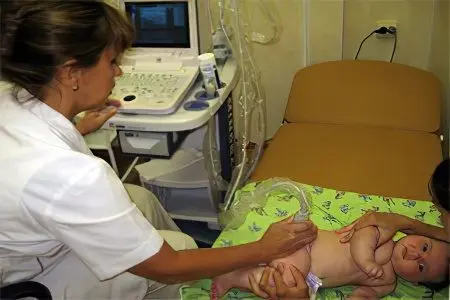
To make a diagnosis and clarify the stage of dysplasia, doctors can use the following methods and studies:
X-ray, which has limitations. Taking into account the age characteristics of the child, the study should be carried out as soon as possible using special protective overlays;
Ultrasound diagnostics, which can be used repeatedly, both for the purpose of making a diagnosis, and for further control. Ultrasound will reliably show the clinical manifestations of the disease, and will also make it possible to determine the tone of the muscles of the lower extremities;
With the help of computed tomography, additional parameters can be identified, for example, to determine the degree of muscle atrophy of the diseased limb;
MRI is used when there is a need for an operation;
General examination to identify external signs. It is first produced by a pediatrician and then by a pediatric orthopedist. If there is a suspicion of dysplasia, the anamnesis of the disease is clarified.
Treatment of hip dysplasia in newborns
The sooner the pathology is diagnosed and treatment is started, the faster the child’s joint will recover. The therapy itself depends on the severity of the disease. If we are talking about pre-dislocation, then doctors practice massage of the buttocks, hips and lower back of the newborn. Recommendations are given for wide swaddling, which was mentioned above. Also, the child is sent for physiotherapeutic procedures, which consist in electrophoresis of the femoral joints using calcium chloride or aminophylline. At home, it is necessary to carry out therapeutic exercises, which consists of a set of exercises.
If the child has a subluxation of the joint, then more radical methods of treatment should be used. First of all, they consist in wearing special stirrups by the baby and following the recommendations for swaddling.
If a newborn has a dislocation, then a splint is shown to him. The wearing time will depend on the severity of the disease. Sometimes, if there are certain indications, surgical intervention is used. It lies in the fact that the head of the femur is set into the articular bag, the remaining elements of the joint are corrected, the muscles and ligaments are tightened and lengthened. It can be used as an open reduction of the joint, and its setting in place using an endoscope.
Rehabilitation measures consist in strengthening the hip muscles, activating regeneration processes, and improving blood supply.
Consequences of dysplasia in a newborn

If there is no treatment, then at an early age it can threaten the child with serious troubles. Children develop limping while walking, it can be both subtle and pronounced. Also, the baby will not be able to move his leg to the side, or will do it with great difficulty. The child will be disturbed by constant pain in the knees and in the pelvic area with a possible distortion of the bones. Depending on the severity of the symptoms of dysplasia, children experience muscle atrophy of varying severity.
Gradually, with the growth of the child, the consequences of untreated dysplasia will be aggravated and expressed in the development of the so-called “duck gait”, when the baby rolls from one leg to another, sticking his pelvis back. The motor activity of such a child will be limited, which will entail the underdevelopment of not only other joints, but will also affect the work of all organs and overall physical development. In the future, the muscles of the leg can completely atrophy, the person will begin to pursue constant incessant pain. In adult patients, hyperlordosis of the spine in the lumbar region is observed. All organs located in the pelvic region also suffer.
All this can be avoided if you start treatment on time and follow preventive measures.
Preventive measures
Preventive measures aimed at eliminating the risks of developing dysplasia are as follows:
Timely ultrasound diagnostics. If this is not done in the maternity hospital, then it must be passed at the age of 3 months;
Mandatory scheduled examination by an orthopedic doctor;
Avoiding any vertical load on the limbs, until such time as it is recommended by the doctor;
Wide swaddling, as well as wearing in a sling;
Regular physical education of the child, in accordance with age;
Compliance with all the recommendations of the doctor and the intake of vitamin complexes by the mother at the stage of gestation.
At the same time, those children who did not receive adequate therapy for up to six months, when prescribed a rehabilitation program at this age, recover only in 30% of cases. Therefore, it should be understood that dysplasia is a curable disease, but it is impossible to delay its treatment.









