Contents
What is hip dysplasia?
Hip dysplasia is a disease associated with impaired development of the hip joint. In general, dysplasia is any deviation in the formation of an organ or system of the human body.
Hip dysplasia is also called congenital hip dislocation. This pathology is congenital. The joint is underdeveloped, resulting in subluxation or dislocation of the femoral head. This is a dangerous and severe violation of the structure of all the constituent elements of the hip joint. These elements are both bones and ligaments, muscles, joints and nerves. Dysplasia leads to misalignment of the femoral head and acetabulum.
Hip dysplasia is a very common disease, and it affects mainly girls (in 80% of cases). Most often, the cause of this pathology is genetic features (the presence of dysplasia in one of the parents) or the incorrect position of the fetus.
Dysplasia can be presented:
physiological immaturity. This means that the formation of the joint components has not yet been completed, but the articular surfaces of the bones are aligned correctly. This is the mildest form of dysplasia, requiring only constant medical supervision and simple treatments. In order for the maturation of the hip joint to proceed normally, it is often necessary to artificially create the necessary conditions for this.
predislocation hips. This is a more complex form of deformation. It consists in the lack of stability of the head of the joint, which is located in the acetabulum and can go beyond it. Predislocation requires competent treatment, otherwise it can cause a disease such as arthrosis. As a result, the joint is deformed, the patient begins to experience severe pain when moving. In many cases, predislocation transforms into hip dislocation. To avoid serious consequences, it is necessary to carry out treatment on time.
hip dislocation. This form of the disease is considered the most severe. At the same time, the articular surfaces of the femoral head largely do not correspond to the acetabulum and are most often located outside the acetabulum. In this case, timely diagnosis and proper treatment are important. In the absence of medical care, the hip joint is deformed, loses its mobility, as a result of which the patient may remain disabled.
All these forms of dysplasia are associated with disorders of the acetabulum, therefore they are called acetabular. Maldevelopment can affect the proximal hip joint. In this case, the cervical-diaphyseal angle is of great importance. It must be age appropriate. In the presence of deviations, dysplasia is distinguished with a decrease or increase in the angle. This can be determined using x-rays.
If the development of bones in the horizontal plane is disturbed, this indicates rotational dysplasia. The axes of the joints of the lower extremities in humans do not coincide, that is, they are located at a certain angle. Failure to comply with this principle leads to dysplasia. The patient’s gait is disturbed, clubfoot is observed.
Statistical studies have shown that dysplasia is characterized by a unilateral lesion. The disease usually affects the left hip joint more often. Identified in the first years of life, such a defect is not yet a serious problem. However, if left untreated, after a few years, it causes lameness, gait disturbance, and pain in the hip joint.
A good prognosis is possible with the diagnosis of dysplasia in the first six months of a child’s life. In this case, only supervision by a specialist is required. If the diagnosis is made 6 months after the birth of the child, the treatment will take years. But in this case, you can completely get rid of problems with the hip joint. The most difficult case, requiring long-term treatment and causing serious complications, is late diagnosis, when the child has already begun to walk.
Signs of hip dysplasia

How to recognize the symptoms of hip dysplasia? First of all, the pathology manifests itself in:
Hip shortening. This symptom appears when the head of the hip joint is displaced relative to the acetabulum. This phenomenon is called congenital dislocation and is considered the most severe form of the disease. You can see the displacement by putting the child on his back and bending his legs. In this case, it will become noticeable that the knees are located at different levels, usually on one leg – lower, and on the other – higher.
Asymmetry of skin folds. This symptom is most pronounced in children under 3 months. Its peculiarity lies in the fact that the asymmetry of the skin folds in bilateral lesions of the hip joint is almost imperceptible. Therefore, the information content of this symptom is maximum when the joint of one leg is deformed. Explore the popliteal, gluteal, inguinal folds. They can have a different shape, depth, located at different levels. On a leg with a dislocation or subluxation, a greater number of folds are observed. This symptom is not enough to diagnose hip dysplasia, because it also occurs in healthy children.
Restriction of hip abduction. This feature is defined as follows. The child is laid on his back, and his legs are spread apart. In a newborn, the angle is 90 ° C. At the age of 7-8 months, this figure is reduced to 60 ° C. The presence of hip dislocation is evidenced by the possibility of abduction by only 40-50%.
Slipping symptom. It is better known as the Marx-Ortolani symptom. Discovered at the beginning of the 20th century, this test remains the most informative method for determining hip dysplasia today. The doctor lays the child on his back and slowly spreads his legs to the side. With dysplasia, a push is felt, as the head of the joint is displaced relative to the acetabulum. In a healthy child, when abducted, the legs almost completely touch the surface under them.
An orthopedic surgeon can determine the presence of hip dysplasia even during the initial examination of the newborn. It is difficult to independently identify a mild form of this disease, and treatment is most effective precisely at the initial stages of its development. With dysplasia, the child experiences pain when the hip is abducted, you can notice the difference in the inguinal folds. However, these symptoms are also characteristic of many other diseases. It is impossible to determine hip dysplasia only by external signs; a more detailed examination is required. Therefore, it is necessary to show the child to a specialist if there is a suspicion of a dislocation or subluxation of the hip joint. The first examination by an orthopedist is carried out immediately after birth, and then carried out regularly every few months. If violations in the development of the hip joint have occurred on both legs, only a doctor can identify this. Outwardly, such a deformation will not be visible.
Timely diagnosis of dysplasia is very important. In adulthood, dislocation or subluxation causes the development of such a serious disease as coxarthrosis of the hip joint. Patients suffering from it suffer from severe pain, have difficulty moving and eventually become disabled. Dysplasia also provokes a violation of posture and gait, contributes to the development of arthrosis.
Causes of hip dysplasia
Disorders during pregnancy. During this period, the body of the expectant mother produces relaxin. This is a special hormone that helps soften the femoral-sacral joints. They must be elastic in order for the birth to be successful. At the same time, the pelvic bones also acquire mobility. Influencing the bones of a pregnant woman, relaxin also affects the bones of the child. They are still poorly formed and easily injured. Therefore, if the mother’s hip joint is resistant to such an impact, then the child has its deformation. It lies in the fact that the head of the joint extends beyond the acetabulum. For this reason, a large number of children are diagnosed with dysplasia immediately after birth. Gradually, the deformity in the hip joint is eliminated. Sometimes this requires the help of specialists, but more often this process proceeds without external assistance.
Women who are pregnant with their first child are at risk. After all, the body produces the greatest amount of relaxin in this case, trying in this way to facilitate childbirth. Also, dysplasia is most characteristic for girls, because the hormone has the strongest effect on their joints, due to greater plasticity than in boys.
Considerable fetal weight. If the body weight of a newborn child exceeds 3 kg, this creates certain difficulties, which lead to the development of dysplasia. The reason for this phenomenon is the increased load on the hip joint of the child. In addition, the significant weight of the fetus, or vice versa, too little body weight of the child limits the ability of the baby to move in the womb. It also leads to dysplasia.
Buttock childbirth. When a baby appears booty first and not head first, as is usually the case, the hip joint can easily become deformed. The head of the joint comes out of the acetabulum, as the bones are still too plastic, and does not return to its place. This problem can be avoided by performing a caesarean section. If the ultrasound shows a non-standard location of the fetus, you should think about the operation.
Genetic predisposition. In women who have had hip dysplasia, the risk of giving birth to a child with the same pathology is higher.
Tugoe pelenanie. It creates extra pressure on the hip joint and increases the risk of its deformity. In underdeveloped countries, where children are not swaddled at all, the problem of dysplasia practically does not arise. In the Land of the Rising Sun, an experiment was even conducted in the 20th century. It consists in conducting a ban on traditional tight swaddling. As a result, a significant reduction in dysplasia in children was noted.
Stop deformity. It becomes a strong gait disturbance, which in turn provokes hip dysplasia. So, with clubfoot, dislocations and subluxations often appear with age.
Bad ecology. The incidence of hip dysplasia is higher in disadvantaged areas. There is an assumption that toxins and environmental pollution also cause deformation of the child’s skeletal system.
It is possible to prevent hip dysplasia by determining the possibility of pathology during fetal development. For example, with a breech presentation, which is determined by ultrasound, it is recommended to perform a caesarean section to avoid joint problems in the newborn.
How to identify hip dysplasia?

Hip dysplasia is determined on the basis of external observations and hardware examination methods. Calm and quiet environment, good and warm lighting, complete relaxation of the child’s muscles – these are the necessary conditions for a review by an orthopedist. intake should be carried out after feeding the baby. In older children, first of all, the asymmetry of the skin folds is determined. If the knee on one leg of a child with abducted legs is lower than on the other, the most severe form of dysplasia is diagnosed – congenital hip dislocation.
The symptom of slippage in some cases does not give a sufficiently complete picture of the joint deformity. In these cases, resort to a modified version of the test. At its first stage, the legs are moved in turn, observing whether slippage of the head occurs in relation to the acetabulum. Then gently press the thumb on the inner surface of the thigh. This can also lead to displacement. But when the head takes the desired position immediately after applying pressure, hip displacement is not diagnosed, although it is possible. The study should be carried out with gentle movements so as not to damage the fragile bones of the child. These diagnostic methods are most effective at the age of up to six months.
X-ray
This research method is used less frequently than others, as it creates a significant radiation load on the child’s body. But it helps to get a complete picture of the structure of the joint and the relationship between the head and the acetabulum. Most of the elements of the hip joint in children are formed by cartilage tissue. It is difficult to distinguish them on an x-ray, so special methods are used to decipher it.
By drawing horizontal and vertical lines, the acetabular angle is obtained. By its value, in accordance with age, the presence of disorders in the development of the hip joint is determined. Gradually, the angle of inclination decreases as ossification occurs. If this process is slowed down or proceeds incorrectly, hip dysplasia is diagnosed.
According to the x-ray, indicators such as the values uXNUMXbuXNUMXbof “h” and “d” are determined, which characterize various types of displacement of the head relative to the acetabulum. Their value is compared with normal and in the presence of significant deviations, dysplasia is detected.
Ultrasound diagnostics
It is harmless to the child’s body. The first such study is carried out in the hospital. In some cases, if there are no external symptoms of dysplasia, it is recommended to perform an ultrasound diagnosis. To make sure that there are no deviations in the formation of the hip joint, parents should insist on a mandatory examination by an orthopedic doctor. In children under the age of six months, ultrasound is the safest and most informative method for diagnosing dysplasia. At the age of 3-4 months, x-rays are possible.
Ultrasound diagnostics has the following advantages over other methods:
availability – ultrasound machines are available in most modern hospitals;
painlessness – the child does not experience discomfort during the examination;
non-invasiveness – ultrasound diagnostics does not involve penetration under the skin, it is an external examination using appropriate equipment;
safety – unlike radiography, ultrasound has no side effects and does not have a harmful effect on the child’s body.
The only drawback of ultrasound is the inaccuracy of its results. Therefore, as an additional source of information, one has to resort to x-rays.
Treatment of hip dysplasia

Treatment of hip dysplasia is more successful the earlier it was started. Recovery of the anatomy and function of the hip joint can take a long time. During this period, it is necessary to achieve fixation of the head of the joint in the desired position, which contributes to the formation of the acetabulum.
In children under 3 months of age, there is no need for radiographic confirmation of the diagnosis, since the most common methods of treatment are used. Their essence is to keep the child’s legs in a state of breeding.
Treatment consists in the use of special orthopedic products and the active development of the affected joints. Orthopedic aids include various splints, stirrups, pillows and appliances. They are designed to hold the legs in a divorced position.
Let’s take a closer look at the main methods of treatment:
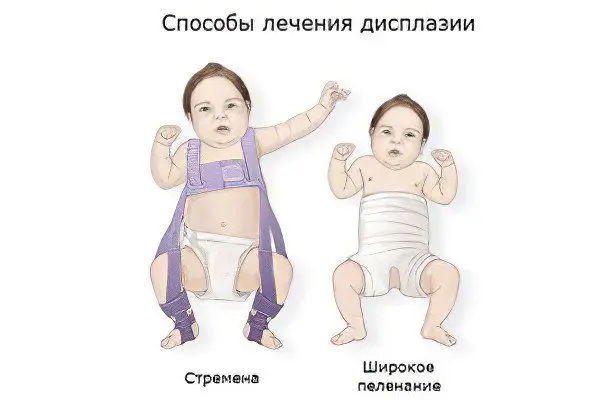
Wide swaddling
It involves the use of 3 diapers, with the help of which the legs of the child are fixed. You can put a diaper on a child, but only if it does not cause skin irritation and dermatitis. The first diaper is needed to spread the legs, and with the help of the second they need to be fixed at an angle of 90%. The use of a diaper makes it possible to prevent convergence. The third diaper wraps the lower part of the child’s body. The hands remain free.
Pavlyk’s stirrup
This apparatus was developed by a Czech scientist and named after him. The invention was first used in the first half of the 20th century, but due to its effectiveness, it is still used in medicine today. Stirrups are a bandage made of fabric and soft straps, which is fixed on the chest of the child. With its help, the centering of the head of the hip joint is achieved, it takes the necessary position. The stirrups help strengthen the ligaments and have a positive effect on the acetabulum. The device does not allow the child to reduce the legs, but at the same time provides the opportunity to move freely.
The size of Pavlik’s stirrups is selected depending on age and height. There are some peculiarities of wearing the device in accordance with the nature of the pathology of the hip joint. For the first time, it is recommended to entrust a specialist to fix them on a child. In case of pre-dislocation, abduction of the hip at the beginning of wearing the brace should be minimal. Gradually, the angle should be increased until the anatomy of the hip joint is fully restored.
Subluxation requires breeding, in which the child does not experience severe discomfort. Over time, the angle should reach 80%. This position must be maintained for several months. If there is tangible discomfort in a child, an anesthetic is used as prescribed by a doctor. Dislocation requires the preliminary reduction of the head of the joint into place, and then its fixation. Muscles make it difficult to spread the hips during the treatment of dysplasia. It is important to prevent sudden hypothermia, a prolonged feeling of hunger, emotional discomfort in a child. This leads to inflammation of the tendons and muscles.
The child must wear stirrups around the clock. Only in this case a positive result will be achieved. To avoid chafing delicate skin and irritation, you need to carefully monitor hygiene. Bathing a child is not worth it, because for this you have to remove the stirrups, but this cannot be done. It is enough to periodically wash the body of the baby. To do this, unfasten the leg belt, supporting the abduction of the hip, or the bandage straps on the chest.
If there is a diaper under the stirrups on the child, you need to change it in time, putting your hands under the buttocks. The perineal and hollow areas are particularly prone to dermatitis and irritation, so they need to be inspected and treated more often. Socks to the knees and a light cotton blouse allow you to avoid rubbing the skin. Pants or dress are worn directly on the stirrups. They should be light so that the child does not sweat. It is also impossible to allow hypothermia of the body.
It is important that stirrups are always kept dry and clean. Do not allow powders, lotions to get on them, as this can cause a rash and inflammation on the skin. Feeding time is a difficult moment when special control over the baby’s hips is required. In any position of the body, they should be retracted at the desired angle.
Frejka pillow

This orthopedic device is used to treat dysplasia, but is not a prophylactic. The main purpose of using such a pillow is to fix the child’s hips in the desired position. At the same time, they are bred at a certain angle. You can use the pillow for children over the age of 1 month.
This orthopedic device is made of soft materials. Therefore, the pillow causes the child a minimum of discomfort, does not rub the skin. Downstairs, it is recommended to wear light, loose-fitting cotton clothing. The size of a pillow for a child is considered appropriate if the distance between the child’s bent knees is completely hidden by it. When choosing a device, you should focus on the age and height of the baby.
An orthopedic doctor can show how to put a pillow on a child and fix it. He also appoints the period of wearing and gives his recommendations. Unlike Pavlik’s stirrups, in some cases it is allowed to remove the pillow during feeding or bathing. But this should be done in accordance with the permission of the attending physician. The angle between the thighs increases gradually as the child gets used to the pillow.
It is important to wear it correctly, otherwise you can not only not achieve the desired positive effect, but also harm the health of the baby. Wearing a pillow is often accompanied by certain difficulties: the child is naughty, eats and sleeps poorly, tries to get rid of the pillow. You need to be patient during the treatment. Warm wraps, massage, adding soothing aromatic oils to the bath while bathing help to minimize discomfort for the child. Frejka pillow can be purchased at the store or made by yourself.
Gymnastics for hip dysplasia
Gymnastics is performed daily 2-3 times. In between exercises, it is recommended to use massage movements. For a session of gymnastics, the child is laid on his back. The most common and effective exercise is imitation of cycling. You should take a child’s leg in each hand and move back and forth. You can repeat any exercise in gymnastics 10-15 times.
The legs can also be bent together or alternately at the hip and knee joint. At the same time, the movements should be soft and not cause pain and discomfort to the child. When alternately bending one leg, you need to fix it with your hand.
The “patty” exercise is not only one of the methods for treating dysplasia, but also an exciting game for the baby. At the same time, the feet must be carefully brought together. If the child likes to perform such movements, there will be no problems with gymnastics and he will be happy to allow the development of the hip joint. Gymnastics is used to treat and prevent dysplasia.
All exercises should be performed with the child on his back. Sitting and standing gymnastics should not be carried out. The child’s legs are not yet strong enough, so such a load negatively affects the state of the hip joint, increasing its deformation and preventing normal development. Gradually, you can introduce such an exercise as turning the baby from back to stomach. It helps to strengthen the muscles of the limbs and torso. Therapeutic gymnastics is carried out in courses, the duration of which reaches 2 weeks, and then a short break is taken. Specific recommendations should be given by an orthopedic surgeon, based on the severity of the disease.
Massage for hip dysplasia

Massage is one of the most effective treatments for hip dysplasia. It is recommended to go through several sessions with a specialist. After all, the joints and bones of a small child are very mobile and not strong, so a careless movement can easily harm them. Over time, massage can be carried out independently, after consulting with a doctor. It is very important to do it regularly. Only under this condition is it possible to achieve a positive result in a short time. It is worth refusing massage if the child has an elevated body temperature, there are unreduced hernias, a heart defect is detected. In these cases, only a manual therapist can develop the hip joint.
At home, massage is performed once a day, when the child is calm, full and does not want to sleep. To begin with, you can stroke the outer part of the legs for 1-2 minutes, making spiral movements in the direction from the lower leg to the thigh. You can not get too close to the genitals, as there is a high risk of damage to the lymph nodes. After that, you need to gently rub the skin. It is important to control the strength of the movements so as not to injure the joints. The greatest effort should be made by massaging the lower back and legs. Movements should be rubbing and stroking. The buttocks should also be beaten and pinched. Movements in the hip joint should be circular.
Grasp the thigh with both hands and roll each leg like this, imitating the modeling of cutlets. Massage of the feet and lumbar of the child helps to improve blood circulation. During rubbing, tapping, tingling, the baby should lie on his stomach. Children often take massage for a game and enjoy all the movements of their mother’s hands. The effectiveness of the procedures is determined by the orthopedic doctor, who should be visited regularly.
Surgery
Surgical treatment is indicated for patients who are not helped by conservative methods. There are many surgical treatments for hip dysplasia. The most popular of them are open reduction of dislocation, operations on the proximal femur, corrective, varus and derotation osteotomies, Chiari pelvic osteotomy.
But, unfortunately, even several operations do not guarantee a complete recovery. There is always a risk that the function of the joints will not be fully restored, and this will lead to gait disorders for life.
Author of the article: Polyakova Elena Anatolyevna, pediatrician, specially for the site ayzdorov.ru









