Contents
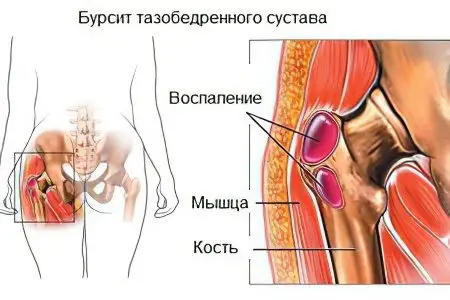
Bursitis of the hip joint is a disease in which its synovial membrane (together with the contents) becomes inflamed.
In most cases, with the development of bursitis, 3 periarticular bags can become inflamed around the hip joint:
Ischial. With inflammation of this bag, the patient develops a strong pain syndrome, the intensity of which increases even with slight physical exertion.
The trochanter. With the development of the inflammatory process in this bag, patients experience severe pain in the femur. Most often, inflammation of the trochanteric bag is detected in women or athletes.
Iliac-comb. The development of the inflammatory process in this bag is accompanied by pain in the inguinal region.
Symptoms of hip bursitis
Bursitis of the hip joint is often accompanied by certain symptoms:
pain (sharp or gradually increasing) in the hip joint;
burning sensation;
problems with: bending the limbs, climbing stairs, walking for a long time, sitting on a hard surface;
sleep disturbance (caused by pain syndrome);
general malaise;
weakness, lethargy, disability;
suppuration (when infection enters the synovial sac);
temperature increase;
swelling (determined both by palpation and visually), etc.
Causes of hip bursitis
The main reasons for the development of hip bursitis include:
various diseases, congenital pathologies and anomalies (different leg lengths, curvature of the spine, arthrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, bone spurs, salt deposits, etc.);
strong physical exertion on the hip joint;
excessive passion for sports;
hypothermia;
overweight (any degree of obesity);
sedentary (sedentary) lifestyle;
previous injuries (falls, damage to the protruding sections of the femur, etc.);
performed surgical interventions on the hip joint;
advanced age;
disruption of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus);
infections penetrating the bursa.
Diagnosis of hip bursitis
Due to the fact that the main sign of the appearance of hip bursitis is a strong pain syndrome, patients are forced to seek medical help. At the appointment with a specialist, the patient will undergo a thorough examination. The doctor, through palpation, will determine which bag is inflamed.
After collecting an anamnesis of the disease, the patient is assigned an additional examination:
Aubert’s test is performed;
an x-ray is taken;
magnetic resonance imaging is performed.
Treatment of hip bursitis
In the treatment of hip bursitis, the first task of the doctor is to relieve the pain syndrome. Patients are assigned:
anti-inflammatory and absorbable drugs;
painkillers;
fixation of the damaged joint;
bed rest (limitation of loads on the hip joint area), etc.
Great effect in the treatment of bursitis bring physiotherapy. Patients are prescribed:
induction therapy;
electrophoresis;
microwave therapy;
UHF therapy;
massotherapy;
physiotherapy exercises (exercises are selected individually by the instructor, depending on the form of bursitis);
applications (ozocerite or paraffin);
dry heat, etc.
In the event that medical and physiotherapeutic treatment has not brought the desired result, patients undergo surgical intervention. During the operation, the patient is relieved of the strained muscles. If indicated, the surgeon may perform excision of the trochanteric bursa, which is inflamed. Very often, during the operation, the surgeon has to drain the fluid that forms in the periarticular sac. To prevent its re-accumulation, the patient is given surgical drainage.
In severe hip bursitis, the surgeon performs a bursectomy, during which the affected bursa is removed. In recent years, modern medical centers have been using the least traumatic method for removing the bursa – arthroscopy (using special medical equipment). Patients tolerate such surgical manipulation very well and recover very quickly. During arthroscopy, the functions of the hip joint are not disturbed, since the patient is operated on with minimal contact with the tissues of his body.
Rehabilitation
All patients who underwent surgical treatment of bursitis should undergo rehabilitation, which will help them quickly return to a full-fledged lifestyle. Patients are advised:
exercise moderately;
massage;
regularly train joints and muscles;
walk (to facilitate walking, it is recommended to use crutches, special walkers or a cane).
Complications
Against the background of hip bursitis, patients can develop various complications. Most often, there is a transition of the acute form of the disease into a chronic one, in which all the capsules of the hip joint become inflamed. This form of complication can lead to limited mobility of the patient.
Prevention of hip bursitis

From the development of bursitis of the hip joint, no one is immune. It is possible to reduce the likelihood of the occurrence of this disease if preventive measures are taken in a timely manner:
minimize stress on the bones and joints of the small pelvis;
get rid of excess weight;
strengthen the immune system;
spend more time outdoors by walking;
to live an active lifestyle;
go in for sports (in moderation to give physical activity to the body);
to fully relax after a busy day at work;
get enough sleep (go to bed at the same time);
eat healthy foods (avoid fatty and fried foods that can lead to obesity);
give up all bad habits, etc.









