Contents
Herpetic stomatitis is a serious disease that reduces the quality of human life. In adults, it is not often diagnosed, but it is characterized by a severe course and is difficult to treat. Do not try to cope with herpetic stomatitis on your own. First you need to make sure that the patient has developed this particular form of the disease. Only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis and choose a treatment. However, each person should know how this disease manifests itself, as well as be able to give themselves the rules of first aid.
What it is?
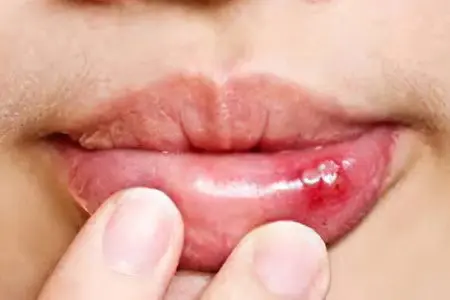
Herpetic stomatitis is a viral infection. The main manifestation of the disease are small ulcers that cover the oral cavity. The herpes virus type 1 or 2 can cause pathology.
The disease is highly contagious, the infection spreads rapidly by airborne droplets, and it can also be transmitted through close contact.
Herpetic stomatitis tends to recur. Its exacerbations most often occur in autumn and winter, when immune forces decrease, hypothermia occurs, the likelihood of contracting SARS increases, people suffer from hypovitaminosis. Young children are most affected by the disease. An acute process can stretch them for several weeks.
How can you get a virus
Infection occurs when the virus enters the oral cavity. This happens during a kiss, when using someone else’s toothbrush. The virus is easily transmitted from one person to another.
The risk of infection increases when you are in crowded places. Cases of herpetic stomatitis are becoming more frequent in the cold season.
How the virus is transmitted:
contact path.
Sexual relations with an infected person.
Airborne route.
Hematogenous way, that is, through the blood.
There is an increased chance of infection in people who use sodium lauryl sulfate paste. The fact is that this component weakens the protection of the oral cavity at the local level.
Causes of herpetic stomatitis

The main factor that contributes to infection is low immunity. Moreover, in this regard, the fall of both general and local defense forces is dangerous.
The main causes of infection with herpetic stomatitis:
Change of climatic zones.
Hypothermia or overheating of the body.
Injury to the lips or mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
Poor oral hygiene.
Violations of the neuropsychic plan.
Exacerbation of chronic diseases (tonsillitis, sinusitis, gingivitis, periodontitis, etc.).
Allergic reactions of the body.
The presence of carious teeth.
Taking corticosteroids. These drugs help to suppress the inflammatory response, at the same time they depress the immune system.
Vitamin deficiency.
Presence of tartar.
Viral and bacterial infections, including SARS and HIV.
The herpes virus, having entered the body once, remains in it forever. Therefore, from time to time he can remind himself.
The cause of exacerbation of herpetic stomatitis are the following factors:
Hormonal imbalance.
Injury to the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
Dehydration of the body.
Poor quality dental prosthetics.
Drying of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
Undergoing chemotherapy.
Serious errors in the diet.
Forms of the disease
Herpetic stomatitis can occur in two forms: acute and chronic.
The acute form of the disease goes through several stages:
incubation stage. It may take up to 3 weeks after infection until the first symptoms appear.
catarrhal stage. During this period, the first symptoms of the disease appear. It lasts from 2 hours to a day.
acute stage. During this period, the maximum activity of the virus is observed. The duration of this phase is 2-4 days.
The stage of extinction of symptoms. It takes up to 4 days.
regeneration stage. At this time, the affected areas of the oral mucosa are restored.
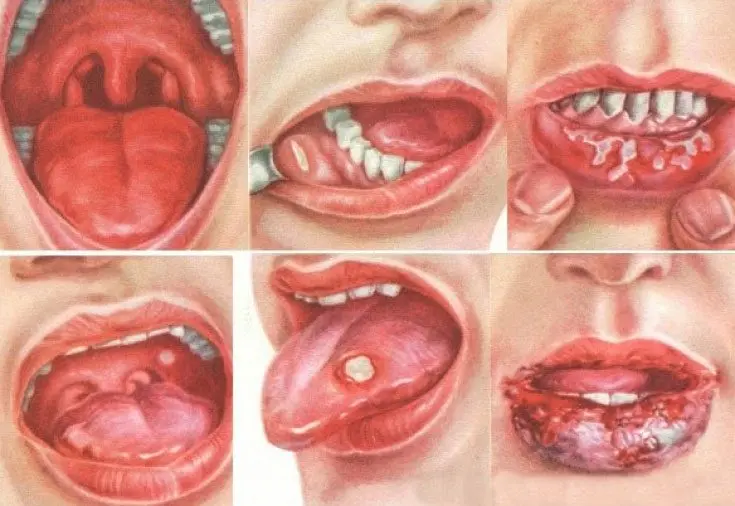
The chronic form can occur in two variants:
The mild course of chronic herpetic stomatitis is characterized by relapses of the disease, which occur no more than once every 6 months.
The severe course of the disease is accompanied by frequent relapses, which can occur more than 6 times a year.
Symptoms of herpetic stomatitis

The main symptom of herpetic stomatitis are ulcers on the lips. They are small and filled with liquid. Other symptoms of the disease will depend on the form of the disease.
Acute herpetic stomatitis
Acute herpetic stomatitis is accompanied by the following symptoms:
Increased general weakness.
Discomfort in the mouth.
Headache.
Drowsiness.
Enlarged submandibular lymph nodes in size.
Increase in body temperature. Sometimes it remains at subfebrile levels and does not last long, and sometimes it reaches feverish values and persists for a week.
The formation of bubbles on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. They can be concentrated on the inner surface of the cheeks, on the lips. Bubbles cause itching and burning. Over time, they burst, after opening a colorless liquid comes out of them.
If the treatment of acute herpetic stomatitis is not started in time, it will turn into a chronic form. Ulcers do not have time to heal, new defects form in their place. This greatly complicates the process of eating, and sometimes makes it impossible.
Chronic herpetic stomatitis
Chronic herpetic stomatitis develops in people with low immunity. It recurs several times a year. Sometimes the number of exacerbations reaches 6. The weaker the person’s own defenses, the more intense the symptoms of the disease. An unpleasant odor emanates from the patient’s mouth. The entire inner surface of the cheeks is covered with scars. There is always a coating on the tongue.
In the chronic form of stomatitis caused by the herpes virus, secondary symptoms of the disease do not appear. That is, the patient’s body temperature does not rise, the lymph nodes do not increase in size, the gums do not bleed. The general state of health as a whole suffers, which is manifested by weakness and increased fatigue.
Herpetic stomatitis in children
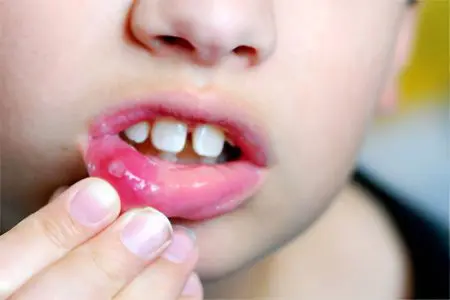
Herpetic stomatitis in childhood often develops. Sometimes the disease is diagnosed even in infants, but children older than six months are predominantly affected by the herpes virus. Until that time, antibodies received from the mother circulate in their blood. They protect the child from the herpes virus.
The onset of infection is acute, accompanied by an increase in body temperature and the appearance of blisters in the oral cavity. The overall immune defense is reduced.
At the age of 3 years, herpetic stomatitis often recurs. This is due to the disappearance of maternal antibodies, as well as the immaturity of the baby’s immunity.
In childhood, the disease can occur in the following forms:
Sharp form. This is how the herpes virus manifests itself after the initial infection.
Chronic recurrent herpes.
Generalized herpetic infection. It develops in infants who were born without maternal antibodies. The lack of protection leads to the fact that extensive areas of necrosis are formed in the oral cavity. This form of the disease can lead to sepsis, with damage to the internal organs and the brain. The more severe the pathology, the higher the risk of death.
Diagnostics
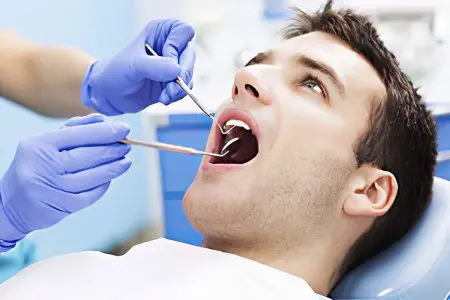
Only a dentist can make a correct diagnosis. The doctor examines the affected area, assesses the general well-being of the patient, studies his medical record. This allows you to assess the severity of herpetic stomatitis and the stage of its development.
If, after examination, the doctor still has doubts about the accuracy of the diagnosis, then laboratory diagnostics are required: virological, immunological, molecular biological, cytological.
For research, you will need to scrape vesicles or erosions. The resulting material is stained according to the Romanovsky-Giemsa method, which makes it possible to identify the herpes virus. The doctor also determines the presence of macrophages and polymorphonuclear neutrophils in the tissues.
Differential diagnosis with other diseases
Herpetic stomatitis can give similar symptoms to some viral diseases.
To correctly determine the infection, it is necessary to carry out differential diagnostics with pathologies such as:
Exudative erythema multiforme.
Some viral infections: herpangina, foot and mouth disease and vesicular stomatitis.
Bacterial stomatitis.
Enteroviral vesicular stomatitis with exanthema.
Herpes of the lips and skin.
Allergy.
It is difficult to make a differential diagnosis only on the basis of an external examination. Therefore, patients are prescribed special tests and samples that are carried out in a laboratory.
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis
Sometimes herpetic stomatitis is mild and goes away on its own. However, this is not always the case. Often, the disease provokes the appearance of severe symptoms, so it will be difficult to cope with it without therapy.
The treatment regimen is based on the characteristics of the course of the disease in each case. Therefore, it is important to consult a doctor and conduct a diagnosis.
[Video] Professor of the Department of Pediatric Therapeutic Dentistry, MGMSU, Ph.D. Strakhova Svetlana Yurievna will tell you what to do with herpetic stomatitis:









