Contents
- Anatomical features of the abdominal wall
- What does a hernia of the white line of the abdomen mean?
- Causes of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen
- Symptoms of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen
- Complications of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen
- Diagnosis of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen
- Surgery to remove a hernia of the white line of the abdomen
white line hernia – This is a violation in which crevices form between the muscles on the white line, through which fat and internal organs appear. A hernia manifests itself in the form of a painful formation, it is treated only by surgery. For any manifestations, you need to contact the surgeon.
Anatomical features of the abdominal wall
The abdominal wall is represented mainly by the abdominal muscles. The layers of the abdominal wall include:
Peritoneum. This is a thin layer of connective tissue lining the inside of the abdominal cavity. It covers all the organs of the abdominal cavity.
Fat layer (preperitoneal tissue).
Transverse fascia. It is a compacted layer of connective tissue that strengthens the abdominal wall.
Abdominal muscles. They cover almost the entire abdomen. They are located on the right and left, outside they are covered with fascia (a layer of connective tissue).
Subcutaneous adipose tissue covered by skin.
There is a narrow area along the midline where the muscle is. Here the fascia of the right and left muscle groups converges. This anatomical formation forms the white line.
The white line is not uniform in width. From above it is wider and is up to three centimeters. Below the navel, it narrows. The likelihood of a hernia in the upper part is the highest. Often the defect is formed under the sternum.
What does a hernia of the white line of the abdomen mean?
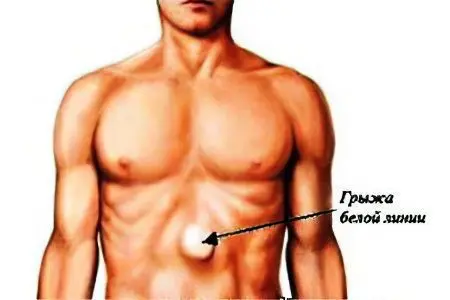
As practice shows, pathology is 3-10% more common in men under the age of 30 years. With this form of the disease, parts of the internal organs and fat begin to show through the holes between the muscles. A typical localization site is the epigastric region.
Depending on the location relative to the umbilical cavity, the following types of hernias are distinguished:
supraumbilical (located above the navel);
Paraumbilical (located near the umbilical cavity);
Sub-umbilical (located below the umbilical cavity).
The location of the hernia of the white line near the navel and under it is infrequent.
Modern methods of treatment make it easy to get rid of the disease, however, to identify it at the initial stage, you need to familiarize yourself with the causes of the development of the pathology and the symptoms accompanying it. A hernia, like any other disease, is easier to treat at the initial stage of development.
At first glance, education does not cause significant discomfort, but the disease is still fraught with danger. The main threat is the pinching of organs that are inside the hernial sac. In some cases, nerve compression occurs.
Causes of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen
A hernia is formed due to congenital or acquired weakness of the connective tissue of the white line. As a result of this, the tissue thins and expands, clefts form in the white line, and diastasis of the rectus muscles (divergence) develops. Normally, the white line should not be wider than three centimeters; when it is modified, the width can be up to ten centimeters.
Factors leading to weakening of the connective tissue:
Hereditary tissue weakness;
Overweight;
Postoperative defects, non-healing wounds.
Risk factors associated with increased intra-abdominal pressure include:
Physical activity, weight lifting;
Pregnancy, childbirth, complicated labor activity;
Chronic constipation;
Infectious diseases accompanied by prolonged cough;
chronic diseases;
Accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity.
Injury to the abdominal cavity can also cause formation. Therefore, you need to train your muscles so that they become stronger and become a defense against a disease such as a hernia.
Symptoms of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen

A hernia may not manifest itself in the form of specific symptoms, but only manifest itself as a protrusion during physical exertion and straining. As for the symptoms that will arise in the future with the development of the disease, it should be noted the pain syndrome, which increases with straining and intense movements. As the disease develops, pain can be of a different nature: sharp, intense, stabbing, prolonged, acute, “dagger”, etc. d.
So, the disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
painful bulging in the midline (usually in the upper section);
nausea, periodically turning into vomiting;
muscle stretch along the midline;
pain during sudden movements, turns, tilts;
pain after eating;
dyspeptic disorders (belching, hiccups, heartburn).
When the condition worsens, the symptoms increase:
during bowel movements, blood may be released;
pain increases and becomes unbearable;
constantly tormented by vomiting;
if at an early stage of the disease a hernia can be corrected independently, then with complicated forms this is impossible.
This is a common symptom, in medical practice there are three stages of the disease: lipoma, initial and formed hernia.
First, fat appears through the crevices in the white line. Further, this stage is replaced by the initial one, at which the bag is formed. With a rupture of the abdominal muscles and the progression of the disease, a small intestine or omentum partially appears in the hernial sac.
The third phase is accompanied by a formed hernia – a painful seal appears on the white line. The hernial ring (through which the internal organs protrude) are oval or round in shape, reaching up to 12 cm in diameter. Often, multiple formations are diagnosed along the white line, which are located one above the other.
The nerve endings of the preperitoneal tissue are often pinched at an early stage and bring pain.
Emergency medical care should be provided when the hernial contents are pinched, especially when the umbilical hernia is pinched, the main signs of which are sharp pains, nausea, vomiting, defecation disorders, etc.
Complications of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen
The most common complication of a hernia of the white line is its pinching. The hernial sac is suddenly squeezed in the place through which it comes out (in the hernial orifice).
Emergency medical attention is required for the following symptoms:
Nausea turning into vomiting;
The presence of blood in the feces, the absence of an act of defecation;
Increasing abdominal pain
Education is not set when lightly pressed in a horizontal position.
When the formation is pinched, the elements of the intestine and other organs that have fallen into the hernial sac are compressed, and the blood flow is disturbed. Gradually, the hernia dies off, but the patient’s condition only worsens. The skin turns pale, the stomach hurts even more, the abdominal muscles harden. Infringement of a hernia poses a danger to the life of the patient.
Diagnosis of a hernia of the white line of the abdomen
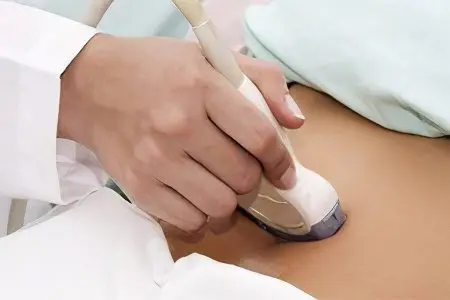
Diagnostic methods include:
Examination by a surgeon;
X-ray of the stomach and duodenum;
Gastroscopy;
Herniography with the introduction of a contrast agent;
Ultrasound examination of hernial formation;
Computed tomography of the abdominal organs.
Surgery to remove a hernia of the white line of the abdomen
A hernia is treated only surgically in a stationary setting. The operation to remove a hernia is referred to as a hernioplasty. To date, about 300 surgical methods for the treatment of hernias of the anterior abdominal wall have been developed. Both simple techniques using the patient’s own tissues and complex reconstructive interventions using artificial materials are used.
There are the following types of operations:
Plastic using local tissues (open intervention with tension plastic). The defect is sutured with a non-absorbable thread with the elimination of a possible divergence of the rectus muscles. Due to the weakness of the connective tissue and a significant load on the postoperative sutures, in 25-40% of cases, a relapse of the disease develops after the intervention, so this method is used infrequently. Another disadvantage is that the long incision leaves a large scar.
Plastic surgery using synthetic prostheses and meshes (open intervention with tension-free plastic surgery). To close the defect after the elimination of diastasis, a mesh of allomaterial is installed. Dentures and meshes provide a strong framework, so the likelihood of recurrence of the disease is low. This is a minimally invasive technique, during the operation a small incision is made in the umbilical region. Through this incision, not only the hernial formation is removed, but also a prosthesis is installed. The mesh can be installed under the aponeurosis (tendon plate), as well as in its lumen and inside the abdominal cavity. Over time, the allomaterial grows into connective tissue, and it becomes impossible to distinguish it from one’s own tissues. The outer seams are also invisible.
laparoscopic intervention. With the advent of high-tech devices, this technique in the treatment of white line hernia is becoming increasingly popular. The incision is not made in this case. Instead, the surgeon makes several holes through which the formation is removed and a mesh prosthesis is inserted. Laparoscopic surgery minimizes the risk of recurrence of the disease and is less traumatic in general. The recovery period after laparoscopy is reduced to ten days (compared to other methods). After that, the patient can return to normal life. This operation is not suitable for patients with heart and lung diseases. Also, its implementation is impossible in the absence of the necessary equipment and qualified specialists.
paraperitoneal intervention. In this case, several punctures are also performed, however, unlike laparoscopy, the peritoneum is not pierced, and instruments are not inserted into the cavity. A special balloon is placed between the peritoneum and adjacent tissues. Due to its inflation, a space is formed that opens access to the hernial formation. The advantages of this method are the same as those of laparoscopy, but the intervention is somewhat more complicated. Because of this, it is impossible to securely fix the mesh prosthesis.
The peculiarity of the radical treatment of a hernia of the white line is that one removal of the formation is not enough. Correction of the divergence of the rectus muscles is required.
The operation can be carried out as planned. The surgeon examines the patient, conducts an examination, makes an accurate diagnosis and sets the date for the operation.
As noted above, now, mainly tension-free techniques are used to eliminate a hernia of the white line and eliminate diastasis.
The advantages of such an operation are as follows:
Reliability, minimal risk of recurrence of the disease;
Simplified intervention technique, which allows it to be used in outpatient practice;
The possibility of using minimally invasive techniques with the introduction of synthetic implants;
Slight tissue trauma, due to which the patient experiences less pain in the postoperative period;
Reduction of the rehabilitation period and temporary disability;
Good cosmetic effect.
How is the operation going?
Before the intervention, the patient takes a number of tests:
Blood and urine for general analysis;
Biochemistry of blood;
Tests for hepatitis, syphilis and HIV;
Passing an electrocardiogram.
During the intervention, the surgeon separates the hernial sac, opens it, assesses the condition of the organs inside and places them in the abdominal cavity. The hernial sac is tied up and cut off, its base is sutured. After that, diastasis is eliminated and the white line is strengthened.
With a strangulated hernia, the operation is performed on an emergency basis. The surgeon opens the bag, evaluates the part of the intestine that has fallen into it. If she died, she is excised. In some cases, a significant part of the intestine dies – then the incision is enlarged and all dead tissue is removed.
The intervention is performed under general anesthesia, the duration of the operation is about an hour (if there are no complications). If a planned operation is performed, the patient leaves the clinic the very next day. Dressings are carried out twice a week. At 10-12 days, the sutures are removed.
Recovery after surgery
With an exacerbation of the disease, surgical intervention is inevitable, but the scale of resection in this case can be expanded. If the formation has already formed, it makes no sense to wear a bandage, since this will only aggravate the situation (squeezing the protrusion is highly not recommended).
Bandages are worn in two cases: to prevent the development of the disease and in the period after surgery to maintain the integrity of the sutures and maintain weakened abdominal muscles.
After the operation, you should also not strain the site of the removed hernia. Heavy lifting is prohibited, physical activity should be avoided in general. After two or three months, when the body is fully restored after the intervention, on the contrary, special exercises are recommended to strengthen the abdominal muscles. You should not make a complex on your own – for this you need to consult a doctor who will recommend an effective restorative set of exercises.
After the intervention, it is necessary to follow a special diet. It is forbidden to consume foods that cause gas formation and stool retention. The diet should be as gentle as possible in order to maintain the integrity of the postoperative sutures and not injure the operated areas. Food should be eaten in small portions. The consumption of liquid dishes and cereals is recommended.
If there are problems with weight, in order to eliminate the risk of re-development of a hernia, it is necessary to normalize body weight and strengthen the muscular corset.
Prediction after surgery. After open interventions with tension methods, the likelihood of recurrence is high: in 25-40% of patients, a hernia occurs again. With tension-free, minimally invasive techniques, the risks of recurrence are low.
In general, the likelihood of recurrence depends on how conscientiously the patient follows the recommendations of the surgeon in the postoperative period.
Prevention of white hernia
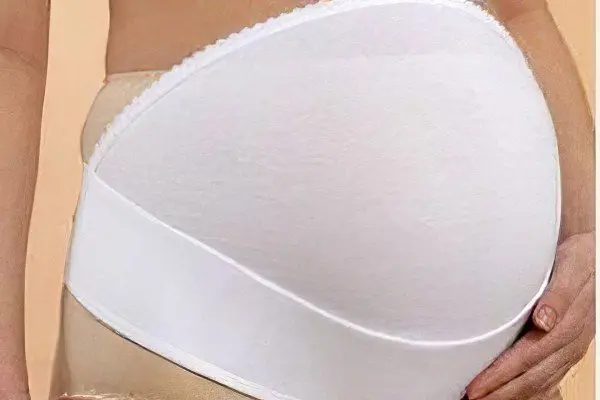

Prevention of white line hernia includes:
The use of a bandage during pregnancy;
Compliance with the principles of healthy eating;
Workouts aimed at strengthening the abdominal muscles;
Normalization of body weight;
Adhere to proper lifting technique.
Separately, you should consider the point that concerns the wearing of a bandage. The abdominal bandage is a knitted tape up to 20 cm wide. It has a special “cushion”, which is placed in the area of the likely occurrence of a hernia.
It is impossible to get rid of a hernia with a bandage. Its use can only aggravate the situation: the bandage, having assumed the functions of the abdominal muscles, weakens them. As a result, they diverge even more, and the hernial protrusion intensifies.
However, in some cases, doctors still recommend wearing a bandage:
A short time before the intervention to prevent increased protrusion;
At the stage when there is only a preperitoneal lipoma, but the hernial formation itself is not yet;
For prevention in people with weak abdominal muscles;
After operations to prevent the recurrence of the disease and reduce pain in the suture area;
People whose work is associated with hard physical labor, professional weightlifters;
Elderly people, debilitated people who have contraindications to surgical intervention.
How to use the bandage correctly:
The bandage is put on in the prone position;
If wearing a bandage is recommended before surgery, the protrusion should be corrected into the abdomen with a slight pressure movement;
The pad should be placed in the area of the hernial formation;
The bandage is wrapped around the torso and secured with a sticky fixative;
A properly fixed bandage should tightly fit the body and press the hernial formation. At the same time, it should not squeeze too much and cause pronounced inconvenience.
To prevent the risk of developing the disease, special preventive measures must be taken. To prevent the disease, pregnant women should wear a bandage, as well as after childbirth, if the stomach does not subside. If there is excess body weight, measures must be taken to reduce it. Moderate exercise will strengthen the abdominal muscles, which also helps prevent the development of a hernia. It is important to monitor the diet – nutrition should be healthy and balanced in order to avoid possible problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Lifting heavy objects should be avoided.
In the postoperative period, it is important to follow all the doctor’s recommendations: follow a special sparing diet and avoid any physical exertion. It is impossible not to treat a hernia, since serious complications that threaten life may develop. It is necessary to understand the full danger of the consequences and take measures to eliminate it at the first sign.
Taking painkillers for a hernia of the white line gives only a temporary effect, but does not contribute to recovery. This is especially fraught with consequences during pinching, as the patient requires emergency medical care.










svaka cast za obrazlozenje, detaljno opisano, saznao sam sve sto me je zanimalo.