Contents
- What does esophageal hernia mean?
- Symptoms of a hernia of the esophagus
- Causes of hernia of the esophagus
- The danger and consequences of a hernia of the esophagus
- Diagnosis of a hernia of the esophagus
- Esophageal hernia treatment
- Esophageal hernia surgery
- Diet for hernia of the esophagus
- Answers to frequently asked questions
Hernia of the esophagus refers to chronic diseases. Pathological changes in the narrow muscular tube and the ligamentous apparatus of the diaphragm lead to serious disturbances in the functioning of all organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Any deviations negatively affect the quality of human life and can cause a lot of unpleasant symptoms and complications. A timely diagnosis will save you from unnecessary problems. It is impossible to start the disease, it is treatable and increases the chances of recovery for those patients who seek medical help at the first sign of illness.
A hernia of the esophagus is more often diagnosed in those over 60. In addition to the age criterion, there is also a connection with gender. Women are more concerned about this disease than men. There is an explanation for everything, like any disease, a hernia of the esophagus has causes and characteristic symptoms. Knowing about them, it is not difficult to determine the presence of pathology. Self-medication in this case is useless and unacceptable, the risk of complications is too high.
How is the disease treated, how effective are modern therapeutic approaches and what to do if there is a suspicion of the development of the disease? We will answer current questions and outline the main points that will allow you to recognize the disease and protect yourself from the consequences.
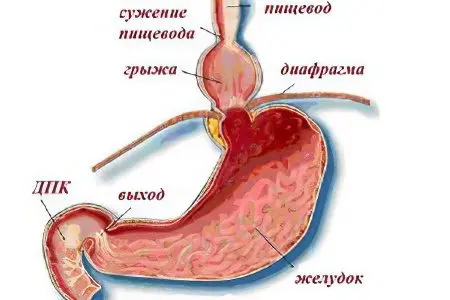
What does esophageal hernia mean?
In a healthy body, each organ takes its place, intended for it anatomically. A muscular plate runs between the abdominal and thoracic cavities. This organ is called the diaphragm. The muscle plays a very important role in the human body, it is the main one and is responsible for breathing. There is a small hole in the diaphragm through which the esophagus passes. Everything that is located under the diaphragm should normally not fall into the thoracic region. This is prevented by connective tissues and ligamentous structures. Any movement into the chest of the esophagus or a separate part of the stomach is considered abnormal. When such a pathology is detected, the patient is diagnosed with a hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm.
With the progression of the disease and the absence of treatment, gastric bile enters the esophagus without problems. Prolonged reflux of contents causes inflammation of the mucous membrane. This organ is not protected from the contents of stomach acid. When inflamed, the mucous membrane is easily damaged, which causes pain. This is one of the main symptoms of a hernia of the esophagus, there are other troubles that accompany the disease.
Symptoms of a hernia of the esophagus
A small hernia of the esophagus does not cause problems for the patient. Quite often there is an asymptomatic form of hernial formations. The disease does not manifest itself in any way and does not cause discomfort. The patient does not even suspect about the problems and continues to live his usual life. Sometimes a serious pathology is discovered by chance during an x-ray or ultrasound.
The disease can manifest itself at any time. As a rule, the activity of clinical manifestations is observed with the progression of the disease and the growth of the hernia. The frequency and severity of symptoms depend on the size of the pathological formation and its type, the presence of concomitant diseases and the complications identified.
Let’s designate the general symptoms of a hernia of the esophagus:
The most common symptom that accompanies almost all known types of disease is heartburn. It can disturb the patient when bending over, after eating, often intensifies at night. Heartburn attacks can be triggered by strenuous exercise, overeating, or drinking too much alcohol. Sometimes the symptom manifests itself in a mild form and does not affect the patient’s well-being. There is also a severe degree of heartburn, when it is difficult for the patient to endure a burning sensation in the chest. This condition can be supplemented by flatulence, nausea and an unpleasant aftertaste in the mouth. When the contents of the stomach are in the esophagus, heartburn becomes sour or bitter. All these manifestations affect the psychological and physical health of a person. Sleep is disturbed, the patient loses efficiency and appetite. (Read also: Causes and symptoms of heartburn, how to get rid of heartburn?)
Pain – Another striking symptom of a hernia of the esophagus. Most patients are familiar with the pain syndrome, which most often manifests itself when bending over and lying down. Pain can be localized behind the sternum, in the hypochondrium, abdomen, in the region of the heart. Pain is usually aching in nature. After eating, they increase, weaken after belching or deep inspiration.
Belching. This symptom can be caused by spasms of the alimentary canal, active work of the stomach and increased intra-abdominal pressure. Involuntary release of air can appear during conversations and eating. Often an attack is accompanied by a characteristic sound and smell. When belching, not only air can be released, but also the contents of the stomach. Taking antispasmodics, which some patients use to relieve a symptom, rarely brings relief, so patients often belch on their own, thereby relieving themselves of discomfort. (Read also: Causes and types of belching after eating)
In 35% of patients diagnosed «hernia of the esophagus» is observed regurgitation. The reasons are the same: eating, tilting, horizontal position. This symptom is typical for formations of medium size and causes a lot of inconvenience. Ingoda, the volumes of vomit are quite large, so the patient has to stock up and carry special containers for vomit.
Common symptoms associated with esophageal hernia include dysphagia or trouble swallowing. This phenomenon can be provoked by haste in the absorption of food, too hot (cold) drinks, neurogenic factors. Dysphagia may be rare or may become permanent. This is usually associated with the addition of complications. With an exacerbation of the disease, complete or partial obstruction of the food consumed is possible. This symptom usually accompanies heartburn. When filling the esophagus, the patient simply cannot swallow food. These unpleasant difficulties cause anxiety and nervousness. Over time, the discomfort increases, which can lead to refusal to eat and serious consequences.
Depending on the type of hernia, clinical manifestations may differ. With a sliding hernial formation of the esophagus, the protrusion goes into the hernial sac. Signs of the disease appear only when the contents of the stomach enter the esophagus. In medicine, this phenomenon is defined by the concept of “gastroesophageal reflux”. The patient may be disturbed by heartburn and pain between the ribs, there are frequent belching and regurgitation.
Another, less common type of hernia is called a periesophageal hernia. When it is present, food stagnates in the stomach. At the same time, pain and discomfort in the chest area are regularly felt. If the disease progresses, the symptoms intensify, usually they are actively manifested after ingestion. In some cases, patients deliberately reduce its volume, and sometimes refuse to eat.
Causes of hernia of the esophagus

The causes of hernias of the esophagus are divided into acquired and congenital. The latter includes the so-called short esophagus. The pathology is rare, but known, a person is already born with a defect. Part of the stomach is located in the chest cavity initially. All other reasons are considered acquired. They usually occur in people over the age of 55, but this does not mean that a disease such as a hernia of the esophagus is not typical for young people. Such cases are known and although the disease is considered age-related, no one is insured.
Let’s highlight the main reasons that contribute to the formation of a hernia:
Increased tissue elasticity and muscle weakness of the diaphragm and esophagus. With age, human tissues and muscles lose their elasticity, they weaken, lose their former activity, which adversely affects their work. Any failures lead to disruption of the functions of the esophageal valve. Muscle weakness caused by age-related changes contributes to the expansion of the opening of the diaphragm, which is the most serious factor provoking the appearance of a hernia. There are frequent cases when the cause of the appearance of pathology is the resorption (resorption) of adipose tissue in the area of the diaphragm. This violation is also associated with age-related changes and explains the frequent occurrence of hernias of the esophagus in the elderly. The young are also at risk, as muscle weakness can be caused by low physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle.
Hereditary predisposition. Muscle weakness is congenital. This pathology can be transmitted to children from parents. Underdevelopment of muscles, long limbs, flat feet, thin bones are also inherited. All these physiological abnormalities are included in the list of causes of esophageal hernia.
Increased pressure in the abdomen. This phenomenon is sudden and regular. In any case, it provokes the expansion of the opening of the diaphragm and the exit of the internal organs or their individual parts into the chest. Intra-abdominal pressure may increase during pregnancy and difficult childbirth, flatulence, ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity), strong, prolonged cough, excessive physical exertion. Among the causes of increased pressure in the abdominal cavity are always overeating, obesity and chronic constipation. There are many risk factors, each of them can provoke the appearance of a hernia.
Violation of motor function and shortening of the esophagus. These physiological abnormalities lead to a pulling up of the esophagus. Such processes can be caused by a number of diseases: cholecystitis, gastric ulcer, pancreatitis, etc. These diseases are usually accompanied by the activity of the stomach, which causes an increase in pressure in the organ. Shortening of the esophagus provokes cicatricial changes. They can appear as a result of thermal (chemical) effects caused by diseases of the stomach and intestines. A regularity was revealed: the longer the disease proceeds, the higher the likelihood of a hernia of the esophagus.
Closed or open damage to the diaphragm. Closed injuries include injuries caused by bruises of the walls of the abdominal cavity and a sharp jump in intra-abdominal pressure. Open injuries are most often associated with the mechanical impact of a wounding projectile. It could be a bullet or a knife. Penetrating through the abdominal or chest cavity, they damage the diaphragm.
In addition to the indicated reasons, the effect on the tone of the diaphragm and the alimentary canal of nicotine, certain medications, caffeine, and hormonal agents is always taken into account.
The danger and consequences of a hernia of the esophagus
Asymptomatic small hernias are usually not treated. The doctor gives the necessary recommendations and, if the patient is responsible for the state of health, complications do not threaten him. A different approach is required in situations where the appearance of a hernia is accompanied by heartburn and frequent pain. In such cases, therapy is mandatory. Proper treatment tactics can avoid serious consequences. The most common complications are: bleeding and erosion of the walls of the esophagus, shortening of the organ, inflammation of the gastric mucosa, incarcerated hernia, cancer of the esophagus.
Any of the complications is accompanied by a deterioration in the patient’s condition. There is shortness of breath and increased heart rate, the skin becomes pale, the temperature often rises. There is a high probability of developing a stomach ulcer affected by a hernia, or chronic gastritis. (Read also: Causes, signs and symptoms of stomach gastritis)
Diagnosis of a hernia of the esophagus
The secrecy and non-specificity of some symptoms, characteristic of a hernia of the esophagus, often leads to the fact that patients lose time and are unsuccessfully treated for other diseases. This can be dangerous, everything related to the diagnosis of internal organs requires not only the participation of professionals, but also special medical equipment. Diagnosis of hernia of the esophagus is quite simple. The doctor prescribes a series of studies and, based on the results obtained, confirms or excludes the presence of pathology.
From instrumental studies for the accuracy of the diagnosis, data may be needed:
Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS). With the help of a fibrogastroscope, the doctor examines the esophagus, stomach, duodenum. The diagnostic procedure is prescribed for almost everyone who suffers from diseases of the intestines and stomach. If during the survey the patient indicated at least one of the characteristic symptoms, the passage of FGDS becomes mandatory in the diagnosis.
X-ray study. Without this procedure, confirmation of the diagnosis is almost impossible. Examination is prescribed for all patients with suspected hernia. The study allows you to assess the condition of internal organs. When conducting, ulcers, narrowing and inflammatory processes in the esophagus may be revealed. This diagnostic method is considered quite effective. It becomes uninformative only in cases of fixed pathologies, when the hernia is localized near the esophagus. In such cases, carry out pH-metry.
pH-metry of the esophagus and stomach. The study is prescribed to determine the regularity of the reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus. To determine the acid-forming gastric function, gastric juice is examined. The procedure is carried out on special equipment. A probe is inserted through the patient’s nose and a skin electrode is placed. All changes are recorded on the block attached to the belt. The data is processed using a computer and special programs.
All diagnostic studies are carried out on an empty stomach. The patient is advised to stop smoking and stop taking medications that may affect the results.
Esophageal hernia treatment
It is desirable to start the examination and start treatment as early as possible. It is not necessary to bring the hernial formation to a serious condition, when irreversible processes begin in the body and the treatment is delayed. A guaranteed positive outcome and full recovery is possible only with a responsible attitude to one’s own health. In the treatment of hernial formations of the esophagus, conservative and surgical treatment methods are used.
Traditional therapy is carried out in order to stabilize the patient’s condition and prevent complications. In cases where a small hernia is detected and there are no clinical manifestations, the doctor advises the patient about the need to correct the diet and lifestyle. The patient should monitor body weight and control physical activity.
Remission can be achieved with drugs whose action is aimed at reducing gastric secretion and protecting the esophageal mucosa from the aggressive effects of gastric juice. With a hernia of the esophagus, a diet and treatment of concomitant diseases is mandatory. If the action of conservative methods does not bring results and the disease progresses, a surgical operation is prescribed.
Esophageal hernia surgery
Sometimes surgery is the only way to prevent serious consequences. The indications for surgery are:
Unsuccessful conservative treatment;
Deterioration of the patient’s condition and the presence of complications (bleeding, erosion, ulcer, inflammation of the esophagus);
Localization of pathology in the hernial ring;
Serious disorders of the esophageal mucosa.
The presence of paraesophageal hernias and increasing risks of infringement of formations.
The operation is not performed during pregnancy, diabetes, serious diseases of the heart and blood vessels, malignant neoplasms.
Each of the existing types of operations has advantages and disadvantages. The choice of the type of operation is made by a specialist, relying on data from preliminary studies. Consider the most common methods of surgical intervention:
Fundoplication according to Nissen
The operation is carried out in an open and closed way. In the first case, access is provided through an incision in the abdominal wall or chest. The closed method involves the use of laparoscopic techniques.
The purpose of the operation is to reduce the diameter of the diaphragm opening. This is made possible thanks to a specially designed cuff.
Disadvantages: The downside is that its fixation is not provided, this can lead to a relapse of the disease.
Advantages: When using the laparoscopic technique, the risk of injury is minimal. The patient quickly recovers and returns to normal life. Reduces the risk of postoperative complications.
Operation Belsey
It is performed in an open way, only thoracic access is allowed. During the operation, the lower esophagus and the esophageal valve are fixed to the diaphragm. The fundus of the stomach is sutured to the anterior wall of the esophagus.
Disadvantages: This complex and painful operation is more difficult for patients to tolerate.
Advantages: Its advantage is the possibility of eliminating concomitant pathology.
Gastrocardiopexy
It is carried out through an incision, the essence is in suturing the esophagus and part of the stomach to the structures located under the diaphragm.
Advantages: Results and forecasts are always good. In addition to the possibility of eliminating other pathologies in the abdominal cavity, gastrocardiopexy almost eliminates the development of complications.
Allison’s method
Access is provided by an incision in the 7,8 intercostal space. During the operation, the doctor sutures the hernial orifice.
Disadvantages: as an independent method, this type of surgical intervention is currently not used. This is due to the high recurrence rate. The use of the Allison technique usually goes in a complex of surgical measures.
Diet for hernia of the esophagus

An increase in intra-abdominal pressure can provoke mechanical damage to the esophagus. All this is accompanied by intestinal obstruction and chronic constipation. These conditions can be corrected with proper nutrition. Diet for hernia of the esophagus is a very important component of conservative treatment. It is also prescribed in cases where the patient is being prepared for surgery. The purpose of the diet is to reduce the acidity of the gastric juice and protect the mucous membranes of the stomach and esophagus.
Food should be fractional. It is best to eat small meals throughout the day. The last dose is 3 hours before bedtime.
Products should not irritate the walls of the esophagus and cause heartburn. It is forbidden to eat very hot and, conversely, too cold food. Foods that cause indigestion and bloating are excluded from the diet.
Prohibited foods include:
Fatty meat, fat;
Bakery products;
soy products;
Beans;
Spicy, salty, smoked;
Citrus fruits, sour apples, cabbage, raw beets;
Rough cereals;
Nuts and seeds;
Black bread;
Seasonings, spices;
Chocolate;
Carbonated drinks;
For a hernia of the esophagus, it is recommended:
Dairy products;
vegetable soups;
boiled fish;
Light cereals;
Lean meat;
Fresh vegetables and fruits (pears, peaches, bananas).
The therapeutic diet and following the diet has a positive effect on the well-being and condition of the patient. The risk of developing complications dangerous to health is significantly reduced.
Answers to frequently asked questions

What are the consequences of a hernia of the esophagus? In the absence of treatment, the consequences are inevitable. Complications can be of a different nature and manifest themselves in different forms. The development of gastritis and peptic ulcer of the stomach is not excluded. It is not uncommon for a patient to experience hidden bleeding. Constant blood loss leads to anemia (anemia). This disease almost always accompanies weakness, malaise, sleep disturbance, pallor of the skin. One of the serious consequences is the intussusception of the organ. This condition is characterized by self-wrapping of the esophagus inside itself. A hernia of the esophagus can be accompanied by complications such as shortening of the organ and strangulation of the hernia. Sometimes the disease develops into cancer. The risk of developing malignant tumors increases if the patient does not receive the necessary treatment for more than 5 years.
What not to do with a diagnosis «hernia of the esophagus“? With a hernia of the esophagus, it is not recommended to overeat. Body weight must be constantly monitored and kept in the normal range. It is forbidden to lift weights, overwork, actively engage in sports. Physical activity should be controlled. It is very important to monitor nutrition and prevent constipation. It is undesirable to make sharp bends forward, after eating this is especially true. You can not wear uncomfortable tight clothes, tight belts, corsets, bandages that squeeze the stomach.
What to do when a hernia is discovered during pregnancy? The appearance of a hernia of the esophagus during pregnancy is a frequent phenomenon. The symptoms are the same, the difference is in the treatment approaches. Surgery during pregnancy is contraindicated, for this reason, doctors use methods of conservative therapy. The main recommendations relate to nutrition. Sometimes medications are prescribed. Usually these are astringent or enveloping drugs, antispasmodics and antacids that help reduce acidity in the stomach. Complications are possible during childbirth. For women with a similar diagnosis, experts recommend a caesarean section.
Do they take to the army with a hernia of the esophagus? It all depends on the presence or absence of violations to which the hernia leads. If the pathology negatively affects the functions of the organs of the thoracic region and regular infringement of the hernia is noted (more than 2 times a year), the conscript is assigned category D, confirming unsuitability for military service. With satisfactory results after treatment and no violations, category B is approved, providing for limited suitability.
How is esophageal hernia coded in the International Classification of Diseases (ICD)? To designate a diaphragmatic hernia (K44), the following encodings are used:
K44 – pathology with confirmed obstruction and the absence of gangrene.
K44.1 – hernia with detected gangrene.
K44.9 – hernia without gangrene and obstruction.
Q40.1 – hiatal hernia (congenital). Q79.0 – diaphragmatic hernia (congenital).
Is it possible to play sports with a hernia of the spine? It is possible, but with caution. Weight lifting and abdominal exercises are contraindicated. Other types of physical activity are acceptable. Before going to the gym, you should consult with your doctor.









