Contents
Hemosiderosis is a violation of metabolic processes in the body, which is explained by the excessive content of a pigment called hemosiderin in tissue cells. This pigment is formed as a result of the breakdown of hemoglobin, which is affected by endogenous enzymes. Hemosiderin is involved in the delivery of certain chemicals to tissues. Certain disorders in the body lead to the development of a disease such as hemosiderosis, including: its excessive absorption in the intestines, disruptions in metabolic processes, and too intense the process of destruction of red blood cells.
Hemosiderosis is not the only designation for this pathology. The disease is also called pigmentary hemorrhagic dermatosis, chronic pigmentary purpura.
Hemosiderosis can be local, affecting only the skin and lungs, or it can be generalized. In the latter case, the pigment begins to accumulate in excess in the liver, bone marrow, kidneys, sweat and salivary glands, as well as in other internal organs.
At the same time, regardless of the form of the disease, it manifests itself with the same symptoms, including: hemorrhagic rashes on the skin (the rash has a reddish tint), hemoptysis, anemia, chronic fatigue syndrome. Most often, older men suffer from hemosiderosis. Children of this pathology are practically not affected.
It is very difficult to treat hemosiderosis, since this disease is not just a defect in appearance. Its causes lie in global disturbances of metabolic processes in the body, which lead to a malfunction in the functioning of all internal organs.
Doctors of various profiles can detect and treat hemosiderosis: dermatologists, pulmonologists, immunologists, hematologists. In this case, the patient is prescribed hormonal steroid drugs, cytostatics, angioprotectors, vitamin-mineral complexes, plasmapheresis.
Types of hemosiderosis
With hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells and the release of hemoglobin from them) outside the vascular bed in any organ or hematoma, hemosiderosis develops. Excessive pigment content in a certain area of the body does not lead to tissue damage, but if they have already been subject to sclerotic changes, then the work of the organ will be disrupted.
Hemosiderin deposits in tissues (idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis):
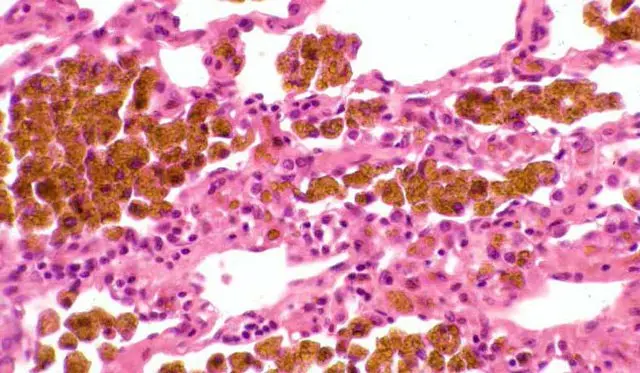
With intravascular hemolysis, general hemosiderosis develops, which is accompanied by massive deposits of hemosiderin in the internal organs. More often than others, liver and spleen cells suffer, but other internal organs can also be affected. They change their light to darker, as a lot of pigment accumulates in them. Most often, general hemosiderosis develops against the background of systemic lesions of the body.
There are also several more forms of hemosiderosis:
Pulmonary essential.
Hereditary.
Dermatological. This form of hemosiderosis is represented by such pathologies as Mayocchi’s disease, ocher dermatitis, Gougereau-Blum disease, Schamberg’s disease.
Hepatic.
Idiopathic.
Causes of hemosiderosis
Until now, the causes of the development of hemosiderosis have not been fully disclosed. Hemosiderosis is not a major disease, but a secondary condition that develops against the background of disorders already present in the body.
The following persons are at risk for the development of hemosiderosis:
People with diseases of the blood and the hematopoietic system (leukemia, hemolytic anemia).
People with infectious diseases: with sepsis, brucellosis, malaria, typhoid.
People suffering from autoimmune pathologies, from disorders in the immune system.
People with diseases of the vascular wall.
Patients with vascular pathologies: with chronic venous insufficiency, with high blood pressure.
People with intoxication of the body.
Women in whose body the Rhesus conflict develops.
Hemosiderosis can occur in people who receive frequent blood transfusions. Also at risk are people with a hereditary predisposition to this disorder. Dermatological diseases, wounds and abrasions on the skin, hypothermia, taking a number of medications, as well as excessive intake of iron with food increase the likelihood of developing hemosiderosis.
Symptoms of hemosiderosis
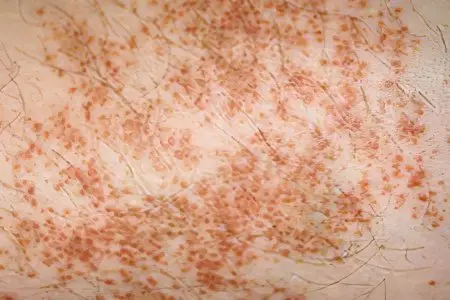
Symptoms of hemosiderosis are largely determined by the location of the lesion. Pathology manifests unexpectedly for a person, but has a smooth development.
If hemosiderosis affects the skin, then the rash can persist on it for several months and even years. In this case, a person suffers from itching, which can be very intense. Pigmentation has the form of a spot with clear boundaries. The spots themselves are colored red, when pressed on the skin, they do not disappear.
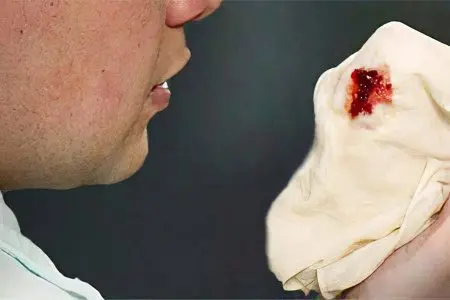
With pulmonary hemosiderosis, the patient begins to be haunted by shortness of breath, which occurs even at rest. A person suffers from a wet cough, during which bloody sputum is released. The body temperature rises to high levels, symptoms of respiratory failure increase, the liver and spleen increase in size, signs of anemia appear. After a few days, relief occurs, while the level of hemoglobin in the body returns to normal.
Hemosiderosis of the lungs
Pulmonary hemosiderosis is a disease with an unexplained etiology. It has a severe chronic course. In this case, the patient often experiences repeated hemorrhages in the alveoli, and the red blood cells disintegrate in the lung parenchyma. In parallel, a significant amount of hemosiderin is released from them. All these pathological processes lead to the fact that the lungs begin to cope worse and worse with their main function.
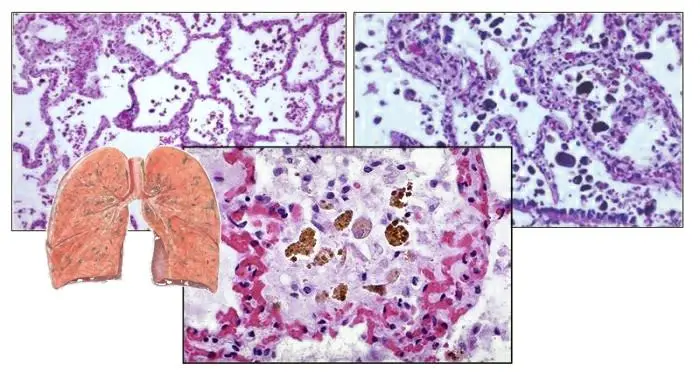
Symptoms of pulmonary hemosiderosis in the acute stage of the disease:
Cough with bloody sputum.
Pale skin.
Hemorrhages in the eye sclera.
Feeling of chronic fatigue.
Dyspnea.
Pain in the chest and joints.
Increased body temperature.
Cardiopalmus.
Hypotension.
Enlargement of the spleen and liver in size.
When the acute stage of the disease is left behind, the person begins to feel satisfactory. At this time, he is able to do his job, lead a full life. However, as the disease progresses, relapses become more frequent, and the calm period becomes shorter and shorter.
If hemosiderosis has a severe course, then the patient develops cor pulmonale, pneumonia, pneumothorax. Even the death of a person is possible.
After autopsy, a number of patients have brown induration of the lungs, which is rarely diagnosed during a person’s life. In the blood of such patients, autoantibodies are formed, which are a spike of antibodies and antigens. This leads to the development of an inflammatory reaction, which is localized in the lungs, since it is their tissue that becomes the target for attacks by autoantibodies. Small vessels penetrating the parenchyma of the lungs expand. Red blood cells come out of them, which disintegrate directly in the lung tissue, which leads to an excessive accumulation of hemosiderin.
Skin hemosiderosis
When the skin is damaged, rashes appear on them, which have a dark color. They are formed due to excessive accumulation of pigment in the skin cells, against the background of the destruction of the capillaries penetrating its papillary layer.
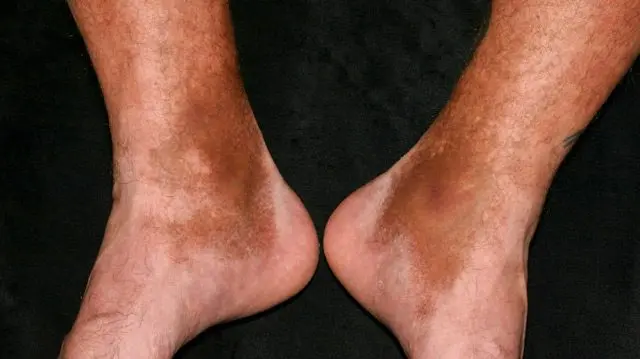
The intensity of the color of the rashes can vary, the same applies to their size. Reappearing rashes have a more saturated color, which is close to red. Rashes that exist on the skin for a long time, on the contrary, turn pale, becoming brown or yellowish. The spots are located on the arms and legs, on the hands and forearms. Their size can reach 3 cm. Also, nodules, plaques, papules and petichias often form on the skin. Patients may indicate itching and burning of the skin.
In the capillaries penetrating the dermis, pressure increases. This leads to the fact that plasma containing red blood cells begins to seep through them. They are destroyed, which entails deposits of hemosiderin. When conducting a clinical blood test, a decrease in the level of platelets and anemia will be detected.
Most often, the cutaneous form of hemosiderosis occurs in the form of orthostatic, eczema-like and itchy purpura, or in the form of Mallorca’s disease.
Schamberg disease
Schamberg’s disease is a common autoimmune disorder that has a chronic course. At the same time, red rashes appear on the human body, resembling a trace from an injection. In the vascular walls, immune complexes begin to be deposited, which lead to the development of an autoimmune inflammatory process in the inner layers of the dermis. For this reason, the skin is covered with small hemorrhages. As hemosiderin accumulates in its papillary layer, the spots increase in size and become brown in color. In the future, they merge, forming large plaques, bordered by a bright red rim.
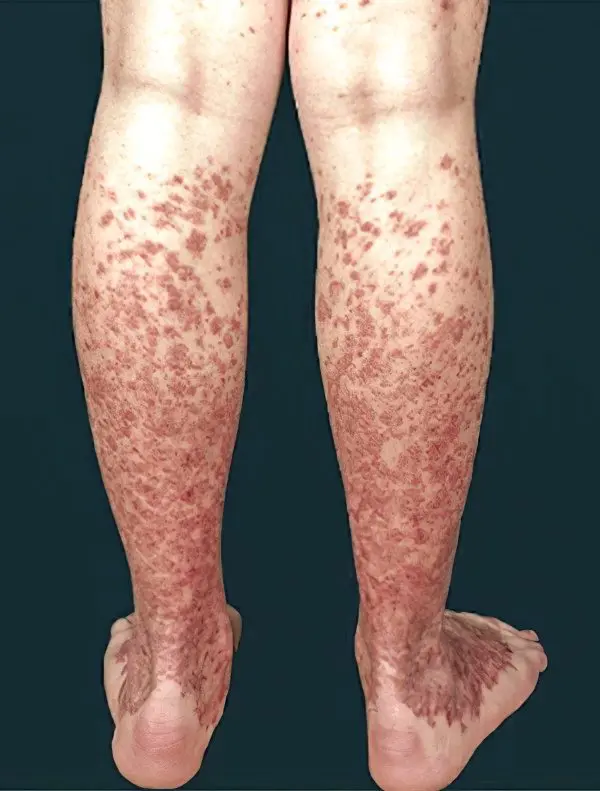
As the disease progresses, plaques merge with each other and begin to atrophy. At the same time, the general well-being of a person does not suffer.
In general, dermatological hemosiderosis responds well to treatment, which is different from hemosiderosis of other localizations. Patient recovery is fast.
Hemosiderosis of internal organs
With severe intravascular hemolysis of erythrocytes, the patient develops generalized or systemic hemosiderosis. Internal organs suffer, their performance is disturbed, which affects the well-being of a person.
In hemosiderosis livers pigment deposition occurs in hepatocytes. The disease can develop as an independent pathology, or as a result of other disorders in the body, and often the cause of hemosiderosis cannot be found out. In this case, an increase in the size of the liver occurs, which becomes obvious even when you click on the area where it is located. As the disease progresses, ascitic fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity, blood pressure rises, the skin becomes yellow, the spleen increases in size, pigmentation areas appear on the arms, under the armpits and on the face. If there is no treatment, then the patient develops acidosis and falls into a coma.
With hemosiderosis of the kidneys they are covered with brown granules. The disease proceeds according to the type of nephritis or nephrosis. A protein component is found in the urine, the level of lipids in the blood rises. A person notices swelling of the lower extremities, pain in the lumbar region, the desire to eat disappears, and dyspeptic disorders develop. In the absence of adequate and timely therapy, renal failure develops, which often causes death.
Hemosiderosis of the liver (left) and kidneys (right):
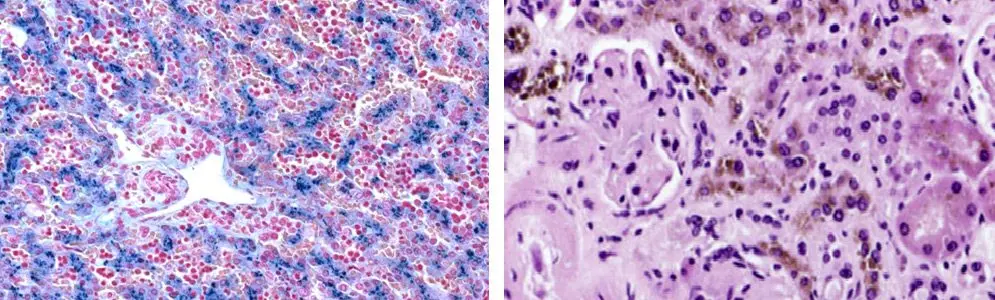
In addition, the accumulation of hemosiderin can occur in the brain, in the spleen and in other internal organs. All these conditions are associated with severe disorders on the part of the affected systems, which often ends in death.
Systemic hemosiderosis is a disease that is associated with a threat to human life.
Diagnosis of hemosiderosis

To clarify the diagnosis, a standard examination of the patient is not enough.
After its completion, it is necessary to appoint the following studies:
Blood sampling for a general analysis with the determination of serum iron and the total ability of the blood to bind iron.
Biopsy of organ tissues with subsequent histological examination of the material taken.
Desferal test. This study allows you to detect hemosiderin in the urine, for which the patient is injected with Desferal. The injection is done intramuscularly.
Microscopic examination of the dermis of the patient in the presence of rashes on the skin.
Auxiliary research methods are:
Passage of X-ray examination.
Passage of CT and scintigraphy.
Performing a bronchoscopy.
Performing spirometry.
Examination of sputum under a microscope and performing its bacteriological culture.
Treatment of hemosiderosis

Therapy of hemosiderosis requires the following recommendations:
Compliance with a diet with the rejection of alcoholic beverages. Be sure to remove from the menu all products that can provoke an allergic reaction.
It is important to avoid hypothermia, injuries, overheating of the body, as well as mental and physical overstrain.
All diseases must be treated in a timely manner.
Chronic foci of infection must be eliminated.
It is important to avoid using cosmetics that can cause allergies.
All bad habits should be forgotten.
Drug therapy involves the use of the following medications:
Reception and local application of hormonal steroid drugs, including: Prednisolone, Betamethasone, Dexamethasone.
Taking drugs to reduce the inflammatory response: Indomethacin and Ibuprofen.
Reception of antiplatelet agents: Aspirin, Cardiomagnyl.
Taking drugs that have an immunosuppressive effect: Azathioprine, Cyclophosphamide.
Priëm angioprotektorov: Diosmin, Hesperidin.
Taking nootropics: Piracetam, Vinpocetine, Maxidol.
Taking drugs against allergies: Suprastin, Tavegil, Diazolin.
Intake of vitamins and minerals: vitamin C, rutin, calcium.
Also, the patient may be prescribed iron preparations, drugs to stop bleeding, bronchodilators. Oxygen therapy is possible. Also, patients are referred for hemosorption, cryoprecipitation, cryotherapy and plasmapheresis. Sometimes a blood transfusion or removal of the spleen is required.
Traditional medicine recommends using an infusion of hazel bark and mountain arnica, as well as a decoction of thick-leaved bergenia.
Prevention of hemosiderosis
Hemosiderosis is a disease that often worsens. Provided that a person receives high-quality treatment, relapses will occur less frequently, but for this you need to follow preventive measures, including: proper nutrition, treatment in specialized sanatoriums, maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
To prevent the development of hemosiderosis, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
Do not self-medicate infectious diseases, but seek medical help in a timely manner.
Maintain vascular health.
Control blood pressure, monitor your weight and cholesterol.
Minimize the risks of intoxication of the body.









