Contents
Hemorrhagic gastritis – what is it?
Hemorrhagic gastritis is a type of inflammatory process in the gastric mucosa. Its peculiarity is that it is not inflammation that primarily occurs, but vascular microcirculatory disorders in the submucosal layer. Their result is hemorrhage and hemorrhagic (bloody) impregnation of the mucous membrane, or the formation of blood clots in the smallest vessels of the stomach. The result of the described processes is inflammation of the mucosa with its leukocyte infiltration at the microscopic level and the formation of small surface defects (erosions), which are determined visually.
Therefore, hemorrhagic gastritis is often called erosive or erosive-hemorrhagic. This is not always correct, since not every hemorrhagic gastritis can become erosive. Both of these options can be independent forms of the disease.
Symptoms of hemorrhagic gastritis
With regard to clinical manifestations, hemorrhagic gastritis cannot be attributed to diseases with specific symptoms. Its main features are characteristic of almost all types of gastritis and gastric ulcer. But there are also specific symptoms, on the basis of which hemorrhagic gastritis can be suspected.
Symptoms of hemorrhagic gastritis are presented in the form of a table.
Complaints |
|
Inspection data |
|
Diagnostic data |
|
Acute hemorrhagic gastritis
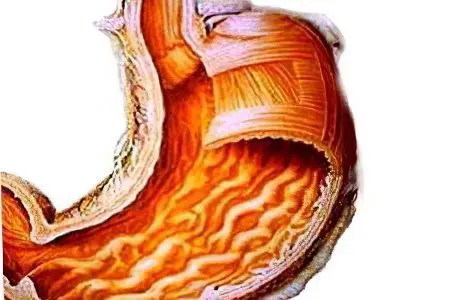
If hemorrhagic gastritis occurs for the first time or is characterized by a fulminant course of its recurrence, it is considered to be acute. It is distinguished by relatively more vivid clinical symptoms of the inflammatory process. Signs of stomach bleeding are rare. The causes of acute hemorrhagic gastritis are the following factors:
Poor quality food products. These can be either dishes spoiled during long-term storage, or products contaminated with toxic substances;
Chemicals, industrial poisons, salts of heavy metals. They can get into the stomach cavity either when working with them, or as a result of deliberate use. In this case, a chemical burn of the mucous membrane occurs, which subsequently turns into hemorrhagic or erosive gastritis;
Excessive amount of alcohol consumed or its poor quality;
Systemic connective tissue diseases and severe intoxication of the body against the background of any diseases that lead to disruption of microcirculatory processes in the stomach;
Closed blunt trauma to the abdomen, when there is a contusion of the stomach, or diagnostic studies, accompanied by damage to the mucous membrane.
The occurrence of acute hemorrhagic gastritis under the influence of these factors suggests that this process has a very rapid onset and is not associated with a violation of secretory mechanisms. Its origin is associated with the impact on the body of harmful environmental factors. This feature determined its vivid clinical picture and manifestations, which are several times stronger than in the chronic course of the disease.
Diet for hemorrhagic gastritis

Dietary recommendations and nutrition for hemorrhagic gastritis are one of the main methods of its prevention and occupy an important position in its treatment. In some cases of the disease, even their observance does not protect against repeated exacerbations of the process. But the control of the rules of dietary nutrition within the framework of table No. 1 in the acute stage of the disease, and No. 5 when the inflammatory process subsides is mandatory. They include:
Excluded: spicy, fried, smoked dishes, spices, fatty and rough foods, fresh bread and pastries, citrus fruits, legumes, cucumbers and tomatoes;
The emphasis should be on light liquid or semi-liquid dishes (soup, cream soup, mashed potatoes, jelly) in a warm form. Hot or too cold food is unacceptable;
Dishes should be boiled or steamed;
Allowed products: bran bread or stale white bread (crackers), buckwheat, rice, oatmeal, meat of dietary varieties (chicken, rabbit) and broths, steam dishes based on them, scrambled eggs and soft-boiled eggs, sour-milk products (yogurt, kefir, low-fat cottage cheese), boiled vegetables, fruit and berry compotes and fruit drinks;
Number of meals. Organization of nutrition involves regular 5-6 times the intake of moderate portions at the same time. Overeating is not allowed.
Treatment of hemorrhagic gastritis
The complex of therapeutic measures for hemorrhagic gastritis should include medications that act on all links in the pathogenesis of this disease. These should be:
Antisecretory agents. By reducing the secretion of gastric juice and hydrochloric acid, conditions are created to reduce inflammatory changes. The main active ingredient of such drugs is omeprazole;
Gastrocytoprotectors – means protecting the mucous membrane from aggressive components of gastric juice and environmental factors: phosphalugel, almagel, maalox, venter;
Hemostatic drugs. Indicated in the presence of signs of gastric bleeding. You need to understand that in case of bloody vomiting, you must definitely call an ambulance, do not self-medicate.
Enzyme preparations. They are prescribed to facilitate the digestive processes;









