Contents
Helminthiasis occurs in people all over the world. The prevalence of a particular parasitic invasion depends on the specific category of the population. So, children are most often infected with pinworms, fishermen with diphyllobothriasis, hunters with trichinosis. Meanwhile, helminthiases contribute to the development of dangerous diseases that were not previously associated with parasites. Recent studies allow us to reasonably assert that there is a clear relationship between oncological diseases and the presence of helminths in the body.
The danger of helminthiases comes down to the fact that they most often have a latent course. Parasites can exist in the human body for years and do not give themselves away. At this time, the patient himself will be unsuccessfully treated for diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, gallbladder, etc. Therefore, it is so important to know the signs and symptoms that indicate the presence of helminths in the human body.
What are helminths?
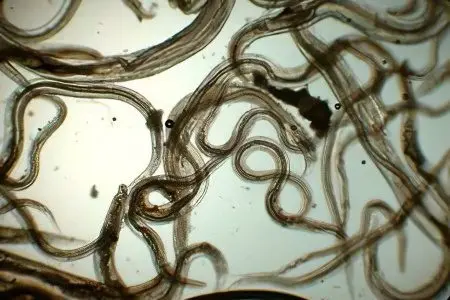
Helminths, colloquially called worms, are parasitic worms that live in humans, animals, or plants. Infection with parasites is called “helminthiasis” and is extremely common: every year, millions of people around the world are infected with helminths. The most common types of helminthiases are ascariasis, hookworm and trichuriasis.
Helminths are considered tapeworms, flatworms and roundworms. A person can be a carrier of four hundred species of parasites such as nematodes, acanthocephalans, flat and annelids. Each of these groups has several classes that parasitize in the human body. For example, trematodes cause trematodosis, tapeworms (cestodes) cause cestodosis, acanthocephaloses cause acanthocephalosis, and nematodes cause nematodes.
Features of the life cycle of helminths most often do not allow them to multiply in the human body (with the exception of pinworms and some other worms).
Helminths can be localized in the intestinal lumen and the intestine itself (ascariasis, trichuriasis, teniarinhoz, strongyloidiasis), in the organs of the hepatobiliary system (liver, gallbladder, biliary tract), lungs (paragonimiasis, tominxosis) and in other tissues.
In addition to mechanical damage, worms harm the body with the products of their metabolism and decay.
Helminthiases can occur in two stages: early (acute) and late (chronic). At an early stage, the main harm comes from the toxic-allergenic effect of enzymes and metabolic products of helminth larvae. As a result of helminthic invasion, an inflammatory reaction occurs. The course of the chronic stage of helminthiasis depends on the type of parasite.
Helminthiasis is a dangerous disease, because it aggravates the course of diseases already existing in a person, inhibits the body’s defenses, and has a detrimental effect on the nervous system, development and working capacity of a person. Parasites also reduce the effectiveness of vaccines and increase the number of pathogenic microorganisms in the human intestine.
The most dangerous is the defeat of helminths of the central nervous system, heart and eyes.
Causes of helminths

In short, the infection with helminths occurs mainly through water and food. Some parasites (schistosomes, hookworms) can enter the human body through the skin. Much less often, parasites can be transmitted transmissibly or by airborne droplets (when a person swallows helminth eggs along with dust and air). But mostly infection occurs due to the consumption of unwashed food, drinking dirty water and non-compliance with basic hygiene rules.
Carriers of parasites and their sources are those organisms in which helminths grow and lay eggs. It can be either a person or an animal. A person is able to be not only the final, but also the intermediate host of worms.
How does helminth infection occur?

If you tell in detail about the causes of infection, then helminth eggs can enter the human body in the following ways:
Contact helminthiases are those infestations that are transmitted from one person to another. Contact helminthiases are the most common, for example, this group includes a disease such as enterobiasis (pinworm infection).
Geohelminthiases are those invasions that are transmitted through the soil (through water), in which there are mature eggs of parasites. They get there with the feces of animals or humans. It is possible to transfer invasive eggs to food by insects (flies, cockroaches, etc.), infection by direct contact with a sick animal is not excluded.
Biohelminthiases are those invasions that a person becomes infected with when eating animal meat and fish that have not undergone proper heat treatment. The danger is barbecue, sushi, meat, dried fish, lard, etc.
Some helminths are able to enter the human body with insect bites.
The leading mechanism of infection is fecal-oral, in which a person puts helminth eggs into his mouth in one way or another. Most often this happens while eating or drinking.
Infection with helminths through the soil. Almost any contact with the soil poses a danger in terms of infection with parasites, therefore, after working with the earth, it is necessary not only to wash your hands with soap and water, but to carefully treat your nails. It is important to monitor the length of nails in children and cut them off in a timely manner.
All products that grow in the ground and that a person consumes raw must be washed under running water and scalded with boiling water. This applies to vegetables, fruits and herbs.
Pets that walk on the street are able to bring on themselves a huge amount of dirt, including parasites. Therefore, the contact of children and pets always carries the risk of infection. Moreover, cats and dogs can be carriers of almost all types of helminths.
Among the insects that spread the infection, flies are recognized as the most dangerous. They are frequent inhabitants of toilets, cattle pens, after which they are completely free to crawl on food, carrying helminth eggs on their paws and wings.

Infection with helminths from a sick person. When female pinworms mature in the child’s body, they crawl out onto the skin of the anal folds in order to lay eggs. One individual leaves about 5000 eggs near the anus. The process of laying them provokes the appearance of severe itching, as a result of which the child begins to comb the problem area. Eggs spread to underwear, to bedding, to the arms of the child. Then he touches toys, door handles, furniture and other household items with these hands. They are touched by other children and adults. Helminth eggs are attached to their hands, after which they are brought into the mouth during meals. The risk of invasion increases many times if you neglect the rules of hygiene and do not wash your hands before eating, after visiting the toilet and public places. This is the mechanism of transmission of helminths from person to person.
Infection with helminths through water. The water way of distribution of helminths is also an actual problem. A huge number of eggs fall into open water, into wells, springs, etc. Therefore, it is so important to use filters with a bactericidal effect, especially for those people who live in rural areas. Always boil before drinking. Parents need to ensure that children do not swallow water while swimming in lakes and rivers. Moreover, you should not drink water from open sources, even from springs.
Children are the most susceptible to helminthiases. This is due to certain reasons. Firstly, it is easier for helminths to get along in the body of a child, since his defenses are not yet fully formed, and the acidity of gastric juice is low compared to the acidity of adult gastric juice. Secondly, the child learns to follow hygiene rules on his own by about 5-6 years. Until that time, he “tastes” the whole world around him. Therefore, the risk of invasion not only of the child, but also of all members of his family remains, at least until the baby enters school.
No helminths are capable of endlessly multiplying and existing in the human body. All of them have a certain life expectancy and after a while they simply die. For example, roundworms live no more than a year, and pinworms no more than 2 months. In order for a person to be infected again, it is necessary to re-enter the eggs in the digestive tract. Only in this way can the life cycle of helminths continue.
Where can helminths parasitize?
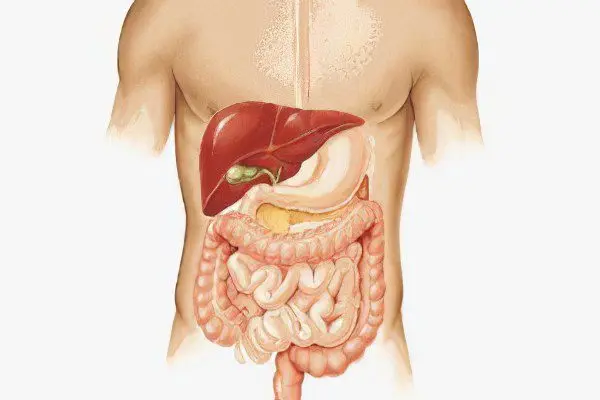
There are tissue and luminal helminths, which depends on the place of their existence in the human body.
Translucent helminths live mainly in the intestinal cavity. About 100 species of parasites are known to inhabit various parts of this digestive organ. These include roundworms, broad tapeworm, hookworms – they all parasitize in the small intestine. The “guest” of the large intestine is whipworm. The lower third of the small intestine is inhabited by pinworms and pygmy tapeworm.
Tissue helminths parasitize inside human organs and tissues. They are found in the muscles, in the brain (cysticercosis), in the lungs (paragonimiasis), in the liver (echinococcosis). Parasites such as filariae can infect the lymphatic tract.
There are also helminths, which can be simultaneously attributed to both tissue and luminal. For example, roundworms in the larval stage can get into almost any organ with the bloodstream, but the worm becomes sexually mature only in the intestinal cavity.
Common symptoms of helminths in humans

Signs of helminths in the human body can be very diverse. The most striking of them are: weight loss, blanching of the skin, itching in the anus, asthenic syndrome. However, these symptoms will be fully expressed with a massive invasion by helminths. To suspect the presence of parasites in the body, you can focus on some other signs that indirectly indicate helminthiasis. Moreover, the patient often perceives them as symptoms of another disease, from which he begins to be treated in vain.
Symptoms of the acute stage of infection with helminths. Usually, symptoms of helminth infection appear two to four weeks after infection. Helminthiases are characterized by an increase in temperature, the appearance of a rash on the skin, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes (conjunctivitis), swelling of the face. Also, diseases of the upper respiratory tract can become a symptom of helminthic invasion. In particular, children are often diagnosed with tonsillitis, swollen lymph nodes (lymphadenopathy), pneumonia, pleurisy, bronchitis and bronchospasm. Parasites can harm all tissues of the body, affecting the heart (myocarditis), liver (hepatitis), diseases of the central nervous system (meningoencephalitis, cerebral vascular thrombosis).
Symptoms of the acute stage of helminthic invasion can occur from 7 days to 4 months, and if the patient has not been provided with effective assistance, the disease flows into the chronic stage, the clinical manifestations of which depend on the type of pathogen of helminthiasis. The patient may retain allergy symptoms, which, with certain helminthiases (their larval forms), can even cause anaphylactic shock. The rest of the symptoms depend on where the helminths are localized, what size they are and how many there are.
For example, helminthic intestinal damage is expressed by digestive disorders, pain in the lower abdomen; with damage to the biliary system, pain appears at the top of the abdomen, in the side. In addition, frequent symptoms are weakness, decreased ability to work, increased fatigue, anemia.
The most dangerous forms of helminthiases are damage to the eyes, kidneys, heart, lungs or brain.
Malfunctions in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. If a person has an intestinal parasitic invasion, then the intestines will be the first to signal the presence of a helminth in the body. Symptoms are reduced to the occurrence of diarrhea, which is replaced by prolonged constipation, vomiting and abdominal pain may occur. The place of localization of pain is the umbilical region and the right hypochondrium. In addition, a person suffers from excessive gas formation.
Such symptoms may be pronounced, or may not be too intense. It depends primarily on how many helminths parasitize in the intestines. Some of them are able to produce hormone-like substances that provoke diarrhea. If large worms parasitize in the intestines, then in large numbers they can cause intestinal obstruction.

neurological symptoms. The more helminths in the body, the more toxic substances they release. These waste products of parasites primarily negatively affect the functioning of the nervous system.
A person begins to suffer from frequent headaches, dizziness, nausea. Often people confuse these symptoms with migraines and take painkillers to stop unwanted symptoms of the disease.
In parallel, there may be pain in the joints, pain in the muscles. Some patients note an increase in body temperature up to 38 ° C and above.
Depression of the nervous system and lack of vitamins contribute to the rapid fatigue of the patient, the development of chronic fatigue syndrome. A person experiences weakness all the time, he has problems with sleep, and in the daytime he becomes more irritable. Children often cry out at night, complain of nightmares. All this leads to a decrease in academic performance and to a lag in development.
Allergic reactions, manifestations of the skin. From the vital activity of helminths, human skin suffers. Allergic reactions almost always accompany helminthiases. At the same time, even some of its own proteins, the immune system perceives as waste products of worms and attacks them. Skin rashes are the result of the release of histamine by mast cells and the accumulation of plasma, which slightly lifts the skin.
Allergic reactions can proceed according to the type of urticaria, allergic rhinitis or bronchitis, the development of bronchial asthma is possible. In addition, the condition of the patient’s nails and hair worsens, cracks appear on the heels, the skin of the feet and palms begins to peel off.
Deterioration of the immune system. Helminthiases always negatively affect the state of the immune system. Existing chronic diseases are exacerbated in a person, and inflammatory processes in various organs may develop. Nasopharynx, reproductive system suffers. Stomatitis, sinusitis, vulvovaginitis, etc. are often observed.
Some scientists believe that nighttime teeth grinding is a sign of helminthiasis.
Symptoms of helminths, depending on their type

Different types of worms will cause different symptoms. In addition, they depend on the massiveness of the invasion and on the place of parasitization of the worm in the body. With ascariasis, the first signs of the disease may appear as early as 2 days from the moment of infection. However, most of the helminths make themselves felt 14-21 days after the invasion. Although the incubation period can be much longer. For example, with filariasis, it ranges from six months or more.
Very often there is a complete absence of any symptoms of the disease, especially if one helminth parasitizes in the body. Signs of invasion may appear only when the parasite reaches a huge size, for example, as in the case of infection with a wide tapeworm.
Symptoms of enterobiosis (asthma). A specific sign of the presence of pinworms in the intestines is severe anal itching, which tends to increase at night. Itching occurs with a frequency of 1-2 weeks, provided that a small number of helminths parasitize in the intestines. In the case when the invasion is massive, itching will bother you on an ongoing basis.
Symptoms of ascariasis (ascaris). Symptoms of ascariasis depend on the phase of development of the helminths. During migration through the systemic circulation, the larvae enter the lungs and other organs. This is expressed in a slight increase in body temperature, in increased weakness, in the appearance of a cough with sputum. X-ray of the lungs, carried out at this time, allows you to visualize volatile infiltrates, which either disappear or appear in other places.
If the invasion is massive, then the development of pneumonia and even ascariasis suffocation is not excluded. At the same time, a person develops allergic reactions, there is a jump in eosinophils in the blood.
When ascaris larvae reach the intestines and begin to grow and multiply, functional disorders of the digestive system come to the fore in the patient. A person loses weight, as roundworms produce substances that block enzymes such as pepsin and trypsin. They, in turn, are responsible for the process of assimilation of proteins.
Ascariasis is dangerous with complications, including: pancreatitis, jaundice, appendicitis, development of intestinal obstruction.
Symptoms of trichuriasis, hookworm, schistosomiasis and diphyllobothriasis. These helminthiases contribute to the development of vitamin deficiency and anemia. Worms produce toxins that have a negative effect on the normal intestinal microflora. Thus, it creates favorable conditions for the reproduction of pathogenic flora.
Symptoms of trichinosis. Helminthiasis is manifested by myalgia, fever, swelling of the eyelids and face.
Symptoms of fascioliasis, clonorchiasis and opisthorchiasis. These are hepatic helminthiases that provoke characteristic symptoms. The patient has an increase in the size of the spleen and liver, there are signs of pancreatic insufficiency. Neurological disorders are no less pronounced, the development of cholecystitis and cholangitis is possible.
Symptoms of strongyloidiasis. Symptoms of this type of helminthiasis are varied. The patient has dyspeptic disorders, allergization of the whole organism occurs, the work of the liver, spleen and gallbladder is disturbed.
Symptoms of urogenital schistosomiasis. A person with urogenital schistosomiasis primarily suffers from dysuric disorders. Blood impurities appear in the urine.
Test for the determination of possible helminthiasis

The test for determining possible helminthiasis involves counting positive answers to the questions presented. By their number, conclusions can be drawn regarding the risk of the presence of helminths in the body.
Itching in the anus disturbs periodically or constantly.
Often a headache, dizziness occurs.
Rashes appear on the skin.
Often there is nausea, which can result in vomiting.
Worried about bloating, unstable stool (constipation is replaced by diarrhea).
The quality of sleep at night has worsened. Worried about insomnia, screams in a dream.
The lower extremities often swell.
Lymph nodes are enlarged.
Allergic reactions occur (bronchial asthma, urticaria, cough and allergic rhinitis).
Periodically there are pains in the abdomen, which go away on their own.
There is a bitter taste in the mouth.
Chases chronic fatigue and fatigue.
There are preschool children in the house. Work at DOW.
The skin and mucous membranes have a yellow tint.
Periodically, the body temperature rises for no apparent reason.
Sometimes joints and muscles hurt.
Gritting of teeth or snoring is heard during sleep.
The diet includes such products as: sushi, dried fish, lard with meat inclusions.
The weight is reduced. Appetite increased or decreased.
Fruits and vegetables that a person eats may not be washed or scalded with boiling water.
If there are more than seven positive answers, then there is a risk of the presence of helminths in the body. If there are more than 15 positive answers, then the probability of helminthiasis is very high and it is necessary to seek the advice of a specialist.
Treatment of helminths
Treatment for worms is called deworming. It can be medical or surgical (some helminths can only be removed by surgery). Folk methods for the treatment of helminthic invasion are also popular. In addition, you should also take care of personal hygiene and follow the rules of cooking. It is very important to take measures to stimulate immunity, because during helminthiases it is depressed.
How to get rid of worms?

To rid the human body of helminths, you will need to take antiparasitic drugs. They have activity against various types of worms, so a doctor should prescribe them. In addition, there are broad-spectrum drugs, but this does not mean that they can be used on their own. About 70 species of helminths parasitize in Russia, including: trematodes, nematodes and cestodes. Only a doctor can determine which parasite lives in the human body on the basis of laboratory tests (fecal analysis, scraping for enterobiasis, blood test for giardiasis, etc.).
Currently, parasitologists have in their arsenal about 10 different drugs that allow treating patients with helminthiases. The dosage and course of treatment is selected in each case individually and depends on the age of the patient, on the type of helminths, on the presence of concomitant diseases, etc.
It is possible to use drugs such as:
Pirantel (Combanthrin, Nemocide, Helmintox).
Nemozol, Vormil based on Albendazole.
Piperazine.
Decaris (Levamizole).
Pirvinium, Vanquin, Pircon (Pirvinium embonate).
Vermox, Vermakar, Wormin, Mebex, Vero-Mebendazole with the main active ingredient Mebendazole.
Medamine (Carbendazim).
Since some drugs are unable to destroy helminth larvae, but only act on adults, the risk of re-infection remains. To minimize it, it is necessary to undergo a second course of treatment after 14-21 days.









