Fish, being at a depth, as a rule, do not see the fishermen, but they perfectly hear how the fishermen talk and move in the immediate vicinity of the water. To hear, fish have an inner ear and a lateral line.
Sound waves propagate perfectly in the water, so any rustles and clumsy movements on the shore immediately reach the fish. Arriving at the reservoir and loudly slamming the car door, you can scare the fish, and it will move away from the shore. Given that the arrival at the reservoir is accompanied by loud fun, then you should not count on good, productive fishing. Large fish, which fishermen most often want to see as the main trophy, are very cautious.
Freshwater fish are divided into two groups:
- fish with excellent hearing: carp, tench, roach;
- fish with good hearing: perch, pike.
How do fish hear?
The inner ear of fish is connected to the swim bladder, which acts as a resonator that calms sound vibrations. Amplified vibrations are transmitted to the inner ear, due to which the fish has good hearing. The human ear is able to perceive sound in the range from 20Hz to 20kHz, while the sound range of fish is narrowed and lies within 5Hz-2kHz. We can say that the fish hears worse than a person, about 10 times, and its main sound range is located within lower sound waves.

Therefore, the fish in the water can hear the slightest rustle, especially walking on the shore or hitting the ground. Basically, these are carp and roach, therefore, when going for carp or roach, this factor should be taken into account.
Predatory fish have a slightly different structure of the hearing apparatus: they have no connection between the inner ear and the air bladder. They rely more on their sight than on their hearing, since they cannot hear sound waves beyond 500 Hz.
Excessive noise in the pond greatly affects the behavior of fish that have good hearing. Under such conditions, she may stop moving around the reservoir in search of food or interrupt spawning. At the same time, the fish is able to memorize sounds and associate them with events. While doing research, scientists found that the noise had a very strong effect on the carp and, in such conditions, he stopped feeding, while the pike continued to hunt, not paying attention to the noise.
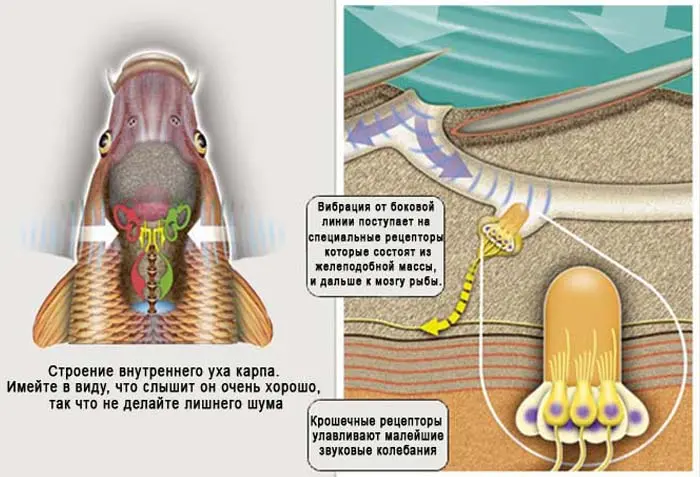
The organs of hearing in fish
The fish has a pair of ears that are located behind the skull. The function of the fish’s ears is not only to detect sound vibrations, but also serve as the balance organs of the fish. At the same time, the fish’s ear, unlike humans, does not come out. Sound vibrations are transmitted to the ear through fat receptors, which pick up low-frequency waves generated as a result of the movement of fish in the water, as well as extraneous sounds. Getting into the brain of the fish, sound vibrations are compared and, if outsiders appear among them, they stand out, and the fish begins to react to them.
Due to the fact that the fish has two lateral lines and two ears, it is able to determine the direction in relation to the sounds made. Having determined the direction of dangerous noise, she can hide in time.
Over time, the fish gets used to extraneous noises that do not threaten it, but when noises that are not familiar to it appear, it may move away from this place and fishing may not take place.