Contents
- How do I know if a hair transplant can solve my problem?
- What questions to clarify with the doctor?
- When is hair transplant ineffective?
- What other methods of hair restoration are there besides transplantation?
- Where do hair for transplant come from? Can body hair be used?
- Preparing for a hair transplant
- How is a hair transplant operation performed? Are there non-surgical methods?
- Hair transplant – does it hurt?
- When do the results start to show?
- What complications can occur after a hair transplant?
- Additional treatment after hair transplant
How do I know if a hair transplant can solve my problem?

Hair transplantation may be the only solution for androgenetic alopecia, as it can help restore the amount of hair in problem areas even when medications and folk remedies have proven ineffective.
Consider the main situations in which it is necessary to prescribe a hair transplant:
A transplant may be necessary in the event of baldness in women, as a result of which the density of hair is lost in different parts of the head.
Hair transplantation from the back of the head helps restore hair density in men with age-related baldness.
Hair transplantation restores the normal shape of eyebrows, mustaches and beards, where the hair has fallen out due to scars.
Transplantation allows you to restore hair growth at the site of the scar and mechanical damage to the tissues of the scalp.
What questions to clarify with the doctor?
Which of the methods (FUT or FUE) will be used for hair transplantation?
What procedures and medications will be needed after the operation, how long should the medication be taken?
The experience of the doctor and his prognosis regarding your situation?
Complications that may arise during the operation?
How long does the procedure take and how many sessions are enough for a satisfactory result? This usually depends on the amount of hair that is planned to be transplanted to the patient.
Patients are often interested in the question of whether the transplant operation will be in vain. After all, the hair that is transplanted by surgery can fall out in the same way as your own, and the operation itself takes a lot of time and is not cheap.
Androgenetic alopecia is one of the common serious causes of baldness, difficult to treat. The reason for it is considered to be a violation of the metabolism of androgens – male hormones, as a result of which dihydrotestosterone is formed, which adversely affects the function of the hair follicle. Dihydrotestosterone is formed more in the parietal and frontal parts of the head, respectively, and baldness usually begins in these areas.
Hair transplantation from the occipital area can help restore the amount of hair, since the hair from this area is more resistant to the action of dihydrotestosterone. Thus, the transplanted hair takes root and remains in place for many years, for this phenomenon there is a medical term “donor dominance”.
A transplant can effectively solve the problem of the so-called cicatricial alopecia, helps to quickly restore the hairline at the site of the scar, but only if its area is not larger than that of a woman’s palm.
To stop further loss of your own hair, located in the frontal and parietal region, it is recommended to constantly use Minoxidil and drugs similar in effect.
When is hair transplant ineffective?
When baldness becomes focal in nature, hair begins to fall out on any part of the head or body, bald spots with smooth edges form. In this case, an attempt to restore hair using the transplant method is considered ineffective, since an exacerbation of the disease can destroy the results of the operation.
When the cause of hair loss is not reliably identified, and doctors cannot claim that hair loss is caused by androgenetic alopecia. The results of treatment with a transplant in this case will be unpredictable.
If hair loss occurs due to radiation sickness or chemotherapy, the transplant operation is useless – the weakened hair will still fall out.
Rapidly progressive androgenetic alopecia is almost impossible to treat with hair transplantation.
There is no reason to perform a hair transplant operation if the patient has too little hair left on other parts of the head.
Systemic diseases, diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension may be contraindications for hair transplant surgery.
What other methods of hair restoration are there besides transplantation?
There are several methods used in modern medicine to regenerate lost hair. The choice of the most effective is made by reason of the dropout. With seasonal hair loss, taking vitamins can help, with androgenetic alopecia, Minoxidil is recommended in the form of foam or lotion.
For hair restoration, medical cosmetics are also used in the form of ampoules, masks and shampoos or tablet preparations. If the cause of hair loss is not weakened follicles, but their dryness and brittleness, then topical agents help to solve the problem without surgery and pills. In some cases, when hair loss is caused by parasitic invasion or systemic diseases, the hairline is restored after the main cause of baldness is eliminated.
Good results are obtained by procedures aimed at restoring microcirculation in superficial tissues. This is a scalp massage, folk recipes based on pepper tincture, darsonvalization salon procedures. In areas where hair loss is caused by insufficient blood supply to the follicles, even a transplant may not be effective.
Hair transplantation is necessary when all other methods have been tried and failed.
Where do hair for transplant come from? Can body hair be used?

When transplanting hair, the patient’s own hair from the back of the head is used, if it is preserved. The hair of other people cannot be used for transplantation, as they are rejected by the body.
For hair transplantation, it is not recommended to use hair from other parts of the body, because even if the operation is successful, the hair will retain its original appearance – color, structure and length, and bear little resemblance to the natural scalp.
Preparing for a hair transplant
Preparation for the operation begins six months before the operation and consists of the following stages:
Therapy of androgenetic alopecia with Minoxidil – exacerbation of the disease can nullify the results of transplantation;
Minoxidil is stopped 14 days before surgery to reduce bleeding during the transplant process;
A week before surgery, limit smoking and taking medications that affect blood clotting;
A few days before the operation, it is necessary to completely abandon alcohol and pass a series of tests: for hemoglobin, glucose, syphilis, hepatitis, and blood clotting. If the operation is performed using the FUE method, then the doctor may prescribe a FOX test – it helps to study the anatomical features of the patient’s skin, how difficult it will be to remove donor hair. To do this, under local anesthesia, grafts containing up to 100 hairs are selected, they are examined under a microscope, and in case of difficulty in extracting hairs during surgery, the FUT method is used.
On the day of the operation or earlier, the hair from the area that is used for transplantation is cut short to 2-3 mm.
Hair transplantation gives good results in the treatment of androgenetic and age-related alopecia, which are among the most common causes of hair loss in men. Women need to undergo a series of additional tests, since the range of diseases that can cause baldness is quite wide, and androgenetic alopecia is relatively rare in women.
Examinations necessary to determine the cause of hair loss:
Complete blood count for the level of hemoglobin and ferrin proteins, as well as the concentration of zinc;
Analysis of the level of the most important sex hormones and some thyroid hormones;
Blood test for adrenal hormones with the determination of testosterone levels;
Assessment of the condition of the scalp and hair, followed by localization of foci of baldness;
Sometimes Trichoscopy is used – a microscopic examination of the hair.
How is a hair transplant operation performed? Are there non-surgical methods?
Hair transplant surgery has no serious complications, is well tolerated by patients and is one of the most popular and effective ways to treat alopecia. Modern surgical instruments and techniques allow androgynous transplantation of fragments consisting of 1-4 hairs, which increases the accuracy of the procedure and ensures their survival in a new place.
A completely non-surgical method of hair transplantation has not yet been developed. Two techniques are used in the operation, which differ in the way donor hair is taken – FUT and FUE.
What is FUT and FUE? Which method is better?
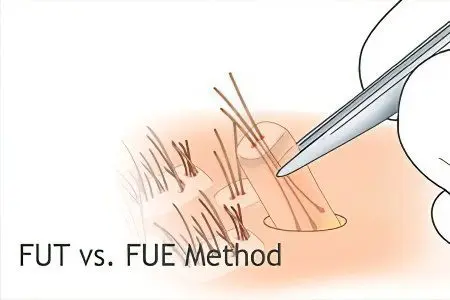
FUT – This is a technology of hair transplantation in strips that are cut from the back of the head, crushed into separate fragments of skin with hair and implanted in the place of the bald spot, where the doctor first makes small holes.
This technique has a significant drawback – noticeable scars remain at the place where the hair is taken for transplantation, which worsens the appearance of the patient’s head. If the hairstyle hides the back of the head, then the scars are invisible to others. However, this is usually not a problem, because 3 months after a successful hair transplant, new ones grow in place of the scar, and it becomes difficult even for a hairdresser to detect it.
FUE – a technology in which hair transplantation takes place one by one, less traumatic for the scalp, but more time-consuming and laborious. The selection of hair for transplantation takes place with the help of special tools, after which they are transplanted in the same way as with FUT technology. This transplantation method minimizes the chance of scarring as it does not require stitches. The recovery process after surgery is less than with a FUT transplant. Another significant advantage of this method is the ability to transplant hair into bald areas not only from the head, but also from other areas of the body.
Hair transplant – does it hurt?
Hair transplant surgery is painlessly tolerated by the patient; local anesthesia with lidocaine or xylocaine is sufficient for its implementation. During hair transplantation, the patient is conscious and feels in which part of the head the doctors are performing manipulations, but there is no pain.
When do the results start to show?
In order for the results of treatment to become apparent to the patient and others, it is necessary to carry out therapy from 8 months to a year, during this time the amount of hair and their density are restored, bald patches and bald spots disappear on the areas of the head affected by alopecia.
Three months after hair transplantation, tangible changes are noticeable at the site of the bald spot – new hair grows, and the bald spot area becomes almost indistinguishable from areas with normal hairline. Transplanted hairs have their own genetic information, are more resistant to the effects of dihydrotestosterone, which provokes androgenetic alopecia. Therefore, it can be expected that a second operation will not be needed, and hair loss in this area will stop.
What complications can occur after a hair transplant?
A common postoperative phenomenon is swelling and soreness of the skin on the head at the site of the operation. This is the reaction of the tissues to the saline solution that is injected during hair transplantation. Ice compresses help relieve swelling and pain. It is observed no more than three days after the operation. Full recovery occurs two weeks after the operation.
Among the rare and dangerous complications after hair transplantation, there may be scars, infectious and inflammatory processes, and divergence of sutures.
Additional treatment after hair transplant
After a successful hair transplant, patients with androgenetic alopecia require additional drug therapy to prevent the hair from falling out again. Men are prescribed Finasteride and Minoxidil tablets for external use, while women, in most cases, have enough topical preparations of Minoxidil.
Author of the article: Herman Olga Leonidovna, trichologist, specially for the site ayzdorov.ru









