Contents
If the gum becomes inflamed, this condition cannot be ignored, the person needs treatment. Such a symptom may indicate the onset of a dental disease. The longer therapy is absent, the higher the risk of complications. In such cases, the likelihood of cyst formation, abscess formation, tooth loss and damage to the periodontal ligaments increases.
Causes of the inflammatory process
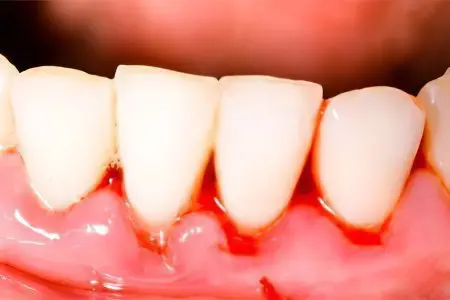
Inflammation of the gums can be caused by various diseases. Sometimes it is temporary, which often happens after a tooth has been removed. A few days after the procedure, pain and swelling subside. No special treatment is required. If signs of inflammation persist for more than 6 days, then you need to see a doctor. There is a possibility that a person develops a complication after the procedure.
Reasons that can provoke inflammation of the gums:
Excessive deposits of tartar or soft plaque. This happens when a person does not follow oral hygiene.
The fall of the body’s defenses.
Deficiency of vitamins and nutrients.
Taking medications.
Genetic predisposition.
Chronic diseases
Hormonal imbalance.
Smoking.
Irritation of the gums with crowns and dentures.
Pregnancy.
Viral infections.
Mechanical damage: burns, biting, cuts, etc.
Frequent stress.
Diseases of the internal organs.
Taking medications.
In childhood, the gums can become inflamed during teething. Also, an additional risk factor is the immaturity of the immune system.
Frequent gum disease
Gum diseases most commonly diagnosed by dentists include:
Gingivitis.
Periodontal disease.
Periodontitis.
Often, the gums become inflamed in people during teething of wisdom teeth, as well as in pregnant women. If a person notices signs of a violation of the health of the oral cavity, you need to contact a specialist. Otherwise, the situation will only get worse.
Main symptoms

All gum diseases have similar symptoms, including:
The appearance of blood. The gums begin to bleed while eating, as well as when brushing your teeth.
The mucous membrane of the gums becomes edematous, red, loose.
The gums begin to lag behind the tooth. Doctors call this symptom a periodontal pocket.
While eating food and while brushing your teeth, a person experiences pain.
The gums may itch. Often a person experiences a burning sensation.
From the mouth begins to smell bad. It is not possible to get rid of the smell, even if you brush your teeth well.
Inflammation of the gums can be accompanied by one or several symptoms at once. If a person notices such pathological signs in himself, you need to visit a dentist. Lack of treatment can lead to tooth loss.
Gingivitis
With gingivitis, the lining of the gums becomes inflamed. The process is not deep, only the upper layer of the gum suffers. However, it is impossible to call such a disease harmless, since it threatens the development of periodontitis. If treatment is started on time, then it is not difficult to cope with gingivitis.
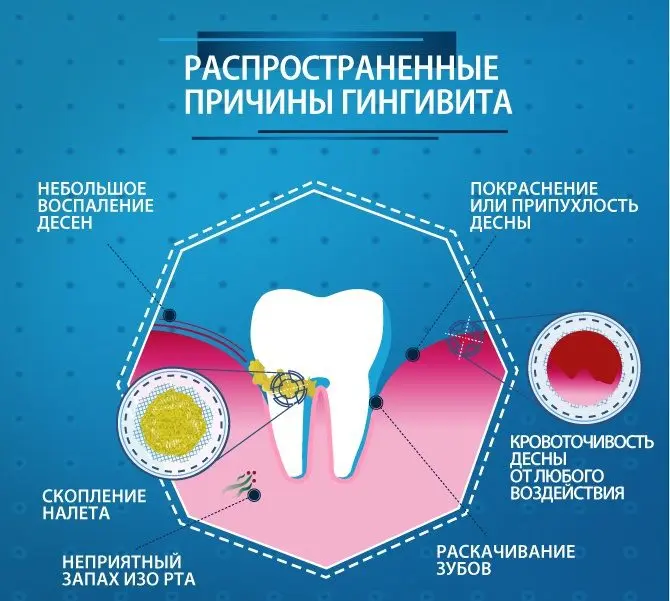
Gingivitis can be acute or chronic.
In addition, dentists distinguish several forms of inflammation, including:
Catarrhal gingivitis. It occurs more often than others. Its development is indicated by halitosis, deterioration of taste, bleeding of the gums, due to which the salivary fluid becomes pinkish in color. If the disease has an acute course, then the person experiences pain. It strengthens with any mechanical impact on the tooth.
Gingivitis ulcerative necrotic. This form of the disease is also called Plaut-Vincent gingivitis. The inflammation has a severe course, the gums become red, give off a painful sheen. Their mucous membrane is covered with ulcerative defects, which causes pain to a person. Body temperature rises to feverish levels. Nearby lymph nodes increase in size.
atrophic gingivitis. With this disease, the gums decrease in size, the gingival papillae disappear. The patient can see the roots of the teeth, which normally should be covered. There are no symptoms of inflammation.
Hypertrophic gingivitis. Inflammation is characterized by an increase in the size of the gums and their bleeding.
Symptoms
When gingivitis has just begun to develop, a person’s gums will bleed. Moreover, it is not always possible to notice this symptom. You can understand that not everything is in order with the gums by the taste of blood in the mouth. Most often it appears during the use of food. The next sign of gingivitis is the appearance of blood on the toothbrush. In the future, the gums become very sensitive, loose. An unpleasant odor comes from the patient’s mouth.
Treatment
To cope with gingivitis, you need to visit the dentist’s office.
The treatment regimen for this disease consists of several stages:
Elimination of dental deposits. Teeth are cleaned with ultrasound, then polished using a special brush and paste. The gel is applied to the gums. Professional cleaning and related activities take about an hour. After 10 days, you will need to come to a specialist for a second appointment.
The use of drugs, the elimination of inflammation. The patient is prescribed antibiotics, most often local treatment is sufficient. Supplement therapy with drugs to increase immunity and to relieve inflammation. If the infection cannot be controlled, then antibiotics are taken orally. Sometimes an antifungal medication is needed.
Antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity. It is carried out at home. To do this, you need to apply a special gel or paste on the gums 3 times a day. Such drugs not only disinfect the mucous membranes, but also stop inflammation.
Tartar removal is an essential component of gingivitis treatment. If the plaque is left, the therapy will not bring the desired effect.
When gingivitis has a running course, they resort to surgical intervention. The patient is undergoing gingivoplasty. This operation is designed to correct the mucous membrane of the gums.
Periodontitis
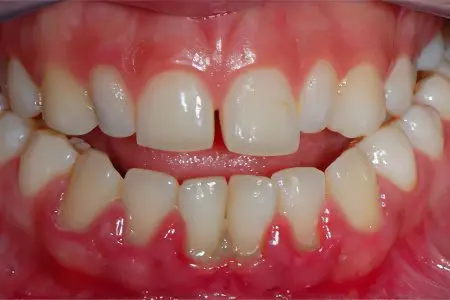
Treating periodontitis is more difficult than gingivitis. With this disease, not only the mucous membranes of the gums, but also their deep tissues suffer. The inflammatory process can spread to bone structures. The main symptom of periodontitis is tartar, from which oozes pus.
The periodontium is represented by a shell that surrounds the tooth and is responsible for its attachment to the gum. It is her inflammation that characterizes such a disease as periodontitis. If you ignore its symptoms, then the pathology will progress, the periodontium will collapse, pockets will form in the gums, the teeth will begin to loosen and fall out.
Periodontitis can occur not only against the background of untreated gingivitis. Its development is facilitated by violations in the structure of the jaw. This is especially true for people whose teeth are very close to each other. Provoking factors in the development of periodontitis, dentists include malocclusion, anatomical defects of the frenulum, hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles.
Periodontitis can be infectious in nature:
Bacterial complication of pulpitis. Infection from the pulp spreads to the periodontium and causes inflammation.
Poor treatment of diseases of the pulp and periodontal tissues.
Incorrect preparation of the oral cavity for the upcoming prosthetics. Periodontitis often develops in people who have crowns.
Symptoms
The main manifestation of periodontitis is swelling of the gums, its sliding down, the appearance of the neck of the tooth. If at an early stage of the development of the disease the pocket does not exceed 4 mm in size, then in the future its depth will increase.
Other symptoms of periodontal inflammation include: ligament atrophy, expansion of pathological gum pockets, and intense bleeding from the gums. The teeth begin to loosen strongly, the bone tissue is destroyed at their very roots.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause of periodontal disease. The patient is removed plaque and stones, replace fillings and dentures, if they injure the gums.
The doctor prescribes drugs to the patient to relieve inflammation. Additionally, physiotherapy procedures may be recommended. A person is taught how to properly brush his teeth, and they select the appropriate oral care products for him.
If periodontitis has a severe course, then the patient is operated on. Sometimes it is necessary to implant bone tissue.
Periodontal disease
Until now, scientists have not been able to find out the causes of periodontal disease. This disease is non-inflammatory in nature, but leads to loss of teeth. Periodontal disease is not accompanied by such pronounced symptoms as periodontitis. Signs of violation blurred.
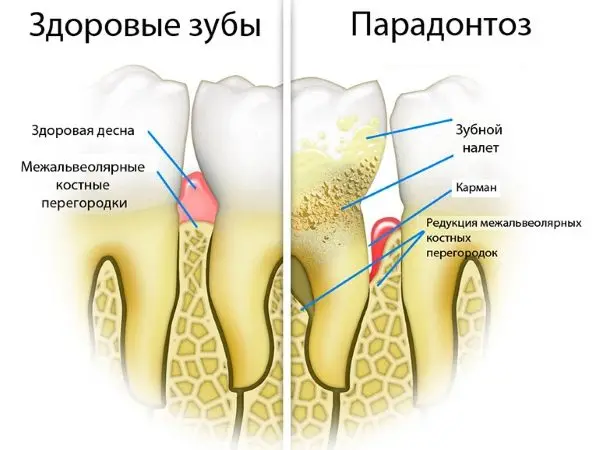
The tissues that surround the tooth, with periodontal disease, cease to receive nutrition. This leads to the fact that the tooth is gradually loosened. If a person does not seek medical help in time, then the tooth will definitely fall out.
Dentists have identified some factors that can contribute to the development of periodontal disease:
Deficiency of vitamins and microelements in the body.
Atherosclerosis.
Decreased immunity.
Diseases of the central nervous system.
Diabetes.
Violations in the work of the endocrine glands.
Symptoms
Symptoms of periodontal disease will differ, depending on the stage of development of the disease:
Symptoms of the first stage. A person has itching and burning in the gum area. Sometimes patients complain of a feeling of numbness in the mouth. When X-rays are performed, no visible disturbances in the bone apparatus of the gums are observed.
Symptoms of the second stage. The gums begin to bleed, their tissues become not as elastic as before. In some places, pockets are formed, in the area of uXNUMXbuXNUMXbwhich an abscess develops. The teeth begin to loosen, during the compression of the jaw, the person experiences pain. When performing radiography, the doctor can visualize rarefaction of bone tissue in the area of interradicular septa.
Symptoms of the third stage. The alveolar process begins to die off, the tooth necks are exposed. The teeth themselves become very mobile. When loaded, they may fall out.
Treatment
To cope with periodontal disease, you need to eliminate the factor that provoked it. Treatment includes both local and systemic therapy. The patient is prescribed drugs that stimulate the blood supply to the oral cavity, drugs to increase immunity and strengthen the gums.
Good effect has a gum massage, as well as physiotherapy. You need to tune in to the fact that in one day or even in one week it will not be possible to cope with periodontal disease. The therapy is long and varied.
Sometimes dentists are not limited to conservative methods only. Some patients require bypass surgery. This procedure helps to fix loose teeth and prevent their loss.
Video: Most often people have periodontitis. What is the difference between these diseases and what may be the causes of its occurrence. Detailed response from a dentist:









