Contents
What is gum cancer?
gum cancer It is considered one of the most common diseases of the oral cavity. Cancer cells infect soft tissues and spread to other organs. Metastasis occurs quite quickly. Often this leads to the formation of malignant tumors in the entire oral cavity and even in the area of the lymph nodes. The sooner the disease is diagnosed, the sooner it will be possible to cope with it.
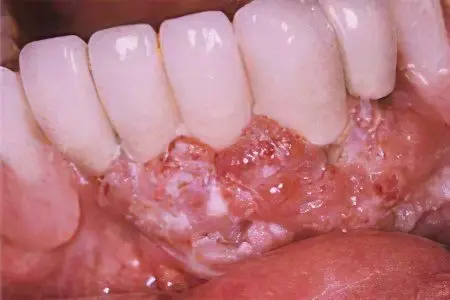
Outwardly, this type of cancer can be identified by an increase in the gums and the appearance of whitish spots on it. In some cases, small ulcers may form. Diagnosing gum cancer based solely on appearance is not easy. Only a specialist can do this. Since cancer is easily confused with some other diseases with similar manifestations: gingivitis, leukoplaxia, ulcers, erythroplakia. However, it differs in that the tumor usually forms on the lower jaw in the area of the alveoli. Increasing in size, malignant cells often reach the bottom of the oral cavity and the end of the alveolar process. With gum cancer, a much greater number of ulcers form on it than in the case of other diseases of the oral cavity. Vessels are clearly visible on the surface of the tumor.
Men suffer from gum cancer more often than women. Moreover, middle-aged and older people fall into the risk group.
Causes of gum cancer
The main causes of gum cancer include:
Smoking and alcohol abuse. Tobacco contains carcinogens. These chemicals contribute to the formation of malignant tumors. They are also part of ethyl alcohol, which is the basis of most alcoholic beverages, and irritate the oral mucosa. As a result, it promotes the formation of cancer cells.
Lack of oral hygiene. Irregular brushing of teeth leads to various infections, which increases the risk of gum cancer. Therefore, it is important to monitor the oral cavity, regularly carrying out hygiene procedures,
Incorrect food. Lack of vitamins leads to weakening of the enamel of the teeth and gums. Hard and rough food injures the mucous membrane. All this causes inflammation, which provokes gum cancer.
Piercing. During piercing of the tongue and lips, wounds form on the mucous membrane. This allows you to create an environment in which pathogenic microorganisms actively multiply.
Caries, injuries and chronic inflammation of the gums. Diseased teeth also create conditions for the formation and reproduction of malignant tumor cells. Often dentists can’t detect gum cancer right away. The cause of the swelling is caries or pulpitis and the diseased tooth is removed. However, as a result, such radical methods only exacerbate the situation, contributing to the development of inflammation.
The main symptoms of gum cancer
Gum cancer can be almost asymptomatic. Therefore, it is not easy to detect in the early stages. However, in most cases, the occurrence of a tumor causes tangible pain in the oral cavity. Often patients go to the dentist with complaints of inflammation, considering it to be the cause of dental problems. The doctor must conduct a thorough examination to exclude in this case the possibility of a malignant tumor.
With gum cancer, in addition to whitish formations on it, the mucous membrane is compacted. A large number of small ulcers appear. The gums start to bleed. Initially, the tumor is small, but soon it begins to grow actively, put pressure on the teeth. The pain gradually increases, as does the bleeding of the gums. In the later stages of the disease, patients have difficulty opening their mouths due to discomfort. In this case, the tumor covers not only the gum, but the entire oral cavity, including the tongue and jawbone.
Methods for diagnosing and treating gum cancer

The most important thing for successful disposal of gum cancer is timely diagnosis. You should visit the dentist regularly. If inflammation is a concern, a full examination should be done before starting treatment, such as removing a tooth. An inexperienced doctor can easily confuse this disease with flux or pulpitis. As a result, cancer can begin to develop even more actively, hitting an open wound at the site of the extracted tooth. Diagnosis involves a biopsy and cytological examination. An orthopantomogram is also done. According to the results of such a picture, the doctor can determine the external condition of the jaws. A detailed image of cells and tissues is obtained using magnetic resonance imaging. In this case, a dye is used to highlight the affected areas with color.
Unlike many other malignant tumors, gum cancer responds well to treatment. Surgical intervention is the most effective among modern methods. In this case, not only the cancerous tumor is removed, but also part of the tissues around. In the later stages, the operation is performed on the lymph nodes. In some cases, it is necessary to remove parts of the tongue and even the jaw bones. After surgery, you may have difficulty swallowing, smelling, or using your taste buds.
Radiation therapy is used prior to surgery. During it, with the help of high-energy x-rays, cancer cells are destroyed. In addition, medical treatment is used. In most cases, the doctor must prescribe a course of vitamins and antibiotics to the patient. Chemotherapy is required to prevent the recurrence of the disease.
In order to prevent the formation of a gum tumor, it is necessary to carefully monitor oral hygiene. Do not forget about routine examinations at the dentist. Death in gum cancer is much rarer than in cases with other types of malignant tumors. However, if the disease is not diagnosed in time, it can lead to various complications and adversely affect dental health. Therefore, if you suspect gum cancer, you should be examined by a dentist and an oncologist.









