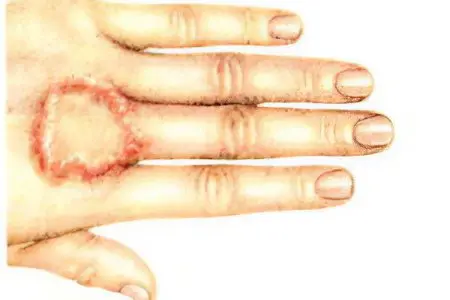
Granuloma annulare is a complex disease, the etiology of which has not yet been fully elucidated. It is believed that the development of this pathology is affected by infections. These include tuberculosis and rheumatism, diabetes (endocrinopathy), allergies, taking a certain group of drugs. A granuloma is a benign chronic condition in which papules and nodules form, forming rings around small areas of the skin.
According to some experts, granuloma annulare refers to skin diseases that occur as a result of impaired carbohydrate metabolism. Granuloma is called erytomatous skin lesion. With this disease, the skin becomes reddish, sometimes the color of normal skin or a yellowish-bluish tint. The rash usually occurs on the feet, legs, hands, and fingers.
There are no symptoms.
Often the disease develops after sunburn, insect bites. Usually not accompanied by ulceration. In adults, more often in women, solitary annular foci are found in the subcutaneous tissue of the forehead. Granuloma annulare is characterized by small foci of collagen fibers with a disturbed structure, around which there is a slight infiltration.
Pathology can not be immediately detected, the diagnosis is made due to the presence of histiocytes among the collagen bundles. Granuloma formation occurs when activated macrophage cells engulf, destroy, or isolate the invading agent. The reason for this phenomenon are infectious agents such as lastomycosis, fungi, candidiasis, cryptococcosis, chromomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, sporotrichosis.
Types of granuloma annulare
Granuloma annulare is divided into two forms:
1.Typical shape This disease affects the skin of the feet, hands, knees, namely their back side. Not so often, but still, papules appear on the gluteal region, on the neck and in the forearm area. In elderly people, and in diabetics, rashes can be localized on the lower and upper limbs, on the trunk.
2. Atypical form It is divided into subcutaneous, disseminated and perforating granuloma.
– With subcutaneous granuloma, there are many nodes on the upper limbs in the elbows, forearms, on the back of the hands, on the fingers, and rarely on the scalp and on the upper eyelid. The subcutaneous form of the granuloma is similar to rheumatic nodules, develops exclusively in childhood, more often in girls.
– In the case of a disseminated form, it is detected, as a rule, in adults and very rarely in children, rashes can spread throughout the body. The papules are purple or flesh in color. Eruptions are multiple, scattered. Due to their merging, a grid is formed. The disseminated form is treated for a long time and is difficult.
– The perforating form protrudes on the fingers and hands after skin injuries. It is characterized by plugs in the center of the ring. A gelatin-like substance is periodically secreted from the nodules. When the ulcers heal, the skin becomes crusted, a small indentation forms in the center of the lesion, and then scars appear. Papules of perforating granuloma annulare subsequently turn into large plaques.
Clinical manifestations of granuloma annulare are easily recognized. In most cases, the diagnosis is made accurately during a visual examination by a dermatologist. Sometimes there is a need for histological examination of biological material.
Treatment of single foci of annular granuloma is carried out using hydrocortisone ointment with ichthyol and phonophoresis. A therapy is used aimed at normalizing the immune system, inhibiting the process of antibody formation. The disease is associated with metabolic disorders, so it is important to use corrective remedies and treat along the way if, for example, there is tuberculosis, diabetes mellitus or one of the dangerous chronic infections.
Among the drugs, ascorbic acid, tocopherol acetate, B vitamins, and products containing iron are prescribed. In many cases, a positive effect can be achieved by chipping the papules with triamcenolone acetonide. The use of niacinamide, dapsone, hydroxychloroquine, isotretinoin is also helpful. A substance called chloroethyl is used to irrigate the affected areas, which, after its application, are covered with “frost”. You can also use carbonic acid or liquid nitrogen. Treatment is complemented by PUVA therapy – a method that includes the use of psoralens and skin irradiation with long-wave ultraviolet radiation. The outcome of the disease depends on the stage, the sooner the patient visits the doctor, the more positive the result.









