Gout, arthritis, gout – what are these different sounding names? Well, they indicate one disease, often colloquially identified as the “rich man’s disease”. Men over 60 usually struggle with it. Despite strenuous efforts and analyses, no reliable source and background of the incidence of this disease has been found so far. And it is acute arthritis. Are there any remedies to manage this disease? How to recognize it and what treatment measures to take?
Gout – what exactly is this disease?
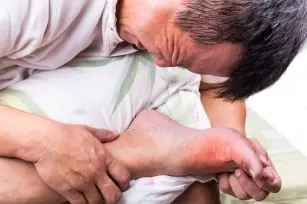
The easiest way to identify this disease is as painful and severely disabling arthritis. It usually attacks violently and with great intensity, mainly involving the metatarsophalangeal joint. Sometimes it also manifests itself with gouty nodules or kidney stones. Elevated uric acid levels may indicate an arthritis problem. Its excess causes crystallization and deposits in joints and tendons, finally contributing to the occurrence of swelling, redness and pain.
Gout – symptoms
you hear about gout or arthritis, and you probably don’t know what you may be dealing with or you don’t realize that the ailments that you encounter may mean this condition. Therefore, it is very important to decipher these mysterious-sounding names and learn about the symptoms that accompany this disease. The simplest suspicion falls on gout when there are recurrent attacks of arthritis. Usually the pain is located in the fingers, although in the development phase of the disease gout also affects the ankle joint or wrists. There is pain, fatigue, fever. Uric acid deposited in the joints leads to bone erosions, which in turn lead to exhausting the body arthritis. Usually, the disease proceeds in stages, gradually progressing and attacking subsequent parties. You may not even notice the beginnings, there is no soreness. The next stage, unfortunately, is not asymptomatic anymore, it is characterized by the occurrence of acute attacks of joint pain from time to time. The most advanced stage of the disease is a statement gout chronic. The diagnosis of gout is made by testing the concentration of uric acid and estimating the daily loss of uric acid in the urine. Sometimes, when diagnosing, doctors also use X-rays, thanks to which erosions and tophi are located.
Gout – causes
This dangerous condition is not fully defined by diagnosticians. However, it is found that the increased concentration of uric acid in the blood is affected by reduced kidney efficiency and an incorrect diet, in which a lot of products rich in purines are consumed. In addition, genetic conditions, past diseases, long-term dehydration or infection of the body are factors that also affect development gout. This risk increases with overweight, hypertension, coronary artery disease, diabetes, and lipid metabolism disorders.
Gout – treatment
You already know the basic factors that affect the development of the disease or increase the risk of its formation. You also know which symptoms may indicate progressive gout. So the question remains, how to treat arthritis? Management when diagnosed with gout is primarily aimed at pain relief and prophylactic prevention of joint pain attacks. Various anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs are used for this purpose, and if necessary, uric acid nodules and kidney stones are removed. The course of treatment depends on the stage of the disease. At the initial stage of diagnosis, only lifestyle changes will be necessary, in the next phase, when acute gout attacks occur, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. In the absence of attacks, it is recommended that uric acid levels be monitored to prevent future recurrences. When chronic gout is diagnosed, further development of the disease is inhibited by blocking the production of uric acid, using allopurinol for this purpose.









