Contents
Gonorrhea is still one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases. In women, the disease is often hidden, so they continue to infect other people, unaware of the presence of an infection in their body.
Treatment of gonorrhea is required for both sexual partners. The sooner it is started, the less likely it is that the patient will develop severe complications, including infertility.
Gonorrhea in women – what is it?
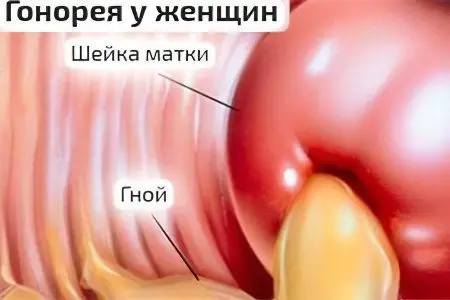
Gonorrhea – This is a sexually transmitted sexually transmitted disease, popularly known as gonorrhea. The causative agent of the disease is gonococcus (Neisseria gonorrhhoeae). This bacterium was named after the scientist Neisser who discovered it. If we turn to the Greek language, then the term “gonorrhea” can be translated as “semen flow.”
Gonorrhea is divided into acute, subacute and chronic. In the first two cases, the disease lasts no more than 2 months. In the chronic form of infection, the statute of limitations for infection is more than 2 months. In this case, gonorrhea can have a latent, asymptomatic course.
The disease tends to spread in an ascending manner. Once in the genital tract of a woman, gonococci lead to inflammation of the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and pelvic peritoneum.
Causes of infection with gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is transmitted sexually. And the type of sex does not matter. Infection occurs through genital-oral, traditional and anal contact. Infection can be transmitted even during petting.
Scientists do not exclude that there is a possibility of infection by household means, but this situation rarely happens. The household route of transmission is realized when hygiene rules are violated, when using other people’s towels, when wearing someone else’s underwear, etc.
Newborn babies can be infected with gonorrhea while passing through the birth canal of a sick mother.
Once in the external environment, gonococci lose their high ability to live. They die when heated to +55 ° C and when exposed to ultraviolet rays.
There are women who are at increased risk of contracting gonorrhea:
Sexual intercourse with different men.
Women under 25 years of age.
Women who have had gonorrhea in the past.
Women with other sexually transmitted infections.
Pregnant women.
Women who lead an asocial lifestyle abuse alcohol and drugs.
When do the first symptoms of gonorrhea appear?

After the infection enters the body, it takes from 3 days to 3 weeks. During this period, any symptoms of the disease may be absent. Although most often gonorrhea makes itself felt 5 days after the infection has occurred. Specific terms depend on the intensity of the immune system.
If the immune system is weak, then the first signs of the disease may appear as early as 1-2 days after the infection has occurred. A recent illness, steroid therapy, treatment of cancerous tumors, etc. can provoke a drop in protective forces.
Late onset of symptoms of gonorrhea is associated with a good functioning of the immune system, or with the use of antibiotics during this period. A person can use them to treat other diseases. The drugs will muffle the symptoms of gonorrhea, so the disease will manifest itself later.
Symptoms of gonorrhea in women
Gonorrhea causes disturbances in those organs that affected the gonococci. During sexual intercourse, they penetrate from the urethra into the genital tract of a woman, populating the cervix. Then the infection rises higher, affecting the uterus itself, the ovaries and appendages. Sometimes the peritoneum is involved in the process of inflammation. The rectum and urethra may be affected. This happens during anal intercourse. Oral contact leads to the development of gonococcal pharyngitis.
Gonococci can cause symptoms such as:
Gonorrheal cervicitis. The woman experiences itching, burning and tickling in the perineum. When examining the cervix, the doctor notices its redness and swelling. From the cervical canal stand out yellow leucorrhoea, which stretch like a ribbon.
Gonorrheal endometritis and salpingo-oophoritis. If gonorrhea has not been stopped in time, it will lead to inflammation of the appendages and uterus. The woman begins to complain of pain in the abdomen, which is concentrated in its lower part. The pain may be sharp or aching. At the same time, there is a change in the nature of the secretions. They may contain pus and blood. Body temperature rises to 39 ° C, general intoxication of the body increases, which is manifested by weakness, malaise, nausea and vomiting. Appetite disappears.
Gonorrheal urethritis, cystitis and pyelonephritis. Gonorrheal urethritis develops when an infection affects the urethra. A woman complains of pain during bladder emptying. The urethra itself swells and becomes inflamed, responds with pain to touch. As the disease progresses, gonococci will invade new areas and lead to inflammation of the bladder and even kidneys.
Gonorrheal proctitis. This symptom is characterized by itching and burning in the anus. The act of defecation becomes painful, there are false urges to empty the intestines. In addition to feces, yellow mucus begins to stand out from the anus, in which blood can be seen. The anus is red, pus is visible in the folds of the anus.
Gonorrheal pharyngitis. This disease may remain undetected for a long time, as it will be disguised as a sore throat. While swallowing food, a woman develops sore throat, lymph nodes increase in size, which are located under the jaw. Body temperature rises, but may remain at subfebrile levels. It often happens that gonococcal pharyngitis does give meager symptoms, which is manifested exclusively by a sore throat. During the examination, the doctor visualizes red tonsils, which will be covered with a yellow-gray coating.
How does urine change with gonorrhea? In acute gonorrhea, the localization of infection occurs in the anterior urethra, so the first portion of urine will always be cloudy, and the second – transparent. If the infection spreads to the posterior urethra, then frequent urination and increasing soreness at the end are added to the already existing symptoms. The portion of urine will be cloudy in both portions.
Symptoms of the chronic form

The symptoms of the chronic form of the disease are subtle. Sometimes they will be missing. You can suspect the disease by vaginal discharge, but they are most often minor. From time to time, a woman experiences pain in the lower back, in the lower abdomen. However, it is difficult to associate such manifestations of gonorrhea with infection.
Chronic gonorrhea causes the menstrual cycle to be disrupted. This failure is due to inflammation of the uterus. Bleeding can happen in the middle of the cycle, the periods themselves differ in duration and soreness. During menstruation, gonorrhea symptoms such as cervicitis, endometritis, and urethritis may worsen.
The gonococci do not damage the vagina, since its mucous membrane is represented by a squamous epithelium. While these pathogens prefer to multiply in cylindrical cells. However, during pregnancy and girls may experience symptoms of vulvovaginitis caused by gonococci.
Complications of gonorrhea in women

Gonorrhea is a dangerous disease, as it can cause the following complications:
Inflammation of the Bartholin glands, which are located near the entrance to the vagina.
Female infertility, which will be due to obstruction of the appendages, or a violation of the structure of the endometrium of the uterus.
Decreased sex drive.
Complications of pregnancy and the period after childbirth. The probability of spontaneous early onset of labor, fetal growth retardation, early discharge of water, ectopic pregnancy increases. If a child is infected with gonococci, then he may die in the first hours after his birth, or even in the womb. The woman herself increases the likelihood of purulent complications and sepsis.
The birth of a child with gonorrhea. The disease can cause conjunctivitis, otitis media, genital infections and even blood poisoning in the fetus.
Spread of the pathogen throughout the body. The dermis, joints, kidneys, liver, heart, brain can suffer.
Conjunctivitis caused by gonococci. Infection occurs with a gross violation of the rules of hygiene.
Chronic gonorrhea in women often causes infertility, since inflammation leads to deformation of the fallopian tubes, the formation of adhesions, infection (obliteration) of the lumen of the tubes with connective tissue, thereby disrupting their patency. This pathology occurs in women in 8-20% of cases of chronic infection.
To prevent all these undesirable consequences, women are recommended at least once a year, and preferably more often, to undergo an examination by a gynecologist in a district consultation, use protective equipment during sexual intercourse, and have a permanent sexual partner.
Complications during pregnancy

Infection with gonorrhea is dangerous during pregnancy, because it develops very quickly due to good blood supply to the genitourinary organs and a decrease in the body’s defenses. In addition, most often the disease is asymptomatic. If infection with gonococci occurs in the first trimester, then this leads to spontaneous miscarriage due to the development of endometritis, at a later date various complications and postpartum pathologies occur.
There is also a big risk:
Early rupture of amniotic fluid
premature birth,
Infection of the child in utero or during his movement through the birth canal,
The development of fetal pathology.
Intrauterine gonococcal infection is a huge problem for doctors and parents, because a newborn can develop sepsis, which poses a real threat to the life of the baby. Even if the child is not infected in utero, then when passing through the birth canal, the gonococci will certainly get into the ears and eyes of the newborn, which will cause him to get otitis media and conjunctivitis in the future.
To avoid all of the above problems, experts recommend that women who want to have a baby, a mandatory examination for the presence of gonococcal infection (gonorrhea) before pregnancy. And besides, during this period, sex should always be protected.
Diagnostics

To clarify the diagnosis, you will need to perform laboratory diagnostics:
Sampling and microscopic examination of a smear from the cervical canal, vagina, rectum, urethra. The material is stained by gram, methylene blue, or brilliant green.
Collection of mucus from the urethra and cervix with its placement in nutrient media.
REEF. In this case, the material is stained with fluorescent dyes.
ELISA with urine testing.
RSK. To implement this serological study, you will need to perform blood sampling from a vein. This highly sensitive diagnostic method allows you to identify the chronic form of infection.
PCR. For the study, urine or a smear of the patient will be required.
At home, you can conduct rapid testing for gonorrhea. Sometimes standard methods do not allow to identify the causative agent of the disease. This often occurs in the chronic course of the infection.
In this case, methods of provoking the disease are used:
Chemical provocation with lubrication of the urethra with a solution of silver (1-2% concentration). Application of a solution of 2-5% concentration on the cervical canal.
biological provocation. A gonococcal vaccine or Pyrogenal is injected into the patient’s muscle.
Provocation with drinks and food. The patient is offered to take alcohol, or eat spicy or salty foods.
Thermal provocation. Diathermy is carried out for 3 days. Smears are taken 3 times, an hour after the procedure.
Physiological provocation. Smear analysis is performed during menstrual bleeding.
To get a reliable result, several types of provocation are simultaneously combined at once. A smear is taken 3 times in 1-2-3 days.
How to prevent infection after unprotected intercourse?

After rape or after questionable intimacy without the use of a condom, preventive measures should be taken. They must be emergency.
The likelihood of infection is reduced if the following recommendations are followed:
Empty your bladder immediately after intimacy. Well, if you can do it several times. Pathogenic microorganisms will be removed from the urethra along with urine.
Wash the inner thighs and perineum with soap and water.
Miramistin or Betadine must be injected into the urethra and vagina using a urological nozzle. The procedure must be performed no later than 2 hours after the incident of intimacy.
The perineum and inner thigh should be treated with an antiseptic. This may be a solution of potassium permanganate, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin.
Miramistin reduces 10 times the risk of contracting sexually transmitted diseases: gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, genital herpes.
No later than 2 days later, you need to visit a doctor, and after another 14 days you need to take a smear for PCR testing.
Treatment of gonorrhea in women
To cope with the infection, the woman will need to take antibiotics. Both sexual partners should receive treatment. During therapy, it is forbidden to drink alcohol, as well as to have an intimate relationship.
If gonorrhea has affected only the organs of the reproductive system, then the patient is prescribed a single injection of an antibacterial drug (it is also possible to take it orally):
Ceftriaxone 0,25 g. This drug is the most commonly prescribed antibiotic for the treatment of gonorrhea. It is used for patients of any gender. Ceftriaxone is active against various types of gonococci.
Gentamicin 2,0 g.
Sumamed 2 g. Alternatively, it is possible to take such medicines as: Azitrox, Zi-factor, Hemomycin, Azitsid, Ecomed.
Cefixime 0,4 g
Ciprofloxacin 0,5 g.
If the disease has spread to the upper parts of the reproductive system, then the treatment regimen is somewhat changed:
Ceftriaxone 1 g intramuscularly. The drug is administered 1 time per day for a week. Also, the patient is prescribed Ciprofloxacin 500 mg intravenously 2 times a day for a week and Ofloxacin 0,4 g 2 times a day for a week. Treatment with ceftriaxone may be supplemented with doxycycline.
In addition to the listed antibacterial drugs, other antimicrobial agents can be used, for example, Clindamycin, Hemomycin, Sumamed, Zitrolide, Tetracycline, Rifampicin, Bicillin, Josamycin, etc.
To boost the immune system and for the most successful fight against the disease, a woman is prescribed a gonococcal vaccine. It can be Pyrogenal, Methyluracil, Levamisole, Prodigiosan.
Autohemotherapy allows you to activate a woman’s own immunity and more successfully resist infection.
It often happens that gonorrhea is accompanied by other sexual infections. Therefore, the treatment regimen can be supplemented with such drugs as: Doxycycline (the course of treatment is 10 days) and Metronidazole (the course of treatment is 5-7 days). The urethra is washed with a solution of silver nitrate, vaginal douching is performed with antiseptic agents. For this purpose, a solution of potassium permanganate, protargol can be used. Miramistin and chamomile decoction are also used.
Increasingly, doctors are faced with resistant gonococci that do not respond to standard therapy regimens. Thus, leading UK health expert Sally Davies points out that in 2013, about 80% of patients with gonorrhea did not respond to tetracycline treatment. Therefore, experts insist on complex therapy of the disease with the use of 2 antibiotics at once. Inside you need to take Azithromycin, and in the form of an injection, Gentamicin is administered. Alternatively, Azithromycin is taken orally with Gemifloxacin.
If the patient develops complications, then surgery is indicated for her. Laparotomy with removal of the uterine appendages and washing of the abdominal cavity is performed with pelvioperitonitis with suppuration (provided that conservative therapy did not achieve the desired result). Acute bartholinitis requires opening and setting up drainage.









