Contents
Goat manure for the garden as a fertilizer is not yet widely used. This is explained by the fact that it is usually not sold. Goat owners prefer to use the fertilizer on their own plots rather than sell it to third parties. The reason for this shortage is quality. Goat manure is on a par with horse manure, which is considered the best natural fertilizer.
The benefits of goat manure for soil and plants
The main advantage of this type of fertilizer is a small amount of moisture in the feces. True, it is also a disadvantage. Due to the lack of moisture in the “nuts”, goat manure contains more nutrients per kilogram than any other type of farm animal feces.
Under most plants, goat “nuts” can be laid without fear that they will burn the roots. Although manure from goats belongs to the category of “hot”, but for full overheating, urine-soaked bedding is also needed. “Clean” pellets will decompose slowly, without overheating the soil and without immediately giving away the entire supply of nutrients. As a result, the plant will be “provided” with the necessary elements throughout the entire vegetative period.
Composition of goat litter
Apparently, due to the lack of interest of large farms in goat breeding, serious studies of the composition of goat manure have not been carried out. And private owners of these animals do not need to give samples for analysis. In any case, all their manure will “leave” in the beds. Only this can explain the strong discrepancies in the data on the chemical composition of manure. But in many ways, the nutrient content depends on which variety was analyzed.
On average, humus contains:
- nitrogen 0,5%;
- potassium 0,6%;
- phosphorus 0,25%.
Some of the elements are inevitably lost during overheating. If humus is made in violation of technology, the losses will be even greater.
Comparative data of different types of manure are presented in the table:
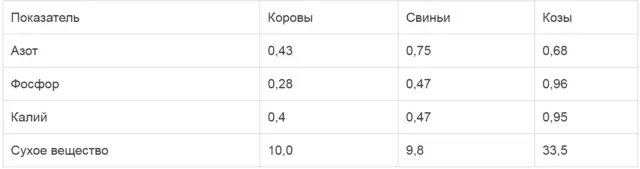
The data is different from the above. But if we take into account that in the first case, indicators are given for humus, and in the second for “clean” excrement, then the picture changes. Fresh goat “nuts” contain much more nutrients than humus. They are superior to cow and pork in most indicators. Although, if you “squeeze out the water” to the same indicators, it turns out that there are 3 times more nutrients in cow dung. Only to remove moisture without loss will not work. And goat – ready-made “granules”.
Pros and cons of using goat manure in the garden
“Clean” “nuts” have undeniable advantages over any other types of manure, except for rabbit:
- there is no unpleasant smell;
- a unique bacterial composition that allows you to use fresh goat manure;
- almost complete absence of eggs of worms dangerous for humans;
- suitable for many garden crops;
- improves soil structure.
Fresh manure mixed with bedding can be used in greenhouses. When overheated, it releases a lot of heat. If you place it under the greenhouse beds, you can plant plants in the greenhouse without fear that the roots will freeze.
Otherwise, too high a temperature during overheating can burn the tender roots of young plants.
Of the minuses, it should be noted the difficulty in preparing humus. Due to the low humidity, goat manure does not well rot in the heap. Some sources indicate as a disadvantage the need for frequent fertilization of the soil: every 1-2 years. But other experts believe it’s all about the numbers. If enough manure is applied, its effect will last up to 5 years. Such contradictions make us wary of this type of fertilizer.
Under what plants can goat droppings be applied
In this case, it is easier to say under which plants goat manure cannot be used as fertilizer: bulbous flowers and garlic. Flowers do not tolerate this type of top dressing. They start to rot and stop blooming.

Hyacinths do not favor goat fertilizer either fresh or rotten.
Even rotted goat manure cannot be added under garlic. Perhaps due to the specific intestinal microflora, the plant begins to hurt. Yields are low as a result.
Having given some of the nutrients to other plants, the manure becomes suitable for garlic. Bacteria that live in the digestive tract of animals also have time to die. As a result, on such a “second-year” fertilizer, garlic grows very large and even.
Cucumbers and tomatoes respond very well to the introduction of fresh manure from goats. Their yield is doubled. Onion responds well. It turns out large and not bitter.
Under root crops it is better to make rotted manure. When planting potatoes, many gardeners do not fertilize the entire beds, but put the humus directly into the hole.
How to use goat litter
As a fertilizer, goat manure is used in two forms: fresh and rotted. The first is convenient to use for digging in the fall and in greenhouses. The second is laid directly under the plants when planting. It can also be applied to the soil in the spring when preparing beds in the open.
Fresh
It can be really fresh if you pick goat “nuts” immediately or half rotted. The latter occurs if the owner cleans the goat’s rue in spring and autumn. Sometimes only in the spring. It is advantageous to keep goats in winter on a deep, decaying litter. It is dry enough not to hurt the legs of the animals, and hot enough to keep the room warm.
When cleaning the goat’s rue in the spring, the owner will receive a semi-overripe mass. Moreover, at the bottom there will be almost ready-made humus, and on top there will be completely fresh excrement. Such goat manure is suitable for making under the beds in the greenhouse.
Dry
Dried manure from any animal is only good as mulch. Or as fuel in treeless regions. This is especially true for goat and horse manure, which are already drier at the exit than any other types of excrement.
Humus
For better overheating, goat manure is recommended to be mixed with compost. This is due to the small amount of “product” produced by goats, and its low humidity. The finished pile should be periodically watered with water, but waterlogging should not be allowed.
Manure for humus is harvested in two ways. The first is frequent cleaning of the goat’s rue and briquetting. The second is keeping goats on a deep litter and removing waste 2 times a year.
The briquettes, as they are filled, are placed in a pile or left for long-term storage. In this case, the blanks are laid on a dense litter and covered with hay. If it is necessary to make humus, the briquettes are crushed, diluted with water to a paste-like state and a collar is made. Vegetable waste and straw are added to manure. It will take about a year for the fertilizer to mature.
The second option is to make a pile 2 times a year immediately from the entire mass of manure. In the spring, goat excrement cannot yet be mixed with compost, so superphosphate and soil are added to the pile. Industrial fertilizer will enrich the organic mass with nitrogen and accelerate the maturation of the collar.
The ripened mass is brought into the ground when digging the garden in spring and autumn.
Aqueous solutions
The preparation of infusion for irrigation depends on what kind of manure will be used. In any case, it will be fresh, since it is more expedient to introduce humus into the soil. But “clean” goat pellets are very different in hardness from manure mixed with bedding.
Manure with bedding is preferable because it is looser and enriched with nitrogen. It must be endured less than just goat feces. It takes 1-2 days to get the infusion.
“Clean” goat “nuts” will have to be kept in water for 7 to 10 days. At the same time, nitrogen will be absent in the infusion.
In both cases, 10 part of manure should be taken for 1 parts of water. It is better to insist in a warm place so that the process goes faster. A greenhouse is well suited for this procedure.
This solution has almost no smell. For irrigation, the resulting infusion must be diluted additionally: add 10 liters of water per liter of fertilizer.

Goat “nuts” are good to use for the preparation of water infusion, if you can get the required number of spools
Norms and dosages of goat droppings
A very interesting topic, since the difference of opinion here is even greater than in the data on the chemical composition. More or less everything is clear only with the arrangement of greenhouse beds.
It is most profitable to arrange such warm beds in the northern regions of Our Country. It is goat manure that has no competitors in this area. Because of its low humidity. You can’t just mix fresh fertilizer with the ground. For the arrangement of beds, a number of operations are provided:
- first dig a trench 0,5-0,6 m deep;
- a layer of fresh manure about 20 cm thick is laid at the bottom;
- covered with soil so that there is 30-40 cm above the organic fertilizer.
Young seedlings can be planted on the finished bed in the greenhouse. Due to the low humidity, goat manure will not provoke the growth of mold. And due to the fact that it warms up well during decomposition, the soil in the garden will be warm. Under this regime, goat waste will be reheated after 1-1,5 months. By this time, the roots of the seedlings will grow to a layer of manure and receive ready-made nutrients.
There are serious disagreements about the periods and norms for introducing rotted manure into open ground. Some goat breeders advise to bring in 5-7 kg per hundred square meters, others say that even 150 is not enough. But they agree that it all depends on the method of applying fertilizer to the soil.
When spreading over the entire area, you need at least 150 kg per hundred square meters. At the same time, it is necessary to re-fertilize after 3 years. If the rate per hundred square meters is 300-400 kg, then the period will be 5 years.
A goat is a medium-sized creature, it does not produce a lot of manure. Therefore, often gardeners make “goat” humus only in the holes for plants. In this case, 5-7 kg will really be enough for a hundred square meters. But you also have to fertilize every year.

There is little benefit from fertilizer poured over the soil, since the nutrient content in it decreases under the influence of natural factors.
Conclusion
Goat manure for the garden is usually used only by the goat breeders themselves. Due to the small amount of waste. But if this fertilizer is available, it is most advisable to use it in a greenhouse. The consumption there will be relatively small, and the return will be as high as possible.









