Contents
Glycated hemoglobin is an iron-containing protein that may indicate an insidious course of diabetes. It begins to be produced when blood sugar levels rise. Glycated hemoglobin is also called glycated hemoglobin.
Even a short-term increase in blood glucose levels leaves a trace in the body. It can be detected 30-45 days after the event. Glycated hemoglobin is formed instead of ordinary hemoglobin, which is transformed against the background of a jump in glucose.
What does it mean?
When the level of glucose in the blood rises, the body is not able to completely process it. Therefore, its molecules interact with proteins (albumin, hemoglobin, lipoproteins), forming a strong connection. Glycation of hemoglobin is an irreversible process, it is called the Maillard reaction.
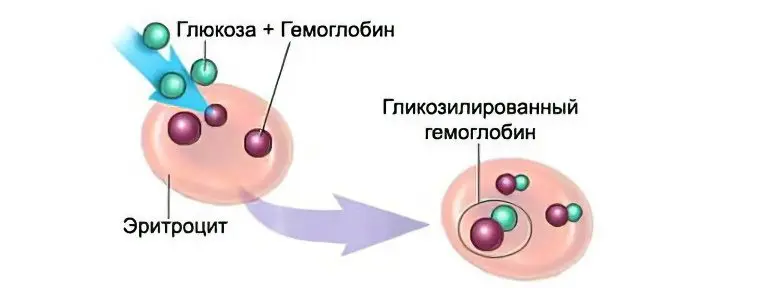
The blood cells that carry hemoglobin have a “lifespan” of 3 months, so its compounds with glucose can be detected even long after the jump in sugar levels in the body.
With latent diabetes mellitus, glucose combines with hemoglobin several times faster. In the future, he is not able to get rid of its molecules, therefore, such hemoglobin can be detected until the erythrocytes that carry it are alive.
The calculation of such destroyed hemoglobin molecules makes it possible to assess the degree of glycation. This allows you to identify the latent course of the disease, even if the sugar level at the time of the study is within the normal range. Glycated hemoglobin is always present in the human body; it is not a pathogenic compound for it. Normally, it should not be more than 6% of the total level of normal hemoglobin.
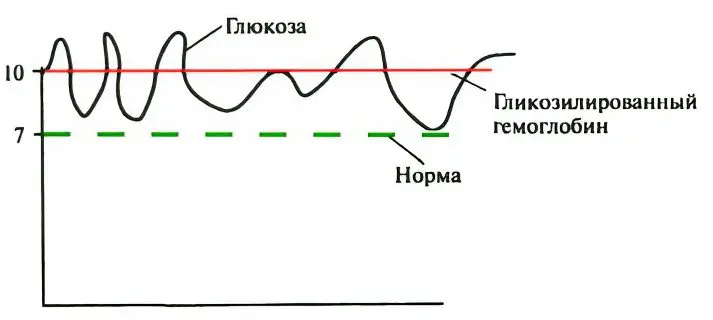
Thus, the study allows you to establish the level of glucose in the blood of a person a month ago or more. The analysis is informative even when the jump in sugar was short-lived. Excess glucose molecules will still react with hemoglobin, which will affect the results of the study.
Norm values

If a person is healthy and does not develop diabetes mellitus, then the level of glycated hemoglobin will be in the range of 4-5,8% of the total amount of hemoglobin in the blood. Excess of these indicators can be observed only in children during the neonatal period. At this time, the child has fetal hemoglobin in the blood, but by the year the baby’s body should completely remove it.
If a person suffers from diabetes, the hemoglobin level can rise to 12% or more.
Interpret the received data as follows:
The level of glycated hemoglobin does not exceed 6% – this is an indicator of the norm.
The hemoglobin level rises to 6-8%. This indicates that there was a jump in glucose, but the body coped with them on its own. The same indicators can be in people with diabetes, but taking medications. In this case, it is they who cope with glucose.
The level of glycated hemoglobin reaches 9%. These data indicate compensated diabetes mellitus, which requires the initiation of treatment or revision of therapy.
The level of glycated hemoglobin rises to 9-12%. This situation requires extreme vigilance, as it indicates that the body itself is no longer able to cope with spikes in blood sugar. If diabetes mellitus is being treated, then such a level of glycated hemoglobin indicates its partial failure.
If glycated hemoglobin exceeds 12%, then the treatment does not give the desired result and requires correction.
Determining the level of glycated hemoglobin is informative in terms of diabetic detection. It allows you to assess the risk of developing complications of this disease.
The analysis is carried out for different purposes:
Detection of the latent course of diabetes mellitus.
Evaluation of the effectiveness of the treatment and control of the development of the disease.
Assessment of carbohydrate metabolism in the body, assessment of the degree of compensatory capabilities of the body.
In addition, this study allows you to expand the information that the doctor receives during the glucose load test. It is recommended for people with suspected diabetes mellitus, but with an undetermined diagnosis. To detect diabetes in pregnant women, other tests should be used. The level of glycated hemoglobin during the period of bearing a child does not allow obtaining the most reliable information.
Relationship between glycated hemoglobin and glucose
The level of glucose in the blood and the level of glycated hemoglobin have a close relationship with each other. It is reflected in the table.
Percentage of glycated hemoglobin in the blood | Mean blood glucose in mol/l | Mean blood glucose in mg/dL |
4 | 2,6 | 47 |
5 | 4,5 | 80 |
6 | 6,7 | 120 |
7 | 8,3 | 150 |
8 | 10,0 | 180 |
9 | 11,6 | 210 |
10 | 13,3 | 240 |
11 | 15,0 | 270 |
12 | 16,7 | 300 |
Why does the level of glycated hemoglobin in the blood rise and fall?
Glycated hemoglobin rises in the blood not only against the background of diabetes mellitus, but also in other conditions, including:
A high level of fetal hemoglobin leads to an increase in the level of glycated hemoglobin. A similar situation can be observed in children under the age of one year. In the future, all indicators should return to normal.
Iron deficiency in the body leads to an increase in the level of glycated hemoglobin.
The absence of the spleen in the body after the operation can contribute to various changes in the blood picture. Including, lead to an increase in the level of glycated hemoglobin.
If doctors encounter high rates quite often, then a low level of this hemoglobin in the blood is rarely diagnosed.
Its insufficient concentration is observed in the following cases:
Low blood sugar.
Increased production of hemoglobin in the body.
Postponed bleeding, which was accompanied by massive blood loss. After such pathologies, the hematopoietic system is activated, which can lead to a decrease in the level of glycated hemoglobin.
Hemolytic anemia, accompanied by accelerated destruction of red blood cells, which are carriers of hemoglobin.
Severe disorders in the work of the kidneys.
Blood transfusion.
Although increased and decreased levels of glycated hemoglobin in the blood may accompany a number of other pathologies, nevertheless, it is more often determined precisely for the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus.
How to submit?
To determine the level of glycated hemoglobin, you will need to donate blood from a vein. For the study, it is collected in an amount of 3 ml.
No preliminary preparation is required. It is not necessary to come to the laboratory on an empty stomach. Glycated hemoglobin is present in the blood for a long time and meals before the test do not have any effect on its level.
For people with diabetes, the study is carried out 1 time in 3 months. This allows the doctor to monitor the course of the disease and evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy. If the analysis raises any doubts, for example, with a patient with hemolytic anemia, then additional studies are prescribed for him. To assess the quality of carbohydrate metabolism in the body, it is possible to donate blood to determine the level of fructosamine. This study provides information on spikes in blood glucose over the past 2-3 weeks.
To undergo a study on your own initiative, you can contact a paid laboratory. The average cost of the analysis is 700-800 rubles (for megacities), although the price of the study varies, depending on the specific locality and medical and diagnostic institution.









