Contents
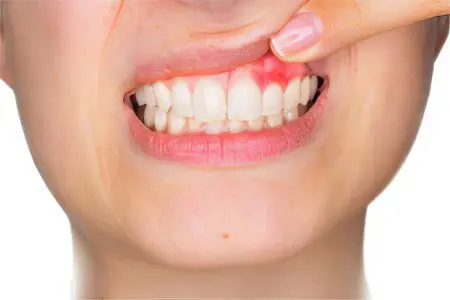
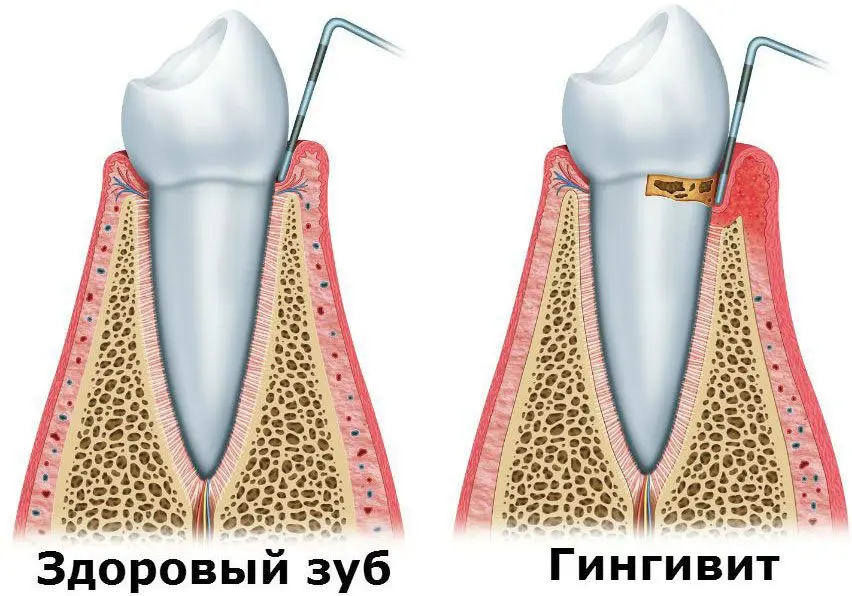
Gingivitis – This is an inflammatory process that captures only the gum. Ligaments of the tooth and bone tissue are not affected. Gingivitis is widespread, affecting 80% of school students and 100% of the adult population. In childhood, gingivitis is diagnosed no more often than in 30% of cases.
Poor oral care is the main cause of gingivitis. The inflammation is often asymptomatic. Its manifestation can be bleeding gums. First, the papilla of the gums becomes inflamed, and then its other parts. The disease quickly becomes chronic. From time to time, the pathology worsens, after which it subsides.
Depending on the form of the disease, gingivitis can be catarrhal, ulcerative and hypertrophic.
Gingivitis reasons
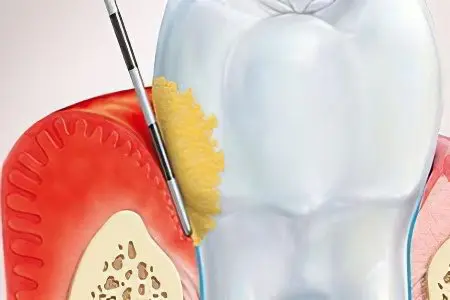
Gingivitis is caused by bacteria that actively multiply in plaque. In order for them to begin to multiply their numbers, certain pathological factors are required. It has been proven that if there are no bacteria on the gums, then a person does not develop gingivitis under any circumstances.
Mechanical damage to the gums leading to gingivitis:
Anatomical disorders, for example, irregular tooth shape, malocclusion, too close teeth, etc.
Presence of tartar. In it, not only bacteria actively multiply, the stone is an obstacle for high-quality brushing of teeth.
The resulting injury to the gums during brushing your teeth, or in case of accidental damage.
Changes in the composition of saliva.
In addition, gingivitis may appear due to incorrect manipulations by the doctor:
Gum injury during dental treatment.
Incorrectly installed seal. In such places, bacteria multiply especially actively.
Wearing removable dentures, under which plaque accumulates. It can also damage the gums.
Setting up bridges. With such designs, caring for the gums will be especially difficult.
Operations performed in the oral cavity.
Wearing orthodontic structures to straighten teeth. They complicate the care of the oral cavity.
Causes of gingivitis in pregnant women
Pregnant women also develop gingivitis due to bacteria found in dental plaque. In the body of the expectant mother, hormonal changes occur, the work of all internal organs changes. Therefore, almost 100% of pregnant women develop gingivitis.
The gums under the influence of estrogen and progesterone become soft and loose, so they are easier to injure. The very composition of the microbial flora in the mouth changes, as bacteria begin to use female hormones instead of the usual nutrients.
Causes of gingivitis in children
Gingivitis in children develops due to microbes that live in plaque. However, it accumulates due to the fact that the processes of self-cleaning of teeth are often disturbed.
The reasons for this may be several:
Earlier removal of milk teeth.
Treatment at the orthodontist.
Violations in the structure of the frenulum of the lips and tongue.
Too viscous saliva, due to the use of soft foods and sweets.
Chewing gum.
Violation of the process of swallowing food, breathing through the mouth.
Caries, pulpitis.
Pathology of the salivary glands.
Gingivitis symptoms
Depending on the form of gingivitis, its symptoms will vary. You can notice them yourself, but you should not forget about regular visits to the dentist.
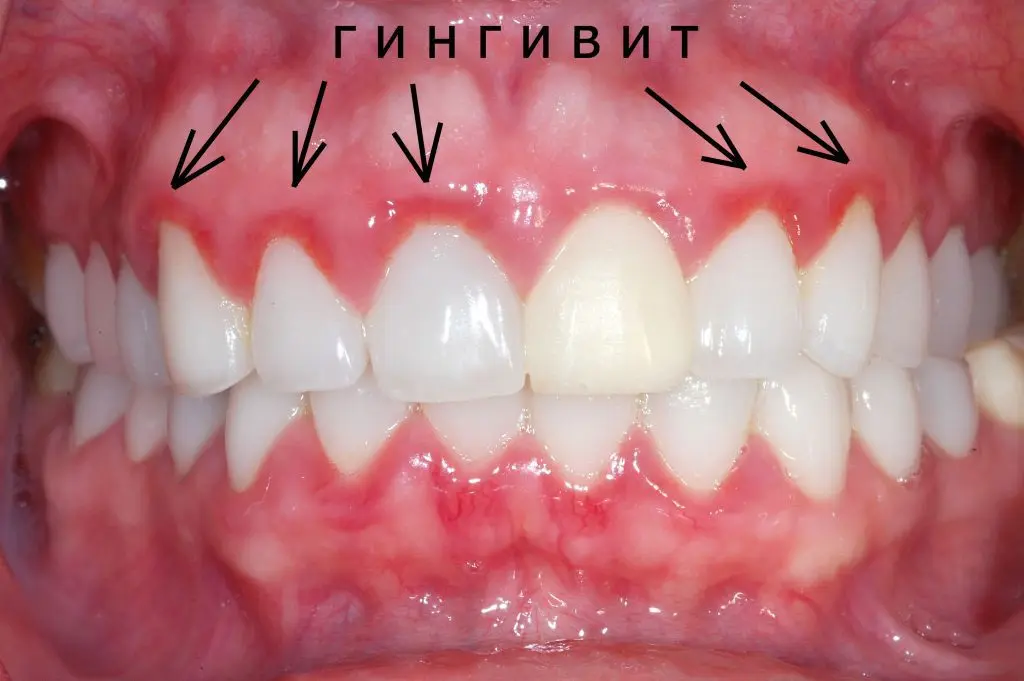
Symptoms of catarrhal gingivitis
As practice shows, catarrhal gingivitis develops in almost 100% of patients with gastroenterological pathologies.
| Acute form of catarrhal gingivitis | Chronic form of catarrhal gingivitis |
Reasons for development | Acute phase of chronic diseases or recent infections. |
|
Symptoms that the patient himself notices | The gums begin to bleed, the blood appears just like that, without a mechanical effect on the gum. The person is in pain. |
|
Dental signs |
|
|
Making a differential diagnosis | The disease must be distinguished from hypertrophic and medicinal gingivitis. | The disease must be distinguished from periodontitis, in which a pocket is formed in the gum, the bony partitions between the teeth decrease, and they themselves become mobile. From lichen planus, which is characterized by itching and burning of the gums, as well as pain when touched. With lichen, all the mucous membranes of the oral cavity suffer. |
Symptoms of ulcerative gingivitis
It has been found that with atypical premenstrual syndrome, ulcerative gingivitis develops in women.
Causes of the peptic ulcer |
|
Symptoms that bother a person |
|
Dental signs |
|
Making a differential diagnosis | It is necessary to distinguish gingivitis from acute leukemia, which is manifested by blanching of the oral cavity, tissue necrosis and changes in the composition of the blood. Ulcerative gingivitis should also be distinguished from syphilis. With this disease, ulcers and other defects of the mucous membranes will not hurt. |
Symptoms of hypertrophic gingivitis
Hypertrophic gingivitis can occur as a fibrosis, or in an edematous form. Most often, this pathology manifests itself in people with vitamin A deficiency.
| edematous gingivitis | fibrous gingivitis |
Causes |
Irritation of the gums, e.g. from fillings or dental restorations. | |
Symptoms that the patient notices | The gum becomes larger and becomes unattractive. The gums bleed and hurt when pressed. | The gum does not bleed, but its appearance changes for the worse. |
Dental signs | Plaque on the teeth, the teeth are too close, the bite is deep. The gums are red, swollen, bleed and hurt. | The teeth are placed incorrectly in the mouth, too close, which leads to problems with dental hygiene. Gingival papillae begin to grow, the gums become pale in color, do not swell or bleed when pressed. |
Making a differential diagnosis | It is necessary to distinguish gingivitis from fibromatosis, in which the entire gum suffers along with the bone. It is also necessary to conduct a differential diagnosis with blood diseases that lead to characteristic changes in the analyzes. | |
Diagnosis of gingivitis
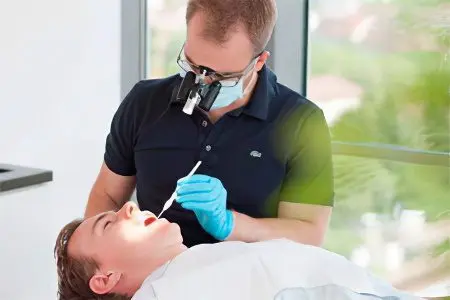
A patient with gingivitis is examined. The doctor specifies how long ago he had the first symptoms of discomfort.
Examination of the oral cavity involves the following activities:
Evaluation of the bite, frenulum of the lips, mucous membranes.
Assessment of the condition of the palate, cheeks, pharynx, tongue.
Assessment of the condition of the teeth, the presence of caries, stone, soft plaque, pulpitis.
Evaluation of the color and structure of the gums, determination of bleeding, the presence of purulent lesions.
After such an examination, the doctor can assess the severity of the pathology.
If necessary, the doctor will refer the patient for additional examination.
It may include:
Radiography. This method allows you to distinguish gingivitis from periodontitis.
Donating blood for a general analysis. The study allows you to assess the state of health in general and clarify the absence of blood diseases.
Blood for biochemical analysis. This study provides information about diabetes.
Donating blood for HIV and syphilis.
A microbiological study that allows you to clarify the representatives of the bacterial flora that lives in the oral cavity.
Gingivitis treatment
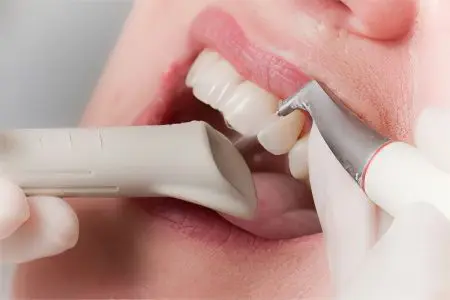
To cope with gingivitis, you need to take into account various factors, ranging from the severity of the inflammation and the stage of development of the disease.
Treatment of chronic form
The patient should be explained how to properly care for the oral cavity, how to brush teeth, etc.
The doctor conducts professional oral hygiene, removes not only soft, but also hard plaque.
The patient is prescribed antiseptics, ointments that relieve inflammation, rinses and gels.
To increase overall immunity, you should take vitamins, as well as drugs that increase the blood supply to the gums.
All diseased teeth should be treated.
In the presence of bite defects, it is necessary to carry out its correction.
Treatment of acute form
Acute gingivitis requires relief of pathological symptoms. For this, the patient is prescribed antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. When the edema passes, the patient is treated according to a scheme similar to that for the treatment of the chronic form of the disease.
Treatment of the ulcer form
Antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity. Since ulcers cause pain to a person, they must first be anesthetized.
Then, enzymatic preparations are applied to ulcerative defects, the ulcers are cleaned.
The antibiotic of choice is Metronidazole. It is used for local therapy.
After the ulcers begin to heal, you can use drugs that accelerate tissue regeneration. It can be vitamins A and E, sea buckthorn oil.
Sometimes an antibiotic is prescribed orally. Use all the same Metronidazole.
The patient is prescribed drugs that stop inflammation and remedies for allergies.
It is possible to use immunomodulators and vitamin complexes.
After the gums have healed, a person will need to cure all diseased teeth.
Treatment of the hypertrophic form
Therapy is carried out according to a scheme similar to the treatment of catarrhal gingivitis. However, the patient may require surgical removal of gum tissue that has grown too much. This can only be done after all diseased teeth have been treated.
If a patient is diagnosed with leukemia, then the treatment of gums is exclusively symptomatic, the patient is not prescribed surgery.
Treatment during pregnancy
Topical treatment of gingivitis during pregnancy is similar to that for normal patients with the same problem, but antibiotics and other drugs are not taken by mouth. If it is impossible to refuse oral therapy, then a preliminary consultation with a gynecologist is required.
Scientists continue to search for effective drugs for the treatment of gingivitis in pregnant women. So, in 2007, it was found that a warm compress with Mexidol and paraffin, which is applied to the gums, has a good effect. You can also brush your teeth with Mexidol paste and use a mouthwash with the same substance.
In 2012, it was established that Vulnuzan ointment can be used during pregnancy.
Treatment of gingivitis in children
To cope with gingivitis in a child, you need to teach him how to properly care for the oral cavity. In order to assess the degree of cleaning of the teeth, special dyes are used. When the disease has a severe course, treatment is required according to the treatment regimen for ulcerative gingivitis in adult patients.
It is important to correct the bite, as well as other orthodontic problems. The child should eat right, often be in the fresh air.
Treatment of gingivitis at home

You can cope with catarrhal gingivitis at home with the use of ROCS series toothpaste. Well eliminate gum bleeding pastes Forest Balsam, Paradontax, Lacalut. You can also use Asepta gum gel and balm.
You need to brush your teeth with high quality, using dental floss. You can rinse your mouth with a shepherd’s purse, a decoction of sage or chamomile.
When a person develops mild ulcerative gingivitis, but there is no way to visit a doctor, you can use the following recommendations:
Drink as much water as possible, follow a diet.
Take drugs inside: Metronidazole (0,5 g 2 times a day), Aspirin (0,5 g 3 times a day), Diphenhydramine (0,05 g 2 times a day).
Do irrigation with Chlorhexidine or Miramistin.
Metrogyl Denta gel is applied to the cleaned gums. This treatment is carried out at least 5 times a day.
In the intervals between the main treatment, the mouth is rinsed with decoctions of chamomile and sage.
When the pain becomes less intense, Carotenol, Solcoseryl, rosehip or sea buckthorn oil are applied to the gums.
Prevention of gingivitis
To prevent the development of gingivitis, you need to properly sanitize the oral cavity, brush your teeth properly and visit the dentist regularly. Professional cleaning should be done at least 2 times a year.









