Contents
Hazelnut or hazel is a popular shrub that can be found in gardens. Despite timely care, often under adverse climatic conditions, a variety of hazelnut diseases can appear. Diseases and pests are very similar to those often found on other plants. If preventive measures are observed, troubles can be avoided and a rich harvest can be harvested.
Hazel diseases and treatment methods
The plant is immune to many diseases, but after a cold winter and during the rainy season, fungal, infectious and bacterial diseases can join. Hazelnut diseases without timely care and treatment can lead to the death of the bush. Therefore, when the first symptoms appear, it is necessary to begin timely treatment.
Bacterial burn
The most dangerous disease of hazelnuts is a bacterial burn. Fungal disease damages the entire aerial part: leaves, shoots, flowers and fruits. The disease appears due to high temperature and humidity. In hot and dry weather, the disease is extremely rare.
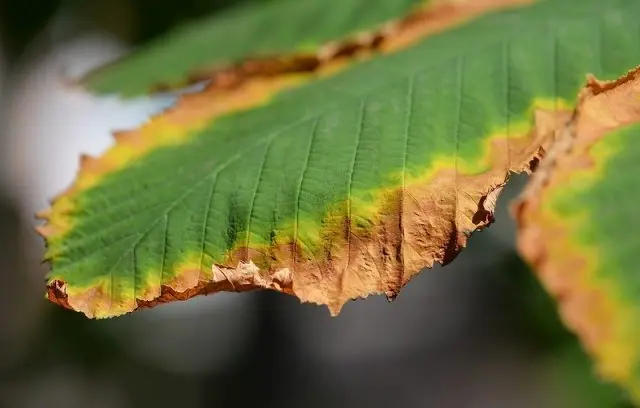

The main signs of the onset of the disease are numerous black spots.
- When a disease strikes a flower, it wilts, turns dark brown and falls off.
- Young branches are covered with dark spots, the tips are bent and painted black.
- The leaves take on a charred, drooping appearance, turning brown.
- Affected unripe nuts turn black and remain on the branch until the end of autumn.
- When a disease appears, the bark becomes covered with cracks, an extensive burn with clear boundaries appears on the trunk.
The disease develops in the spring, when the active growing season begins. The disease on hazelnuts appears with pollen. Carriers are birds, insects, rainwater. With an increase in air temperature and humidity by 80% or more, the disease begins to actively progress.
Branches become infected from the affected bark and leaves. The source is a non-sterile tool, diseased bushes, fruits and rooting cuttings. A year after infection, a thick, viscous exudate flows out of the sores, which is easily carried by the wind, while infecting neighboring plantings.
The treatment of the disease is carried out as follows:
- Pruning damaged shoots to healthy tissue.
- Spraying hazelnuts in the phase of bud swelling with 3% zinc sulfate.
- Treatment of hazel with copper-containing preparations.
- Autumn top dressing with potash fertilizers.
White rot
White rot or sclerotinia is a dangerous fungal disease that leads to decay of the root system. The main signs of the disease are:
- wilting of the aerial part;
- the formation of white plaque on the leaf plate, fruits, stem;
- the root system is covered with a snow-white mucus-like mass;
- black sclerotic formations are visible on the cut of the shoot;
- the leaf plate becomes watery and discolored, sometimes covered with a white coating.
The pathogen infects the walnut bush through the soil. The disease affects hazelnuts with a sharp drop in temperature and high humidity.
The disease primarily affects walnut wood. It loses elasticity, acquires a fibrous state and a snow-white color, becomes less durable and breaks easily.
To get rid of the disease, it is necessary to carry out complex treatment. At the initial stage of the disease, damaged shoots are cut to healthy tissue, the cut site is treated with potassium permanganate or crushed chalk. Next, hazelnuts are treated with fungicides, changing them once a season so that addiction does not occur. If the disease has affected most of the shrub, it is better to get rid of it so that the disease does not spread throughout the garden.
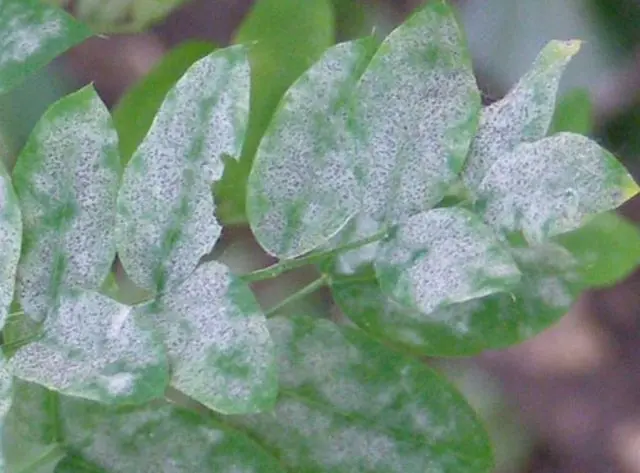

brown spot
Brown spot or phyllosticosis is a fungal disease that often affects hazelnuts. The disease spreads through soil and water. The disease is quickly spread from one hazelnut bush to another by wind, insects and birds. It progresses rapidly at high humidity and air temperature.
To recognize the disease, you must carefully examine the walnut bush. When infected, dark red spots of irregular shape form on the leaf plate. At the initial stage of the disease, the central part of the spot is much lighter than along the periphery. Over time, the outer side of the leaf becomes covered with small swellings.
The disease often affects old, weakened leaves during the fruiting period. The peak of the disease occurs in early July, especially in rainy weather. The mass development of the disease leads to early leaf fall, which significantly reduces the yield of nuts in the next season.
Since brown spot is a fungal disease, it must be treated with fungicides. These can be purchased drugs, or they can be folk remedies. When using chemicals, the treatment is completed a month before the collection of hazelnuts. In the treatment of the disease folk remedies used:
- Spraying the bush and the trunk circle with iodine chloride (30 g of potassium chloride, 40 drops of iodine per bucket of water).
- Treatment of the bush with diluted whey.
- Spraying the bush with garlic infusion.
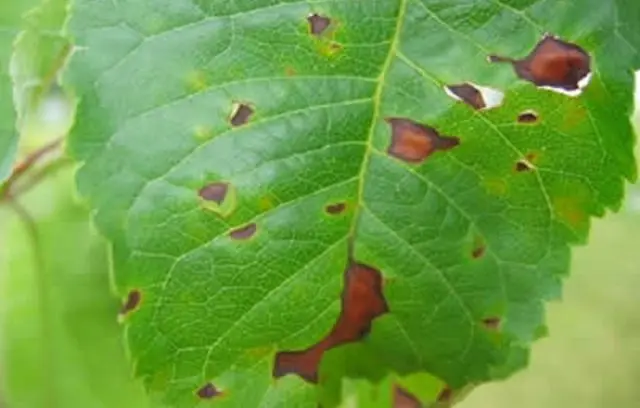

Mučnistaâ rosa
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects leaves and young shoots. The affected foliage is covered with a white bloom, turns yellow, curls and falls off. New leaves appear deformed and weakened. Young shoots do not ripen during infection, do not become stiff, and as a result die from the first autumn frosts.
When the first symptoms of the disease appear, it is necessary to start timely treatment, otherwise the disease will quickly spread to neighboring bushes. Without the timely removal of white plaque, photosynthesis fails, which further aggravates the condition of the hazelnut.
Powdery mildew often appears at moderate humidity and high air temperature. Insects, wind and rainwater are considered carriers of the disease. The fungus overwinters on the affected leaves, so if you do not remove the fallen leaves, powdery mildew attacks the walnut shrub with renewed vigor in the spring.
When a disease occurs, treatment should be started immediately:
- Trim all affected shoots to living tissue.
- Once every 7 days, treat the shrub with soda ash with soap or infusion of garlic.
- Spray the nut with an antibacterial mixture. Terramycin 100U, Penicillin 100U, Streptomycin 250U diluted in warm water in a ratio of 1:1.
- A good result is the treatment of shrubs with slurry. 1 part of manure is diluted with 3 parts of water and left to infuse for 3 days. The finished solution is diluted 1:3.
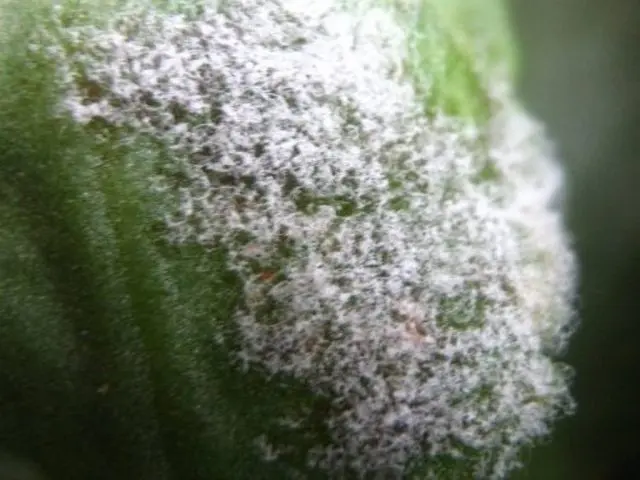

Rust
Rust is a common, dangerous disease. The fungus infects the entire aerial part of the walnut bush. As a result, cold resistance, yield and quality of fruits are reduced. When infected, the nut begins to quickly lose moisture, the process of photosynthesis and metabolism worsens, and the growth of shoots decreases sharply. If timely measures are not taken, hazelnuts may die.
You can determine the disease by the outside of the leaf plate. In the initial stage of the disease, small dark brown spots appear on it, which eventually spread over the entire leaf plate.
If you do not immediately start treatment, then in the middle of summer large growths appear on the inside of the foliage. With the further development of the disease, the foliage dries up and falls off. Untimely leaf fall weakens hazelnuts and reduces cold resistance.
Rust removal is carried out in several ways:
- Spraying hazelnuts with copper and sulfur-containing preparations. Processing is carried out before and during flowering.
- In early spring, the affected shoots are cleaned to healthy wood, followed by treatment with disinfectant solutions.
- Pruning of affected shoots 5 cm and skeletal branches 10 cm below the lesion. Pruning is carried out before sap flow.
- After pruning, the bush is treated with fungicides at intervals of 10-13 days.

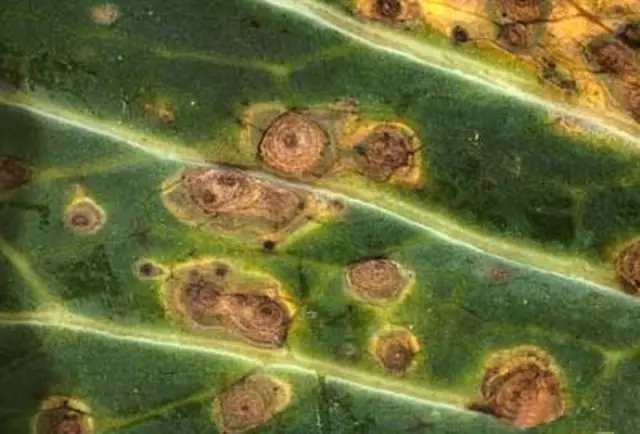
Black spot
Black spot or phomopsis is a dangerous fungal disease that affects the entire aerial part of the hazel. The disease develops intensively in wet weather, affecting the leaves and the lignified part of the nut.
You can recognize the disease by carefully examining the bush. Lignified shoots become discolored, dark spots appear on the bark. If you do not start treatment, the fungus penetrates deep into the wood, forming rotten areas. Over time, hazelnuts stop growing and developing, and infected shoots die off. If the disease affects the foliage, then it becomes covered with dark brown spots with a clarified middle. Over time, the leaf plate dries up and falls off. Without treatment, the plant refuses to bloom and bear fruit.
Black spot is spread by wind, rainwater and insects, through mechanical damage to the shoots.
The disease perfectly tolerates a cold winter on plant debris. Experienced gardeners have noticed that if fallen leaves are removed in a timely manner, then the fungus will not have enough food, and it will die after 5 days.
To get rid of the disease you need:
- treat hazelnuts with copper-containing preparations;
- apply herbal solution.
To do this, cut grass is poured with water in a ratio of 1: 1 and left to infuse for 1 week. The resulting solution is filtered and the bush is treated after sunset.

Hazelnut pests and their control
Hazelnuts are loved not only by gardeners, but also by pests. Insects feed on shoots, leaves and nuts. The greatest harm is caused by insects that destroy the crop. If you do not fight them, they can destroy up to half of the crop.
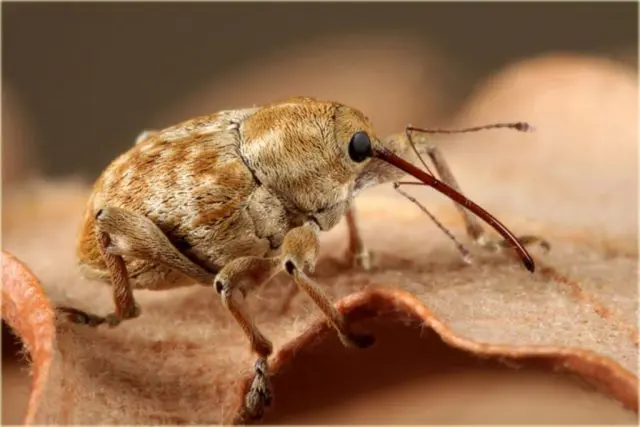
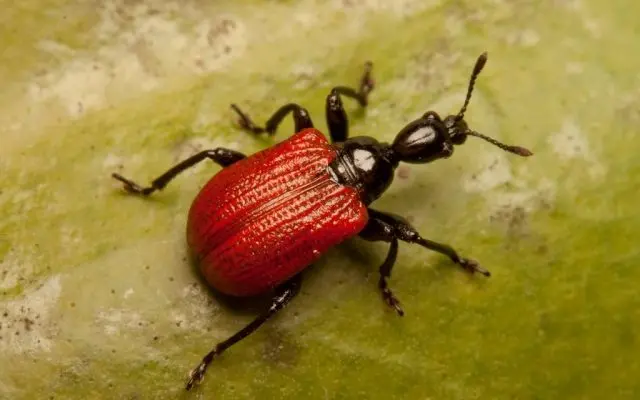
Fruited walnut
The walnut or walnut weevil has been fruited in all regions of Our Country where hazelnuts are grown. This insect easily destroys up to 50% of the crop. The beetle hibernates in the ground, lays larvae in early spring, which hatch at a temperature of + 15 ° C. The beetle begins to attack the plant in late May, early June.
Insects are located in the crown, where they destroy leaves and young shoots. Females gnaw through unripe fruits and lay eggs in them. The revived larvae feed on the nut, completely eating away the kernel. After the destruction of the crop, the larvae leave the nut and burrow into the ground.
To get rid of bugs, you must:
- treat the soil with insecticides in early spring;
- in early May, the crown is treated with acaricides;
- collect and destroy fallen fruits in a timely manner;
- in spring and autumn, the trunk circle is loosened;
- early in the morning a wide canvas is spread around the bush, the bush is shaken, and the fallen beetles are immediately disposed of.

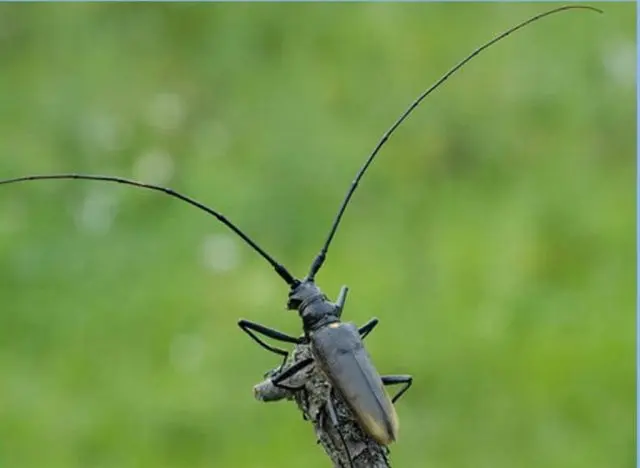
nut barbel
Walnut barbel is the most dangerous pest that can destroy shrubs in a short time. Adult beetles begin flying around orchards from early May to mid-June. In mid-June, an adult lays eggs under the bark of young branches. The larvae appear at the end of June. In the first days, the larvae gnaw through the core of the branches, as a result of which the shoots begin to dry out, the upper leaves turn yellow, curl and crumble.
Without treatment, the larvae hide in the bark for the winter and, upon the arrival of warm days, begin to destroy 3-year-old shoots.
Treatment is carried out immediately after the first signs of the disease are detected:
- dried shoots are removed and burned;
- in mid-June, the nut is sprayed with insecticides.

Oreshnikov tube cover
Hazel pipeworm is a small beetle that feeds on young foliage. Often it can be found at the end of May when the foliage blooms. Females gnaw the leaf plate by ½ length, wait for it to dry and twist it into a tube where they lay their eggs. The hatched larvae feed on dry foliage, and for the winter they burrow into the soil of the near-stem circle.
The beetle, according to gardeners, does not cause severe damage to the tree. But in order for the plant to look healthy and develop well in early spring, before bud break, the crown and the ground are treated with insecticides.

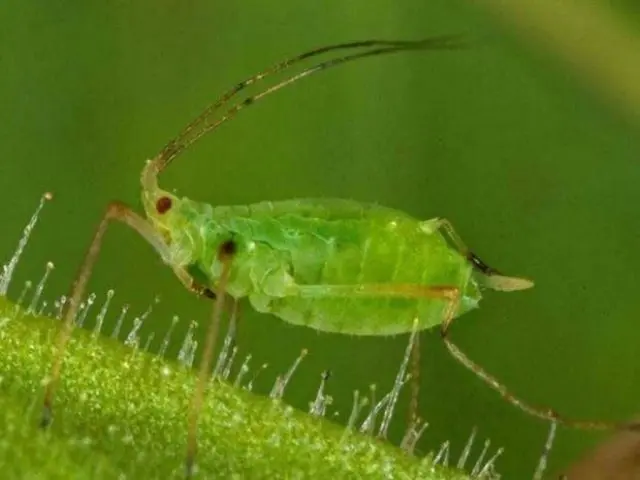
aphid
Aphid larvae appear on the nut in late spring. Pests suck the juice from the plant, which leads to slow growth and rapid death. Also, the aphid colony is a good distributor of fungal diseases.
Premature leaf fall reduces the taste of fruits and productivity. With inactivity, aphids can quickly spread throughout the garden.
You can get rid of insects in 2 ways: removing them from the foliage or treating the bush with soapy water. In case of mass infection, the nut is treated with insecticides a month before harvest.

Prevention of pests and diseases of hazelnuts
The yield of hazelnuts depends on timely prevention. To protect the nut from diseases and pests, you must follow simple rules:
- carry out timely watering and top dressing;
- remove damaged, dried branches;
- in autumn, cut out shoots that thicken the crown;
- in early spring, treat the walnut and the soil of the near-trunk circle with copper-containing preparations;
- when the first signs of the disease appear, remove damaged leaves and fruits;
- in the fall, get rid of fallen vegetation;
- destroy adult insects before oviposition begins.
Conclusion
Hazelnut diseases are better prevented than treated. Subject to the rules of care and timely prevention, the walnut bush will delight you with a rich harvest of tasty, healthy fruits.