Contents
- What are free radicals
- Action of free radicals
- Free radicals in the human body
- How to deal with free radicals in the body
- Free radicals and antioxidants
- How to protect yourself from the effects of free radicals
- An Overview of Antioxidant Foods
- Antioxidant gel for the skin around the eyes AOX + Eye Gel, SkinCeuticals
- Resveratrol BE Concentrated Antioxidant Gel, SkinCeuticals
- Broad Spectrum Serum Phloretin CF, SkinCeuticals
- Firming care against signs of aging at different stages Slow Age, Vichy
- Anti-aging care for normal and combination skin Redermic C, La Roche-Posay
The more discoveries are made in the beauty industry, the better we, the users of cosmetics, should understand scientific terms. At least then, to appreciate the innovative formulas of creams and understand what important work they do for our skin. Let’s start with free radicals.
What are free radicals
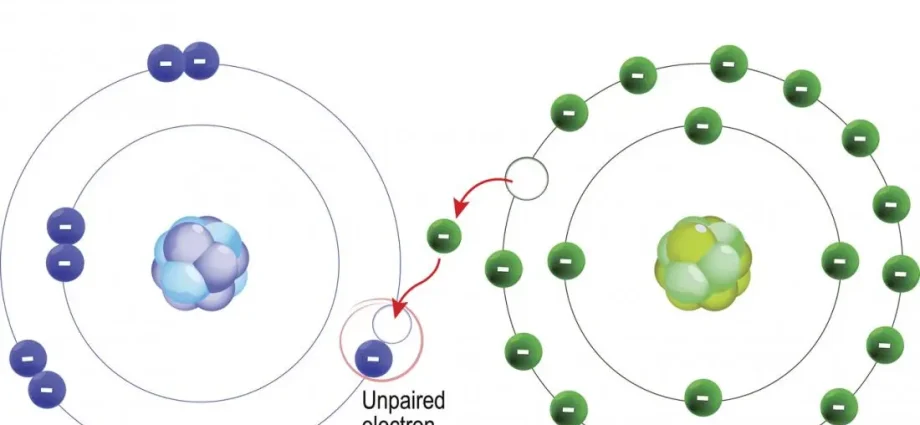
When we talk about free radicals, we most often mean oxygen molecules with an unpaired electron. They are very active (they are also called active oxygen) and tend to take the missing electron from any other molecule, which as a result itself becomes a free radical.
Free radicals are caused by:
- atmospheric pollution;
- excess ultraviolet;
- radiation;
- smoking (and passive too);
- medications;
- stress.
It is clear that it is practically impossible to hide from free radicals, you can only minimize the interaction with them.
In short: almost any foreign action or phenomenon that upsets the balance of the internal system becomes a source of free radicals for a living organism.
Find out what you miss in your daily skin care by answering our quiz.
Action of free radicals
The main damaging effect of free radicals is oxidative stress (oxidative stress, oxidation, oxidation). Free radical theory is considered one of the main theories of aging. And it’s hard to argue with her.
In a lifetime, a person pumps about 17 tons of oxygen through himself – about one and a half tons of free radicals are formed. From such an impact, metals rust, to say nothing of the fragile human body.
Free radicals in the human body
It is clear that natural chemical processes are constantly taking place in our body, including oxidation, which involves free radicals. This is normal and part of life.
Moreover, in moderate doses that we get from clean air, we need free radicals – in particular, they are involved in providing cognitive functions of the brain (memory, attention, psychomotor coordination, speech, thinking, orientation, etc.).
The problem is their excess. On the one hand, we receive them from the outside:
- we inhale;
- swallowed with food and drinks.
Free radicals on the skin:
- oxidize sebum in the pores, which contributes to the appearance of black dots;
- destroy the hydrolipidic barrier of the skin, causing dryness, inflammation, aging.
On the other hand, our body, especially in a state of stress, itself becomes a factory for the production of free radicals. The half-life products of many hormones (both stress hormones and female steroids) are the same toxins (along with chemicals from drugs or food) that cause the formation of free radicals, designed, strictly speaking, to destroy these toxins.
If simplified:
- the more toxins – the more free radicals;
- the more free radicals – the more intense oxidative stress;
- the more intense oxidative stress (oxidation processes in the body) – the worse a person feels and looks.
By the way, it is lipids that are most easily oxidized – fats that make up the membranes of almost all human cells, starting with skin cells, which are the first to get in the way of free radicals.
In moderate doses, which we easily get from clean air, we need free radicals – in particular, they provide the cognitive function of the brain.
How to deal with free radicals in the body
Ideally, one should move to a utopian world where life is possible:
- without stress;
- in an environmentally friendly environment;
- with regular physical activity;
- with a diet dominated by unrefined, natural products that undergo minimal heat treatment;
- without chemicals and harmful radiation.
Keep in mind: gadgets are a source of electromagnetic radiation, and polluted air is a source of free radicals.
Getting rid of free radicals in the body is impossible, and there is no need. They must perform their destructive work aimed at the destruction (oxidation) of harmful substances and microorganisms, thereby protecting us from them.
Since free radicals have strictly defined functions in the body, nature has provided protection against their excessive activity – antioxidant.
Its natural level is designed to cope with natural oxidative stress. But human antioxidant protection is not designed for oxidative stress, greatly enhanced by civilization. Therefore, modern man needs additional antioxidants.
Keep in mind: gadget radiation is also a source of charged particles.
Free radicals and antioxidants
So free radicals are oxidizing agents. The antidote for them is antioxidants. You will be surprised, but this word first appeared in Russian: the term “antioxidants” was used in one of the scientific institutes in Moscow at the turn of the 1960s and 70s.
Antioxidants neutralize the activity of free radicals by binding them. Such a system helps cells protect themselves from oxidation, making them less vulnerable. The main antioxidants that laid the foundation for this category of substances are some enzymes (coenzyme Q10), vitamins A, C and E. Hormones also differ in antioxidant action – for example, melatonin.
In addition to the listed substances, many vitamins, microelements, enzymes and hormones, present in the body in sufficient quantities, form the same antioxidant defense.
How to protect yourself from the effects of free radicals
Obviously, antioxidant protection weakens over the years, so it is worth thinking about strengthening it. At the same time, it is naive to believe that you can eat fast food and inhale the city smog, and then drink an antioxidant pill and thereby neutralize all the negative consequences. An integrated approach and a sober look at your lifestyle are important.
In addition to giving up bad habits, it makes sense to pay attention to foods rich in antioxidants.
dark berries, especially grapes, the peel and seeds of which contain one of the champions in antioxidant activity – resveratrol. It is believed that the richer the color of a berry, fruit or vegetable, the richer it is in polyphenols – antioxidant substances.
Compliance with the rule “5 different vegetables and fruits a day” is a serious contribution to your own antioxidant protection.
Green tea, according to many experts, is an even more powerful source of antioxidants than grapes and red wine derived from them.
Oily sea fish and varied (that’s right) vegetable oils.
Cosmetical toolsenriched with antioxidants are also needed. Of course, they will not turn back the clock, but they are quite capable of improving skin turgor, making it smoother. In addition, such funds are indispensable for damage, inflammation and some skin diseases. For example, most after-sun products work precisely thanks to the antioxidants in the composition.
Don’t be afraid of free radicals. It is better to limit their presence in your life, switch to an antioxidant diet and take care of your health.
An Overview of Antioxidant Foods
Antioxidant gel for the skin around the eyes AOX + Eye Gel, SkinCeuticals
The serum-in-gel formula fights wrinkles and signs of photoaging on the thin skin of the eyelids. It contains a star trio of antioxidants: L-ascorbic and ferulic acids, phloretin.
Resveratrol BE Concentrated Antioxidant Gel, SkinCeuticals
Resveratrol, an antioxidant derived from the skin of grapes, has been called the molecule of youth. It works best at night, destroying the effects of stress accumulated during the day. As always with SkinCeuticals, the essential antioxidant does not work alone. Here it is supported by baicalin and alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E).
Broad Spectrum Serum Phloretin CF, SkinCeuticals
Packed with a massive dose of antioxidants, including brightening L-ascorbic and ferulic acids, it’s great for those battling age spots. After a month of regular use, you will notice that the pigmentation has become lighter, and the skin is more elastic and toned. A prerequisite is to apply a cream with SPF 30 or 50 over the serum.
Firming care against signs of aging at different stages Slow Age, Vichy
The antioxidant baicalin in combination with vitamins C and E contributes to the neutralization of free radicals. The probiotic bifidus strengthens the protective barrier, enhances the skin’s resistance to external factors. The SPF 25 filter protects against photoaging.
Anti-aging care for normal and combination skin Redermic C, La Roche-Posay
An effective remedy for skin with signs of aging. The high concentration of vitamin C neutralizes the damage caused by free radicals to skin cells. In addition to this antioxidant, the formula contains:
- mannose – against redness, uneven tone and relief of the face;
- fragmented hyaluronic acid for hydration;
- madecasosside for recovery;
- neurosensin as an antistress component.